Germany’s Merz arrives in China for two-day visit with focus on trade | International Trade News
Chancellor says he wants to deepen trade relationship while making it fairer during visit that sees signing of several agreements.
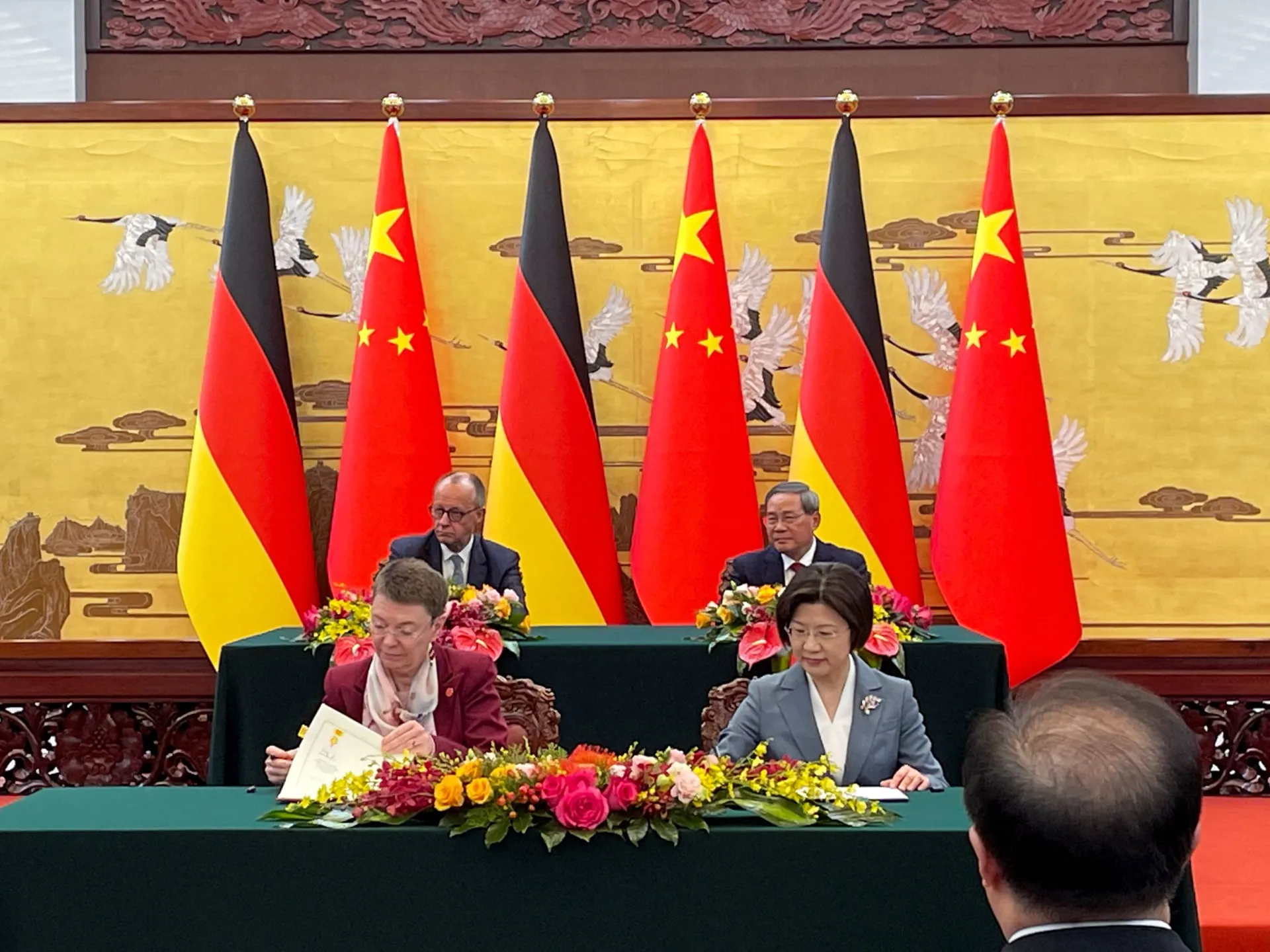
German Chancellor Friedrich Merz has kicked off his inaugural visit to China with a focus on resetting trade relations and deepening cooperation.
Speaking in Beijing on Wednesday, Merz told Chinese Premier Li Qiang that Germany sought to build on the decades-old economic ties with China, while emphasising the need to ensure fair cooperation and open communication.
Recommended Stories
list of 4 itemsend of list
“We have very specific concerns regarding our cooperation, which we want to improve and make fair,” said Merz, in an acknowledgement of the strain faced by Germany’s manufacturing sector from Chinese competition.
Li, who met Merz shortly after his arrival in Beijing’s Great Hall of the People, called on both sides to work together to safeguard multilateralism and free trade, in a reference to US President Donald Trump’s tariff policy that has upended the global trading system.
“China and Germany, as two of the world’s largest economies and major countries with important influence, should strengthen our confidence in cooperation, jointly safeguard multilateralism and free trade, and strive to build a more just and fair global governance system,” Li said.
During the meeting, representatives from both sides signed several agreements and memorandums, including on climate change and food security.
“We share responsibility in the world, and we should live up to that responsibility together,” Merz said, adding there was “great potential for further growth”.
He added that open channels of communication were essential, as he announced visits by several ministers in the months ahead.
‘More equal playing field’ sought
Reporting from Beijing, Al Jazeera’s Rob McBride said the visit, in which Merz was being accompanied by a large delegation of German business executives, was important for both Europe’s economic powerhouse and the world’s second-largest economy.
Alongside the signing of deals with Chinese companies, a key focus of Merz’s visit would be “looking for a more equal playing field when it comes to trade”, he said.
“There is a real concern in markets like the European Union about cheaper, sometimes subsidised Chinese products that are looking for markets other than the US, suddenly flooding other marketplaces such as Germany … undercutting many domestic manufacturers there,” he said.
Germany’s imports from China increased 8.8 percent to 170.6 billion euros ($201bn) last year, while its exports to China dropped 9.7 percent to 81.3 billion euros ($96bn).
McBride noted Beijing was seeking to pitch itself as a “responsible advocate of free trade compared to the sometimes unpredictable and chaotic tariffing policy of the US”.
He said the visit would also see Merz attend a banquet with Chinese President Xi Jinping, and visits to German companies with strongly established presences in China, such as Siemens and Mercedes-Benz.
Geopolitics and human rights would also be on the table, he said, with Germany particularly concerned about Beijing’s support, tacit or otherwise, for Russia amid its war on Ukraine.
Western leaders court Beijing
Merz is the latest in a string of Western leaders to visit Beijing in recent months, including the UK’s Keir Starmer, France’s Emmanuel Macron and Canada’s Mark Carney, amid the fallout from Trump’s tariffs on long-established trade relationships.
The chancellor said on Friday he was going to Beijing in part because export-dependent Germany needs “economic relations all over the world”.
“But we should be under no illusions,” he said, adding that China, as a rival to the United States, now “claims the right to define a new multilateral order according to its own rules.”