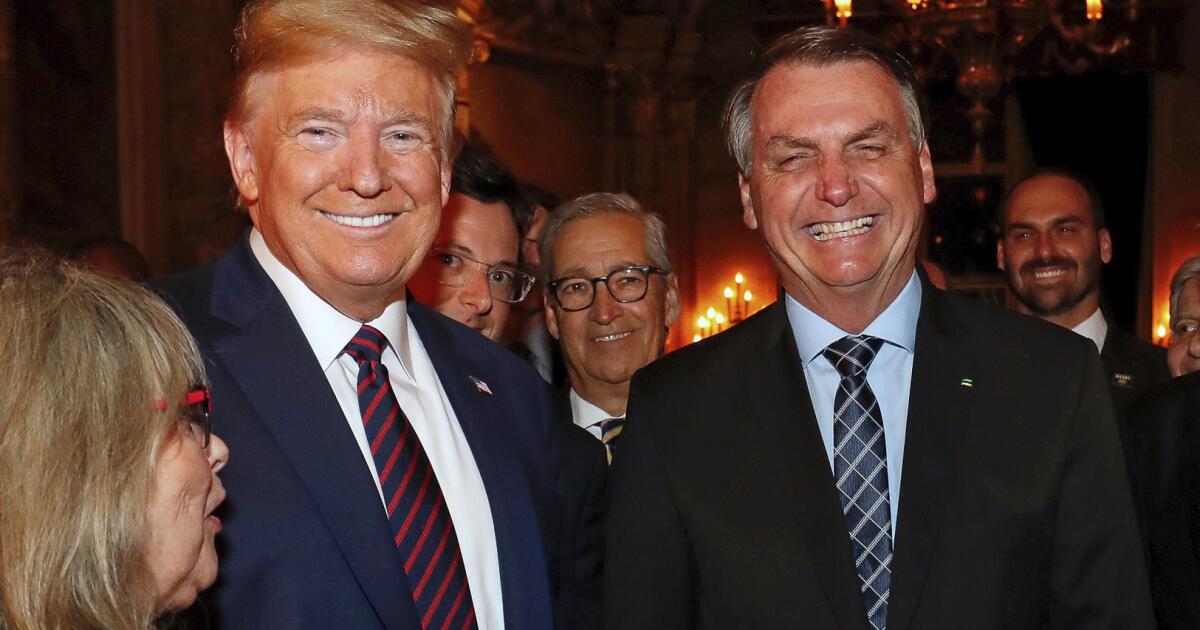
SAO PAULO — President Trump has made clear who his new Latin America priority is: former Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro, a personal and political ally.
In doing so, he has damaged one of the Western hemisphere’s most important and long-standing relationships, by levying 50% tariffs that begin to take effect Wednesday on the largest Latin America economy, sanctioning its main justice and bringing relations between the two countries to the lowest point in decades.
The White House has appeared to embrace a narrative pushed by Bolsonaro allies in the U.S., that the former Brazilian president’s prosecution for attempting to overturn his 2022 election loss is part of a “deliberate breakdown in the rule of law,” with the government engaging in “politically motivated intimidation” and committing “human rights abuses,” according to Trump’s statement announcing the tariffs.
The message was clear earlier, when Trump described Bolsonaro’s prosecution by Brazil’s Supreme Court as a “witch hunt” — using the same phrase he has employed for the numerous investigations he has faced since his first term. Bolsonaro faces charges of orchestrating a coup attempt to stay in power after losing the 2022 election to President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva. A conviction could come in the next few months.
The U.S. has a long history of meddling with the affairs of Latin American governments, but Trump’s latest moves are unprecedented, said Steven Levitsky, a political scientist at Harvard University.
“This is a personalistic government that is adopting policies according to Trump’s whims,” Levitsky said.
Bolsonaro’s sons, he noted, have close connections to Trump’s inner circle. The argument has been bolstered by parallels between Bolsonaro’s prosecution and the attempted prosecution of Trump for trying to overturn his 2020 election loss, which ended when he won his second term last November.
“He’s been convinced Bolsonaro is a kindred spirit suffering a similar witch hunt,” Levitsky said.
Brazil’s institutions hold firm against political pressure
After Bolsonaro’s defeat in 2022, Trump and his supporters echoed his baseless election fraud claims, treating him as a conservative icon and hosting him at the Conservative Political Action Conference. Steve Bannon, the former Trump adviser, recently told Brazil’s news website UOL that the U.S. would lift tariffs if Bolsonaro’s prosecution were dropped.
Meeting that demand, however, is impossible for several reasons.
Brazilian officials have consistently emphasized that the judiciary is independent. The executive branch, which manages foreign relations, has no control over Supreme Court justices, who in turn have stated they won’t yield to political pressure.
On Monday, the court ordered that Bolsonaro be placed under house arrest for violating court orders by spreading messages on social media through his sons’ accounts.
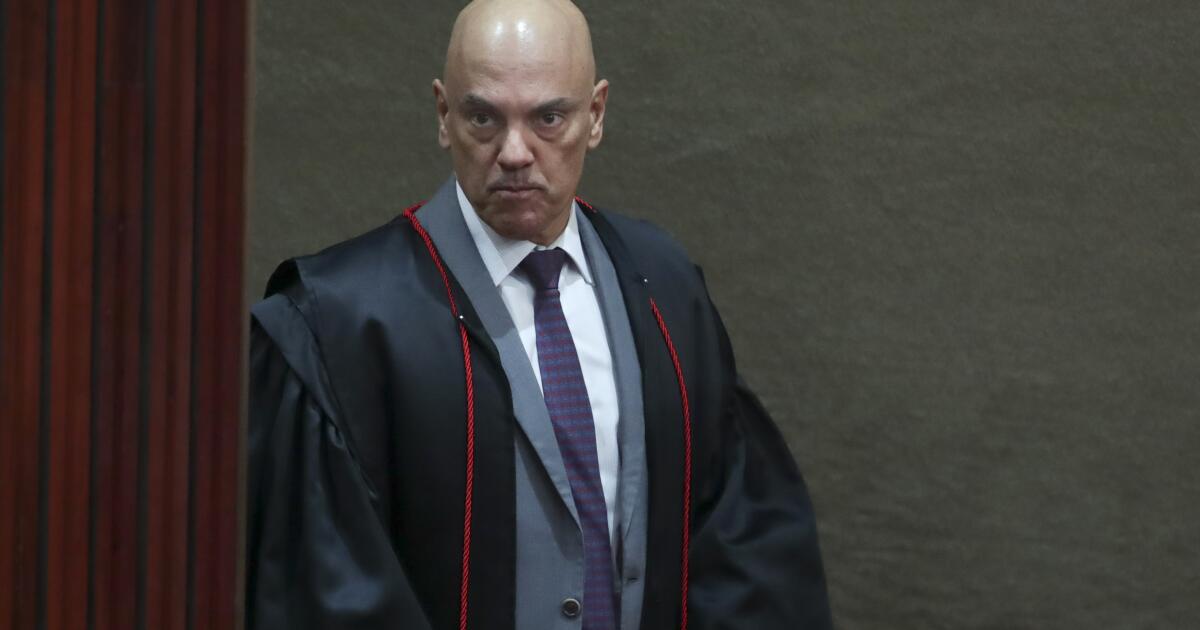
Justice Alexandre de Moraes, who oversees the case against Bolsonaro, was sanctioned under the U.S. Magnitsky Act, which is supposed to target serious human rights offenders. De Moraes has argued that defendants were granted full due process and said he would ignore the sanctions and continue his work.
“The ask for Lula was undoable,” said Bruna Santos of the Inter-American Dialogue in Washington, D.C., about dropping the charges against Bolsonaro. “In the long run, you are leaving a scar on the relationship between the two largest democracies in the hemisphere.”
Magnitsky sanctions ‘twist the law’
Three key factors explain the souring of U.S.-Brazil ties in recent months, said Oliver Stuenkel, a senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace: growing alignment between the far-right in both countries; Brazil’s refusal to cave to tariff threats; and the country’s lack of lobbying in Washington.
Lawmaker Eduardo Bolsonaro, Jair Bolsonaro’s third son, has been a central figure linking Brazil’s far-right with Trump’s MAGA movement.
He took a leave from Brazil’s Congress and moved to the U.S. in March, but he has long cultivated ties in Trump’s orbit. Eduardo openly called for Magnitsky sanctions against de Moraes and publicly thanked Trump after the 50% tariffs were announced in early July.
Democratic Massachusetts Rep. Jim McGovern, author of the Magnitsky Act, which allows the U.S. to sanction individual foreign officials who violate human rights, called the administration’s actions “horrible.”
“They make things up to protect someone who says nice things about Donald Trump,” McGovern told The Associated Press.
Bolsonaro’s son helps connect far right in U.S. and Brazil
Eduardo Bolsonaro’s international campaign began immediately after his father’s 2022 loss. Just days after the elections, he met with Trump at his Mar-a-Lago estate in Florida.
As investigations against Bolsonaro and his allies deepened, the Brazilian far right adopted a narrative of judicial persecution and censorship, an echo of Trump and his allies who have claimed the U.S. justice system was weaponized against him.
Brazil’s Supreme Court and Electoral Court are among the world’s strictest regulators of online discourse: they can order social media takedowns and arrests for spreading misinformation or other content it rules “anti-democratic.”
But until recently, few believed Eduardo’s efforts to punish Brazil’s justices would succeed.
That began to change last year when billionaire Elon Musk clashed with de Moraes over censorship on X and threatened to defy court orders by pulling its legal representative from Brazil. In response, de Moraes suspended the social media platform from operating in the country for a month and threatened operations of another Musk company, Starlink. In the end, Musk blinked.
Fábio de Sá e Silva, a professor of international and Brazilian studies at the University of Oklahoma, said Eduardo’s influence became evident in May 2024, when he and other right-wing allies secured a hearing before the U.S. House Foreign Affairs Committee.
“It revealed clear coordination between Bolsonaro supporters and sectors of the U.S. Republican Party,” he said. “It’s a strategy to pressure Brazilian democracy from the outside.”
A last-minute tariff push yields some wins
Brazil has a diplomatic tradition of maintaining a low-key presence in Washington, Stuenkel said. That vacuum created an opportunity for Eduardo Bolsonaro to promote a distorted narrative about Brazil among Republicans and those closest to Trump.
“Now Brazil is paying the price,” he said.
After Trump announced sweeping tariffs in April, Brazil began negotiations. President Lula and Vice President Geraldo Alckmin — Brazil’s lead trade negotiator — said they have held numerous meetings with U.S. trade officials since then.
Lula and Trump have never spoken, and the Brazilian president has repeatedly said Washington ignored Brazil’s efforts to negotiate ahead of the tariffs’ implementation.
Privately, diplomats say they felt the decisions were made inside the White House, within Trump’s inner circle — a group they had no access to.
A delegation of Brazilian senators traveled to Washington in the final week of July in a last-ditch effort to defuse tensions. The group, led by Senator Nelsinho Trad, met with business leaders with ties to Brazil and nine U.S. senators — only one of them Republican, Thom Tillis of North Carolina.
“We found views on Brazil were ideologically charged,” Trad told The AP. “But we made an effort to present economic arguments.”
While the delegation was in Washington, Trump signed the order imposing the 50% tariff. But there was relief: not all Brazilian imports would be hit. Exemptions included civil aircraft and parts, aluminum, tin, wood pulp, energy products and fertilizers.
Trad believes Brazil’s outreach may have helped soften the final terms.
“I think the path has to remain one of dialogue and reason so we can make progress on other fronts,” he said.
Pessoa and Riccardi write for the Associated Press. AP writer Mauricio Savarese in Sao Paulo contributed to this report.