A federal judge will decide later this week whether to allow an L.A. County sheriff’s deputy to take a plea deal that would spare him from prison time months after he was convicted of punching and pepper spraying an unarmed woman who filmed him during a 2023 arrest.
In a Monday court hearing, Judge Stephen V. Wilson and Assistant U.S. Atty. Rob Keenan sparred for more than two hours over the federal government’s highly unusual legal maneuver to offer L.A. County sheriff’s Deputy Trevor Kirk a misdemeanor plea deal just two months after he was convicted of a felony in the excessive force case.
Kirk was convicted in February of one count of deprivation of rights under color of law after he was caught on camera rushing at the victim, hurling her to the ground and then pepper spraying her in the face while planting a knee on her neck during a 2023 incident outside of a Lancaster supermarket.
Wilson said he would rule on the motion to accept the plea in the next “three or four days.”
He faced up to a decade in prison at sentencing.
But that was upended after the Trump administration last month appointed Bill Essayli, a former California assemblyman, as U.S. attorney for Los Angeles. On May 1, prosecutors reached a rare post-trial plea agreement with Kirk.
The government recommended a one-year term of probation for Kirk and moved to strike the jury’s finding that Kirk had injured the victim, which made the crime a felony. Kirk agreed to plead guilty to a lesser-included misdemeanor violation of deprivation of rights under color of law.
The agreement caused turmoil in the U.S. attorney’s office, with assistant U.S. attorneys Eli A. Alcaraz, Brian R. Faerstein, Michael J. Morse and Cassie Palmer, chief of the Public Corruption and Civil Rights Section, all withdrawing from the case. Keenan, the only assistant U.S. attorney who signed off on the plea agreement, was not previously involved in the case.
Alcaraz, Faerstein and Palmer submitted their resignations following the “post-trial” plea agreement offer, sources previously confirmed to the Times. A filing submitted in the case last week also confirmed Palmer is departing the federal prosecutor’s office.
The incident mirrored turmoil at the U.S. Attorney’s Office in Manhattan that followed pressure by Trump Administration officials to drop a corruption case against New York City Mayor Eric Adams.
Essayli, a former California assemblyman, is a staunch Trump ally and hard line conservative appointed at a time when the President has sought to weaken the independence of the Department of Justice. He made the post-conviction plea offer to Kirk the same week Trump issued an executive order vowing to “unleash” American law enforcement.
In court Monday, Wilson grilled Keenan, appearing increasingly perplexed at the government’s logic in offering Kirk a deal. He questioned if prosecutors had a “serious and significant doubt” as to the deputy’s guilt and continually pushed Keenan to justify the deal.
“If the government hasn’t offered any explanation for its change of course, the court must grant the motion?” Wilson asked.
Keenan said he believed the court was legally obligated to do so, claiming the deal was “a pure exercise of prosecutorial discretion.”
In June 2023, Kirk was responding to a reported robbery when he threw a woman to the ground and pepper-sprayed her in the face while she filmed him outside a Lancaster WinCo. The woman — who is only identified in federal court filings as J.H. but named as Jacey Houston in a separate civil suit — matched a dispatcher’s description of a female suspect she was not armed or committing a crime at the time Kirk first confronted her, court records show.
But in a 31-page position statement filed May 13, Keenan dissected the victim’s actions leading up to and during the confrontation with Kirk. Keenan said Kirk used the pepper spray after “continued resistance by J.H.”
“In contrast to other excessive-force cases, defendant did not use pepper spray after J.H. was cuffed or otherwise secured,” Keenan wrote.
Keenan said the evidence didn’t show that Kirk sprayed Houston in the face with an intent to cause bodily injury. He also described her injuries as “limited in duration and severity” and said they did not constitute “serious bodily injury.”
In the filing, Keenan appeared to question the government’s evidence relating to a reported “blunt head injury,” calling it “vague and ill-defined even at trial.”
In court Monday, Keenan described Kirk’s use of force as “excessive, but just “barely so,” at one point attacking the credibility of the victim in the case, suggesting she exaggerated her injuries in a victim impact statement she made before the court.
Wilson did not accept that analysis.
“The jury was completely justified in finding he used excessive force in taking her to the ground and pepper spraying her,” the judge said. “Had he ordered her to be handcuffed … that would be a different case,” the judge said.
Earlier in the morning, Houston said Kirk should never be allowed to be a police officer or own a firearm again, given the “uncontrollable rage” he aimed at her on the day of the incident.
“I was certain that I was going to die,” she said, describing the moment Kirk grabbed her.
Houston’s attorney, Caree Harper, has said Keenan’s filing distorts the reality of what happened in the parking lot that day.
“J.H. is a senior citizen. She committed no crime. She had no weapon. She did not try to flee. She did not try to resist. J.H. sustained a black eye, a fractured bone in her right arm, multiple bruises, scratches, and significant chemical burning from the pepper-spray,” Harper wrote in a court filing. “J.H. screamed in pain and struggled to fill her lungs with oxygen.”
Wilson had previously denied a motion from Yu for an acquittal, finding that footage of the incident was sufficient evidence for a jury to find Kirk had used “objectively unreasonable force.”
“J.H. did not have a weapon, did not attack Defendant, was not attempting to flee, and was not actively committing a crime,” Wilson wrote in his ruling last month.
The judge also noted that, while Kirk acted aggressively toward Houston from the outset, his partner managed to lead the arrest of the other robbery suspect without using force.
Keenan painted the concessions Kirk made in the post-trial agreement as “significant.” He said Kirk was agreeing to admit that he “used unnecessary force” while attempting to detain Houston and that he did so “willfully.”
In early 2024, shortly after the Winco incident, Kirk was arrested by his own department on suspicion of domestic violence against his wife. His attorney dismissed it as a non-issue, noting the victim did not want Kirk to be prosecuted, contending the alleged abuse was reported by a third party. A spokesman for the Los Angeles County district attorney’s office said the case was rejected due to insufficient evidence.
In her filing last week, Harper also said Kirk was arrested on allegations he threw his wife on the ground in January 2023. Harper alleged Kirk “threatened to bury [his wife] in the desert,” records show.
Sheriff’s department arrest logs only display the 2024 arrest. A sheriff’s department spokeswoman did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Support for Kirk began gaining steam on social media after his indictment last September. In January, Nick Wilson, founder of a first responder advocacy group and spokesperson for the Los Angeles Sheriff’s Professional Assn., wrote a letter to Trump urging him to intervene before the case went to trial.
Former Sheriff Alex Villanueva, who has become increasingly popular in right-wing circles online, has also championed Kirk’s case, posting an Instagram video of himself and Wilson consoling the deputy at the courthouse after trial. Both Villanueva and Wilson have insisted Kirk did nothing wrong.
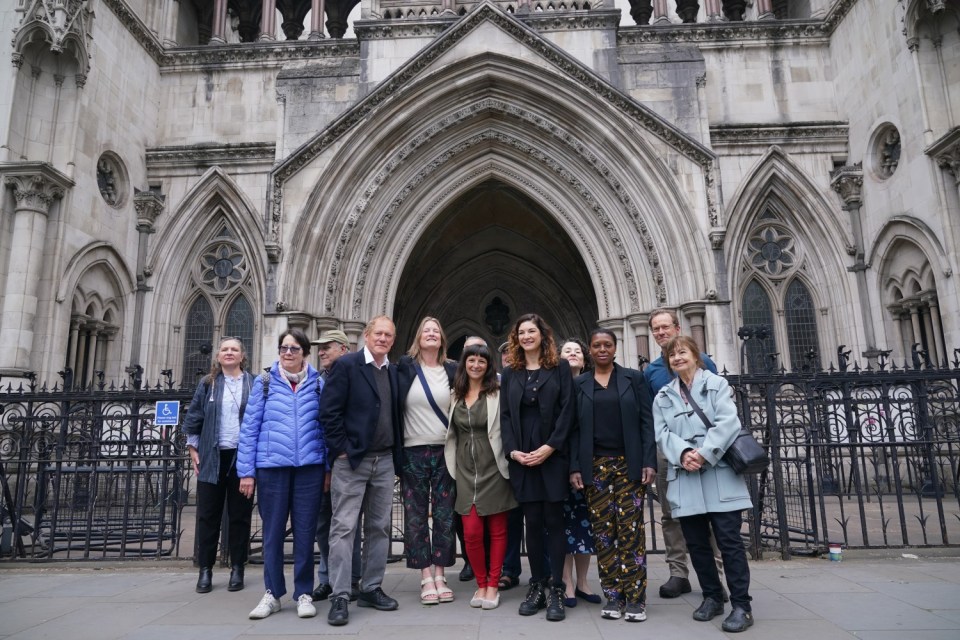
Villanueva, Wilson and Essayli were all present in court Monday. At one point Harper approached Essayli directly and asked about the legality of the plea deal he was offering.
Essayli, seated in a plastic chair because all of the benches in the courtroom were filled, threatened to have Harper removed from the courtroom. Harper noted that only judges and federal marshals have the right to remove someone from a courtroom. A U.S. Attorney’s office spokesman declined to comment.
Some deputies have also blamed current Sheriff Robert Luna for pushing federal prosecutors to go after Kirk, a fact Luna has denied. Some deputy groups have staged forms of protest against Luna as a result.
But in a sentencing recommendation obtained by The Times, Luna asked Wilson to sentence Kirk to probation, blaming his actions that day on poor training.
He noted prior department leaders had effectively ignored a monitoring agreement with the U.S. Department of Justice that was meant to mandate reform policies on use-of-force issues at the Lancaster and Palmdale stations. Luna’s letter did not address whether or not Wilson should act on Essayli’s request to vacate the jury verdict.
“I’m not suggesting that the failures of the Department should immunize Deputy Kirk or any other deputy taking responsibility for their actions,” Luna wrote. “No deputy who is found by a jury to have used excessive force or who has agreed to a plea deal should have such immunity.”