How Staying Passive on Iran Could Impact Russia and China
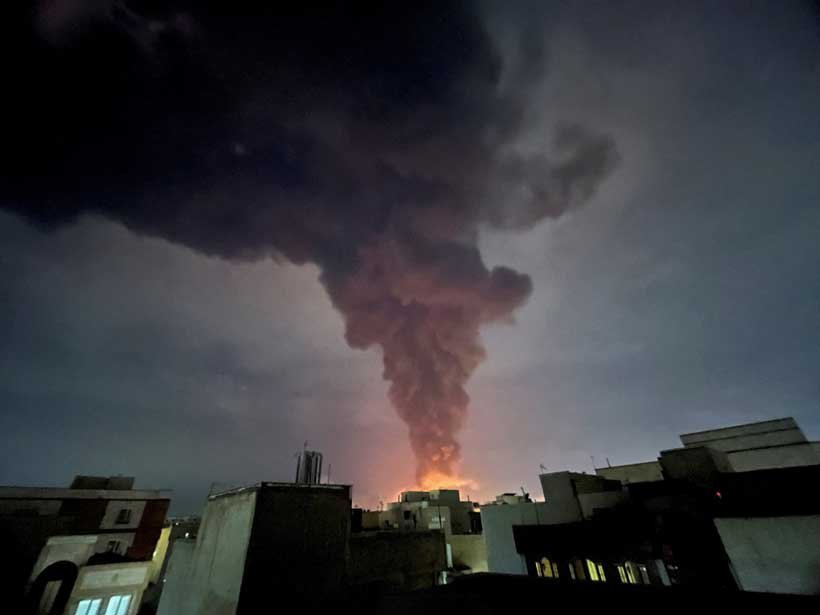
Middle Eastern crises seldom stay localized. They frequently go well beyond the battlefield in terms of politics, strategy, and psychology. Officials in Beijing, Moscow, Taipei, and Kyiv will be keeping a tight eye on events surrounding Iran today, in addition to those in Tehran, Washington, and Tel Aviv. Power perceptions are shaped by situations like this, and in international politics, perception can be almost as important as actual power.
The current state of affairs presents an unsettling question for China and Russia. A large-scale military operation against a prominent regional actor will unavoidably send signals about the balance of power in the international system if it continues without significant opposition from other big states. The Middle East is not where those signals will end. They will visit other geopolitical hotspots, like Taiwan and Ukraine, where credibility is crucial to deterrence.
Iran has progressively evolved into more than simply another diplomatic friend in Beijing’s eyes. It now plays a part in China’s larger Eurasian economic and strategic strategy. Beijing has been building energy and transportation networks that connect western China to the Arabian Sea through projects like the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. Chinese planners considering long-term energy security have taken note of the geographical proximity of the Pakistani port of Gwadar to Iran’s Jask Oil Terminal.
Beijing has long sought variety, which these lines provide. Chinese strategists have been concerned about dependence on maritime chokepoints like the Strait of Hormuz and the Strait of Malacca for decades. The energy lifelines of the second-largest economy in the world could be threatened by any interruption there. Iran fits into China’s attempt to lessen that vulnerability because of its location and resources. Trade in energy has already strengthened ties between the two nations. Iran has quietly emerged as a major supplier of cheap crude to China in spite of U.S. sanctions. Both nations are able to avoid some aspects of the Western financial architecture since many of those transactions go through China’s Cross-Border Interbank Payment System and are settled in renminbi.
However, the partnership has grown beyond oil. Beijing and Tehran signed a long-term strategic agreement in 2021 with the goal of working together on infrastructure, energy, and technology for decades. Later, China backed Iran’s admission to groups like BRICS and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. Then came a diplomatic surprise: Beijing assisted in mediating the reestablishment of ties between Saudi Arabia and Iran in 2023, a development that surprised many Western observers.
Taken together, these actions indicated a significant development. China was starting to portray itself not only as a regional economic force but also as a diplomatic player with the ability to influence its political environment.
That ambition makes the current moment particularly sensitive for Beijing. Governments in the Middle East and a large portion of the Global South frequently evaluate great powers based on their actions during times of crisis rather than their words during times of peace. Some capitals may discreetly reevaluate how reliable such support would be in an actual security crisis if China seems unwilling to protect the strategic environment surrounding its alliances.
The ramifications go well beyond Iran. Chinese officials have made it clear time and time again that they would not support Taiwan’s formal independence efforts and will not allow outside meddling in the Taiwan Strait. The legitimacy of those warnings is just as important to deterrence as military prowess. Some Washington policymakers may assume that China is unlikely to take more aggressive action in other areas if Beijing’s response to significant geopolitical shocks involving its partners primarily consists of diplomatic criticism.
Russia faces a different—but no less consequential—set of calculations. Moscow has positioned itself as a major Middle Eastern political mediator for the majority of the last ten years through its military engagement in Syria. Russian soldiers established a key base on the Mediterranean coast and assisted in stabilizing Bashar al-Assad’s regime starting in 2015. From such a vantage point, Moscow participated in almost all meaningful discussions regarding the future of the area.
However, that impact has been diminished. The political landscape has drastically changed as a result of the fall of the Syrian government and the growing power of actors supported by the West in Damascus. In addition to losing a strategic ally, Russia has also lost a significant portion of the regional clout it developed over the course of almost 10 years of diplomatic and military engagement.
In that context, Iran now occupies a far more important place in Moscow’s strategic thinking than it once did. Defense and energy cooperation are two areas where the two nations’ relationship has grown. Iranian drones have contributed to Russia’s military actions in Ukraine, establishing a clear connection between the conflict in Eastern Europe and events in the Middle East. The message would reverberate much beyond the immediate battlefield if Iran were to sustain a significant military defeat at the hands of a concerted operation by the United States and Israel. While opposing major powers stayed mostly on the sidelines, observers from all around the world would see that Washington still had the capability to change regional dynamics.
These impressions build up in geopolitics. Credibility develops gradually, frequently over years, but it can deteriorate rapidly. Some governments may start to doubt the geopolitical benefit of aligning with Moscow if Russia seems incapable—or unwilling—to react when a close ally is under severe strain. However, competing nations might feel more confident to test Russian interests in other disputed areas, such as the Black Sea or Ukraine. However, Moscow’s choices are far from straightforward. In order to lessen the impact of Western sanctions, Russia has been fostering stronger commercial connections with a number of Gulf governments in recent years. Openly supporting Iran might make those relations more difficult. But staying completely silent runs the danger of conveying a contrary message: that when tensions rise, Russian alliances provide little strategic defense.
It seems unlikely that either China or Russia will move quickly to engage in direct combat. There would be significant risks of escalation. However, great-power competition seldom relies solely on choices made on the battlefield. There are plenty of other ways to be influential. Both nations have permanent seats in the UN Security Council. They can guarantee that any military action is politically disputed on the international scene by imposing debates, contesting legal justifications, and introducing resolutions, even symbolic ones. Beyond the Security Council, diplomacy is also important. Sovereignty and non-intervention have long been valued in nations like South Africa, Brazil, and India. Even if it doesn’t instantly change the situation on the ground, coordinated pressure from a larger group of states could influence how the issue is portrayed worldwide.
Another option is economic levers. The energy markets continue to be extremely vulnerable to geopolitical shocks. Major exporters continue to have the power to affect supply and pricing decisions by working with producers in organizations like OPEC+. Even little changes can serve as a reminder to the globe that regional conflicts have far-reaching economic repercussions. Great powers are also capable of sending quieter signals. Regional balances are not changing in isolation, as seen by intelligence collaboration, defensive technology transfers, and conspicuous naval deployments in nearby waterways. These actions convey that other important actors are keeping a close eye on them even while they avoid open confrontation.
Ultimately, this moment’s significance goes well beyond Iran. Expectations about how power functions in the international system are gradually shaped by incidents such as these. The precedent starts to take hold if armed action consistently reshapes regional orders without significant opposition from opposing nations. That precedent unavoidably affects Taiwan’s future for China. For Russia, it relates to both the larger security balance throughout Europe and the continuing conflict in Ukraine. Credibility is crucial in both situations.
Moments like this become inevitable tests if Beijing and Moscow want to maintain an international system where power is more widely spread. It is not always necessary to escalate conflict in order to respond. It often involves proving that significant changes in regional power will not happen completely unchallenged through diplomacy, economic pressure, and strategic signaling. There is meaning in silence as well. In places far from the Persian Gulf, how Tehran interprets that silence now could influence strategic decisions tomorrow.