Congress’s role questioned as Democrats vow to rein in Trump on Venezuela | Donald Trump News
Washington, DC – It has become a familiar pattern. United States presidents conduct unilateral military actions abroad. Congress shrugs.
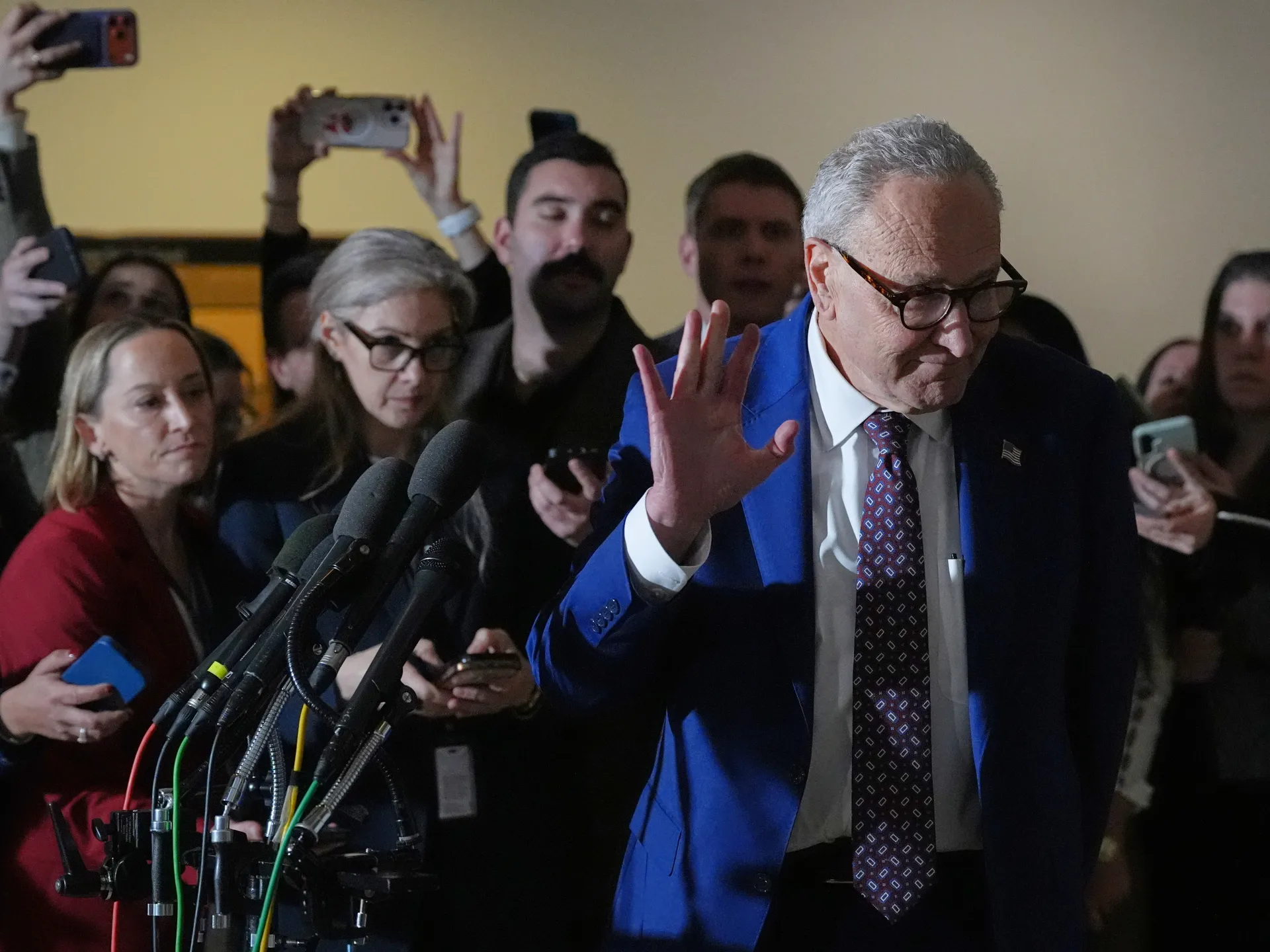
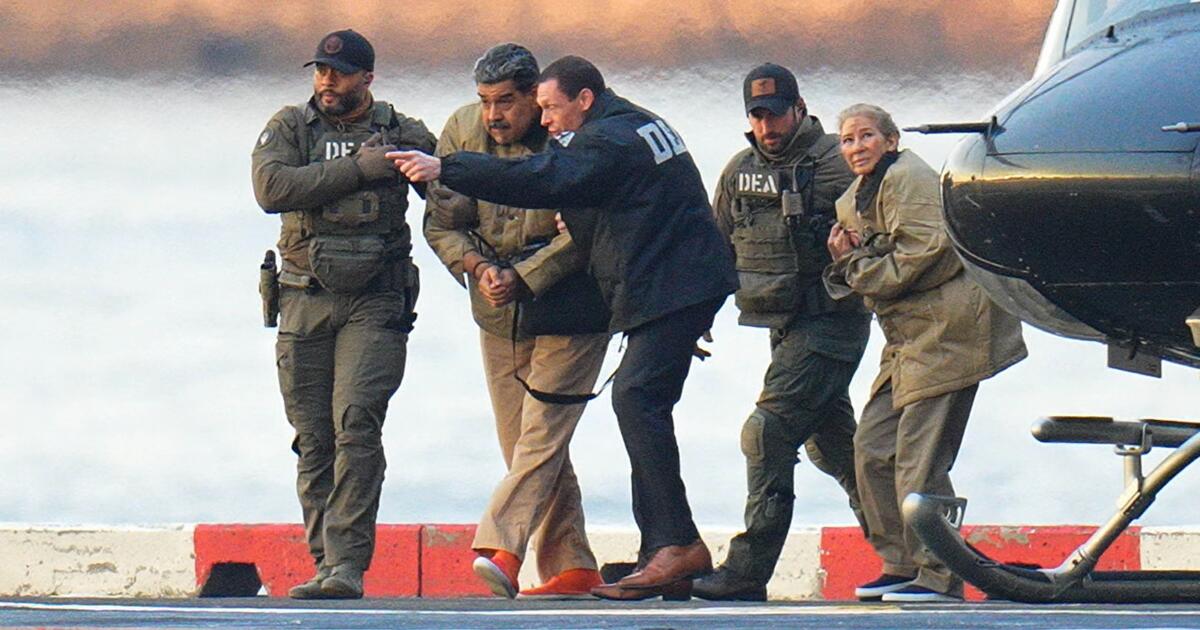
On Saturday, in the hours after the US military abducted Venezuelan leader Nicolas Maduro, Democrats in the Senate pledged to raise yet another resolution to rein in US President Donald Trump’s military actions.
Recommended Stories
list of 4 itemsend of list
Chuck Schumer, the top Democrat in the chamber, has said the party will push for a vote within the week. By all accounts, the odds of its success remain long.
Since Trump took office for a second term in 2025, Congress has weighed multiple bills that would force him to seek legislative approval before initiating a military strike.
But the latest attack on Venezuela offers a stark instance of presidential overreach, one that is “crying out for congressional action”, according to David Janovsky, the acting director of the Constitution Project at the Project on Government Oversight.
Experts say it is also one of the clearest tests in recent history of whether Congress will continue to cede its authority to check US military engagement abroad.
“There are a lot of angles where you can come at this to say why it’s a clear-cut case,” Janovsky told Al Jazeera.
He pointed out that, under the US Constitution, Congress alone wields the authority to allow military action. He also noted that the Venezuela attack “is in direct contravention of the UN Charter, which is, as a treaty, law in the United States”.
“Any of the fig leaves that presidents have used in the past to justify unilateral military action just don’t apply here,” Janovsky added. “This is particularly brazen.”
An uphill battle
Since August, the Trump administration has signalled plans to crank up its “maximum pressure” campaign against Venezuela.
That month, Trump reportedly signed a secret memo calling on the US military to prepare for action against criminal networks abroad. Then, on September 2, the Trump administration began conducting dozens of strikes on alleged drug-smuggling boats off the Venezuelan and Colombian coasts.
That deadly bombing campaign was itself condemned as a violation of international law and an affront to Congress’s constitutional powers. It coincided with a build-up of US military assets near Venezuela.
Trump also dropped hints that the US military campaign could quickly expand to alleged drug-trafficking targets on Venezuelan soil. “When they come by land, we’re going to be stopping them the same way we stopped the boats,” Trump said on September 16.
The strikes prompted two recent votes in the House of Representatives in December: one that would require congressional approval for any land strikes on the South American country, and one that would force Trump to seek approval for strikes on alleged drug-smuggling boats.
Both resolutions, however, failed roughly along party lines. A similar resolution in the Senate, which would have required congressional approval before any more attacks, also fell short in November.
But speaking to reporters in a phone call just hours after the US operation on Saturday, Senator Tim Kaine said he hoped the brashness of Trump’s latest actions in Venezuela would shock lawmakers into action.
Republicans, he said, can no longer tell themselves that Trump’s months-long military build-up in the Caribbean and his repeated threats are a “bluff” or a “negotiating tactic”.
“It’s time for Congress to get its a** off the couch and do what it’s supposed to do,” Kaine said.
In an interview with CNN’s Dana Bash, US Senator Chris Murphy also agreed that it was “true” that Congress had become impotent on matters of war, a phenomenon that has spanned both Democratic and Republican administrations.
Bash pointed to former President Barack Obama’s 2011 military deployment to Libya, which went unchecked by Congress.
“Congress needs to own its own role in allowing a presidency to become this lawless,” Murphy responded.
Republicans ho-hum about resolutions
Under the US Constitution, only Congress can declare war, something it has not done since World War II.
Instead, lawmakers have historically passed Authorizations for Use of Military Force (AUMFs) to approve committing troops to recent wars, including the US invasions of Iraq and Afghanistan and the strikes on alleged al-Qaeda affiliates across the Middle East, Africa and Asia.
No AUMFs have been passed that would relate to military action in Venezuela.
When lawmakers believe a president is acting beyond his constitutional power, they can pass a war powers resolution requiring Congressional approval for further actions.
Beyond their symbolism, such resolutions create a legal basis to challenge further presidential actions in the judiciary.
However, they carry a high bar for success, with a two-thirds majority in both chambers of Congress needed to override a presidential veto.
Given the current makeup of Congress, passage of a war powers resolution would likely require bipartisan support.
Republicans maintain narrow majorities in both the House and Senate, so it would be necessary for members of Trump’s own party to back a war powers resolution for it to be successful.
In November’s Senate vote, only two Republicans — co-sponsor Rand Paul of Kentucky, and Lisa Murkowski, of Alaska — split from their party to support the resolution. It failed by a margin of 51 to 49.
December’s vote on a parallel resolution in the House only earned 211 votes in favour, as opposed to 213 against. In that case, three Republicans broke from their party to support the resolution, and one Democrat opposed it.
But Trump’s abduction of Maduro has so far only received condemnation from a tiny fragment of his party.
Overall, the response from elected Republicans has been muted. Even regular critics of presidential adventurism have instead focused on praising the ouster of the longtime Venezuelan leader, who has been accused of numerous human rights abuses.
Senator Todd Young, a Republican considered on the fence ahead of November’s war powers vote, has praised Maduro’s arrest, even as he contended the Trump administration owed Congress more details.
“We still need more answers, especially to questions regarding the next steps in Venezuela’s transition,” Young said.
Some Democrats have also offered careful messaging in the wake of the operation.
That included Debbie Wasserman Schultz, a Democrat who represents a large Venezuelan diaspora community in Florida.
In a statement on Saturday, Wasserman Schultz focused on the implications of Maduro’s removal, while avoiding any mention of the military operation that enabled it. Instead, she asserted that Trump owed Congress an explanation about next steps.
“He has failed to explain to Congress or the American people how he plans to prevent the regime from reconstituting itself under Maduro’s cronies or stop Venezuela from falling into chaos,” she wrote.
In December, however, Wasserman Schultz did join a group of Florida Democrats in calling for Congress to exercise its oversight authority as Trump built up military pressure on Venezuela.
What comes next?
For its part, the Trump administration has not eased up on its military threats against Venezuela, even as it has sought to send the message that Maduro’s abduction was a matter of law enforcement, not the start of a war.
Trump has also denied, once again, that he needed congressional approval for any further military action. Still, in a Monday interview with NBC News, he expressed optimism about having Congress’s backing.
“We have good support congressionally,” he told NBC. “Congress knew what we were doing all along, but we have good support congressionally. Why wouldn’t they support us?”
Since Saturday’s attack and abduction, Trump has warned that a “second wave” of military action could be on the horizon for Venezuela.
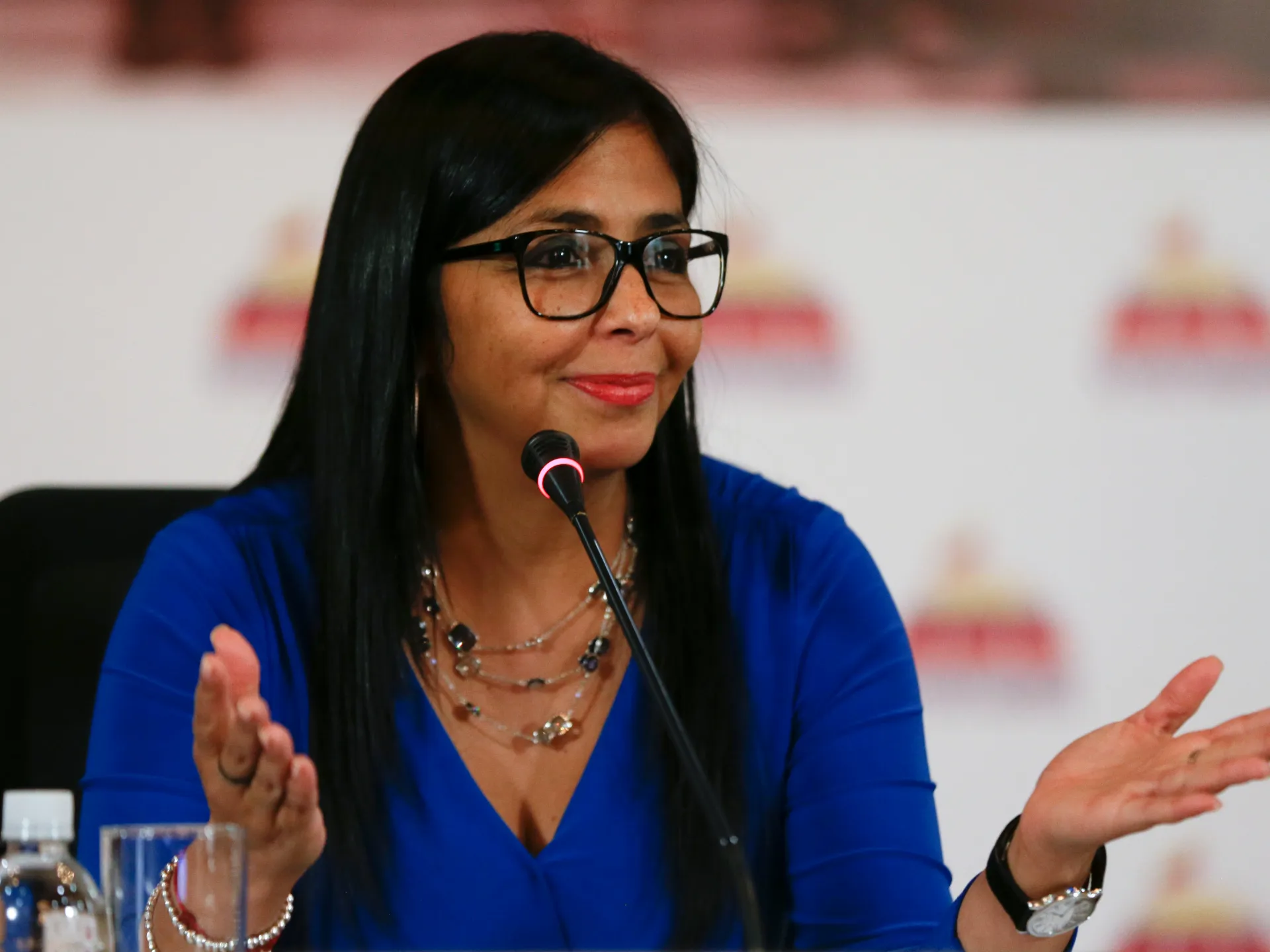
That threat has extended to the potential for the forced removal of Maduro’s deputy, Delcy Rodriguez, who was formally sworn in as the country’s interim president on Monday.
“If she doesn’t do what’s right, she is going to pay a very big price, probably bigger than Maduro,” Trump told The Atlantic magazine.
The administration has also said that strikes on alleged drug-smuggling boats near Venezuela will continue and that US military assets will remain deployed in the region.
Constitutional expert Janovsky, however, believes that this is a critical moment for Congress to act.
Failure to rein in Trump would only further reinforce a decades-long trend of lawmakers relinquishing their oversight authorities, he explained. That, in turn, offers tacit support for the presidency’s growing power over the military.
“To say this was a targeted law enforcement operation — and ignore the ongoing situation — would be a dangerous abdication of Congress as a central check on how the United States military is used,” Janovsky said.
“Continued congressional inaction does nothing but empower presidents to act however they want,” he added.
“To see Congress continue to step back ultimately just removes the American people even farther from where these decisions are actually being made.”