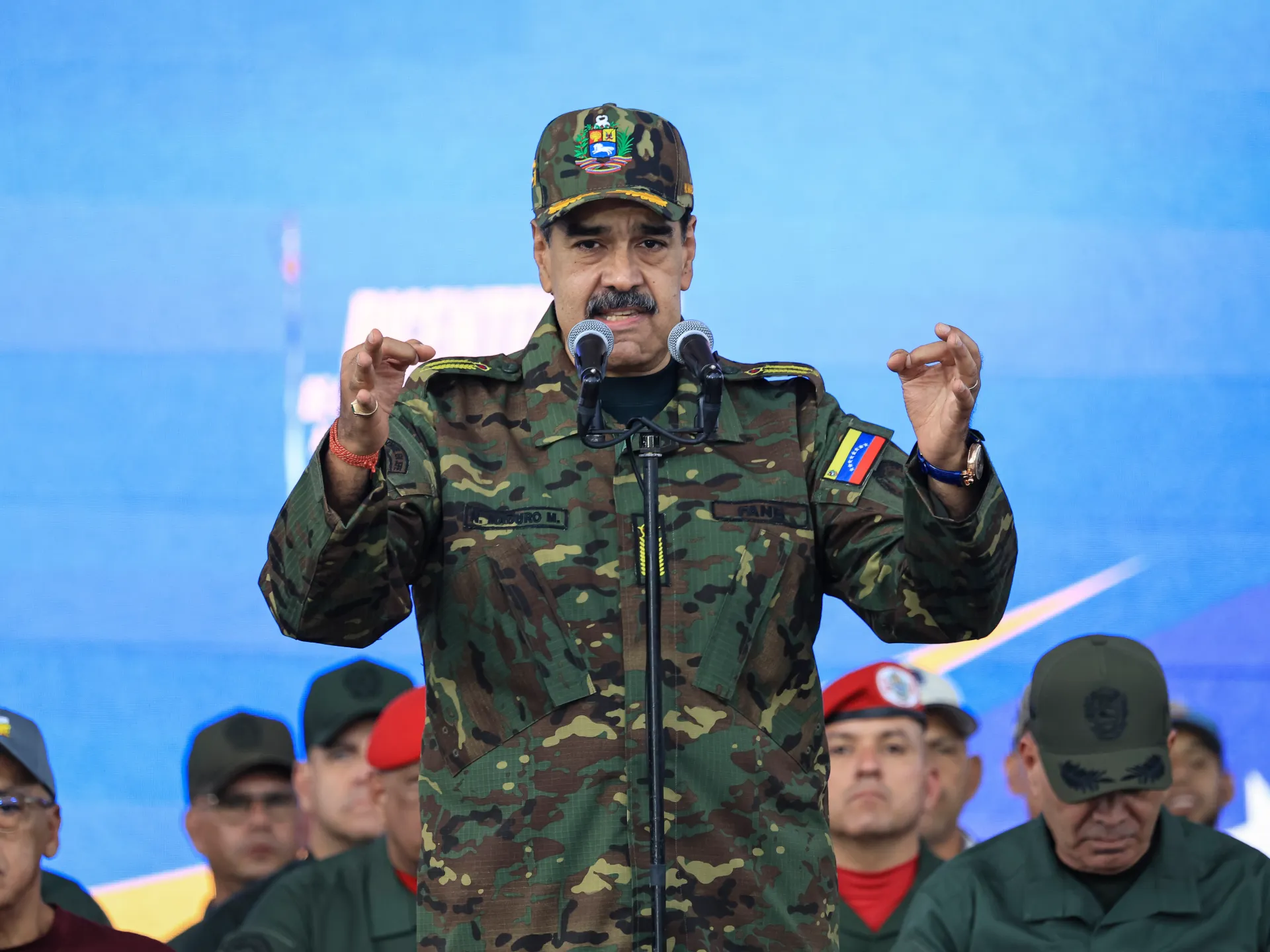
Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro is to appear in a New York court on Monday, two days after he was abducted by US special forces in a military operation in Caracas.
The US military arrested Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores, on Saturday and brought them to New York, where they face multiple federal charges, including drugs and weapons charges.
Recommended Stories
list of 4 itemsend of list
Here is more about Maduro’s scheduled court appearance:
When and where will it take place?
Maduro is to appear before a federal judge at noon (17:00 GMT).
The appearance is scheduled to happen in the Daniel Patrick Moynihan United States Courthouse in the Southern District of New York. Maduro is to appear before US District Judge Alvin Hellerstein.
A court spokesperson told NBC News that Flores, who is also listed as a defendant in a US indictment unsealed on Saturday, will appear in court on Monday as well.
What are the charges?
According to the indictment, the US accuses Maduro of being at the forefront of corruption to “use his illegally obtained authority” to “transport thousands of tons of cocaine” to the US with his coconspirators.
Additionally, the indictment alleges that Maduro has “tarnished” every public office he has held. It adds that Maduro “allows cocaine-fueled corruption to flourish for his own benefit, for the benefit of members of his ruling regime, and for the benefit of his family members”.
Maduro faces four counts:
- Count 1, narcoterrorism conspiracy: US prosecutors say Maduro and his coconspirators knowingly provided something of financial value to US-designated “foreign terrorist organizations” and their members. The indictment lists these organisations as the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), a leftist rebel group that signed a peace deal in 2016 but has dissidents who refused to lay down their arms and are still involved in the drug trade; Segunda Marquetalia, the largest dissident FARC group; National Liberation Army, another leftist Colombian rebel group; Mexico’s Sinaloa Cartel; Los Zetas/Cartel del Noreste, another Mexican drug cartel; and Tren de Aragua, a Venezuelan gang.
- Count 2, cocaine importation conspiracy: It accuses Maduro and his codefendants of conspiring to manufacture, distribute and import cocaine into the US.
- Count 3, possession of machineguns and destructive devices: The indictment accuses the defendants of possessing, carrying and using machineguns in relation to the above drug‑trafficking counts.
- Count 4, conspiracy to possess machineguns and destructive devices: It further accuses the defendants of conspiring to use, carry and possess those weapons in furtherance of drug trafficking.
The indictment also says Maduro and his codefendants should forfeit to the US government any proceeds and assets obtained from the alleged crimes.
Is there evidence for these charges?
There is little evidence that drugs are trafficked from Venezuela on a large scale. The 2023 United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime World Drug Report said global cocaine production hit a record of 3,708 tonnes, up nearly one‑third from 2022, with most coca cultivation taking place in Colombia, followed by Peru and Bolivia.
Trafficking routes into the US in 2023-2024 primarily passed through Colombia, Peru and Ecuador, not Venezuela, although it does serve as a minor transit corridor for Colombian cocaine moving into the eastern Caribbean.
Who is named in the indictment?
Maduro
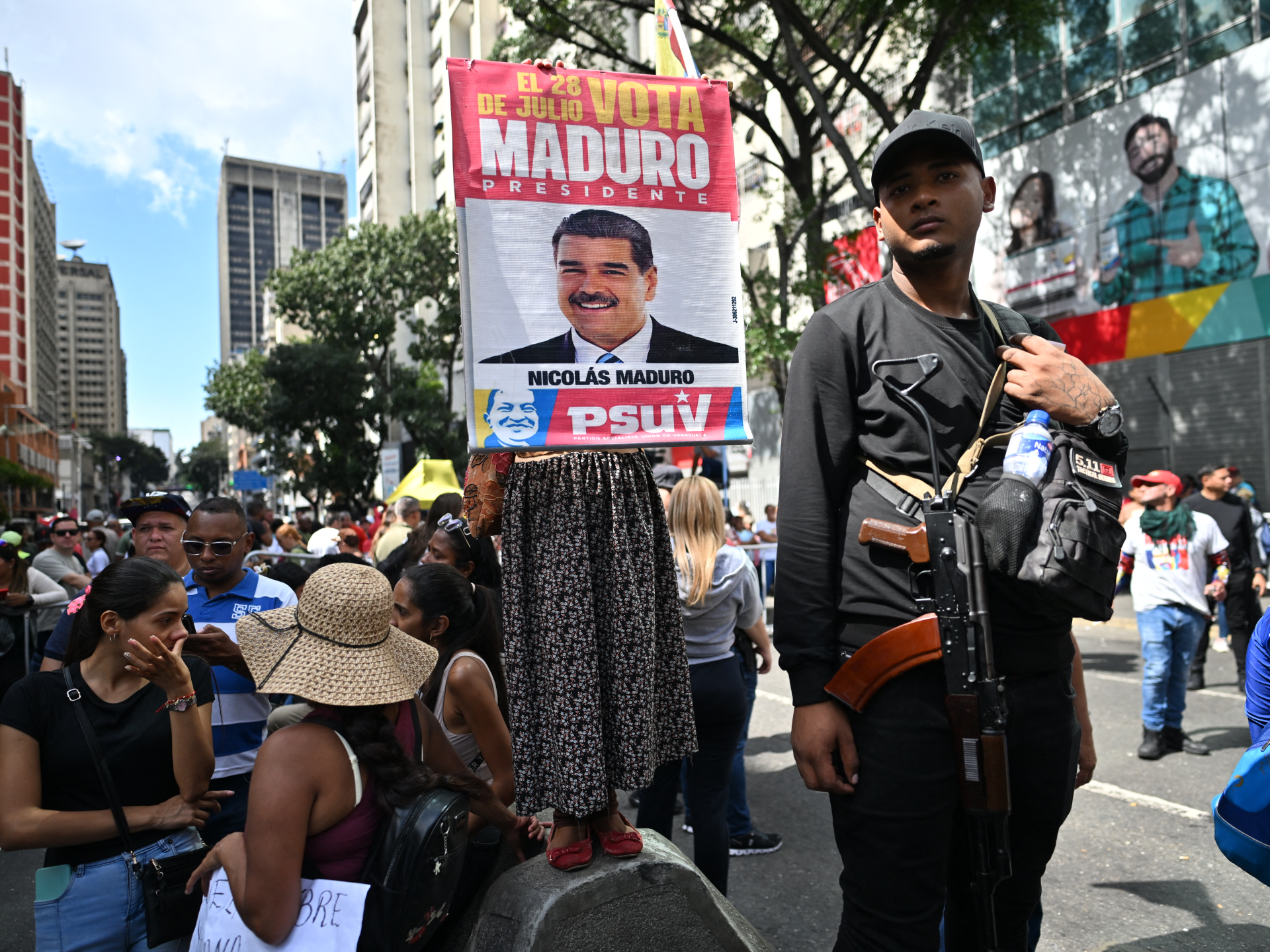
Maduro, 63, who became Venezuela’s president in 2013, was declared the winner of 2024’s election. His re-election was rejected as fraudulent by the US and independent observers, such as the Carter Center. A UN expert panel said the 2024 vote failed to meet international standards.
Nine Latin American countries called for a review of the results with independent oversight.
Maduro defended the election results and accused his opponents of undermining the country’s sovereignty.
Since returning to the White House nearly a year ago, US President Donald Trump has expanded sanctions and punitive measures against Maduro and senior officials in his government.
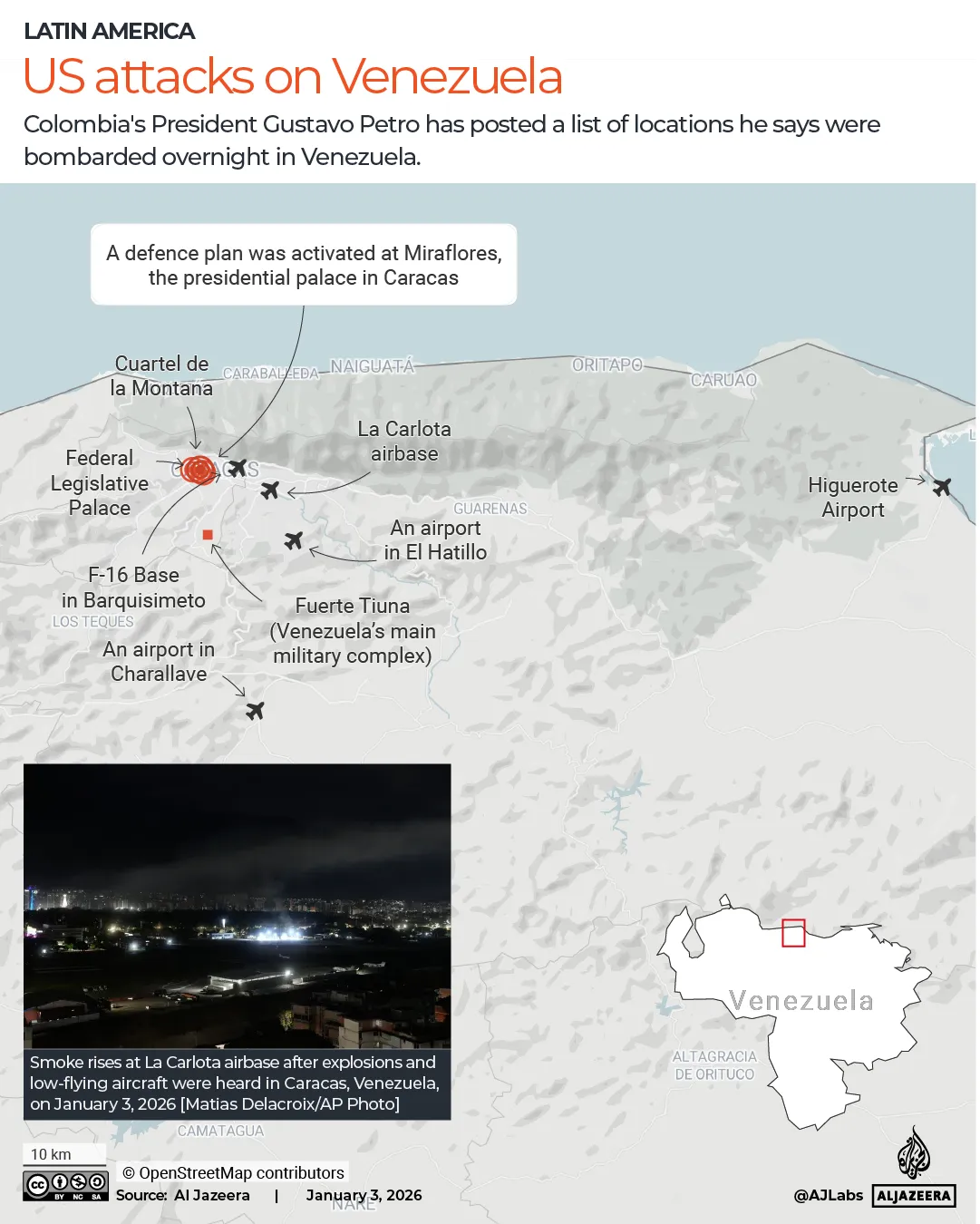
The Trump administration ramped up military pressure starting in August when it deployed warships and thousand of its service members in the Caribbean near Venezuela. It has since carried out dozens of air strikes on alleged Venezuelan drug boats, killing more than 100 people.
Maduro has pushed back by mobilising Venezuelan military personnel.
During this time, the Caracas-based news network Globovision quoted Maduro as saying: “From the north, the empire has gone mad and, like a rotten rehash, has renewed its threats to the peace and stability of Venezuela.”
But a day before Saturday’s US attack on the country, Maduro had offered to hold talks to combat drug trafficking.
Flores
Flores, 69, has been married to Maduro since 2013.
Known as the “first combatant” rather than first lady, Flores is a veteran lawyer and politician who rose to prominence by defending future President Hugo Chavez after his failed 1992 coup. She helped secure his release and later became a key Chavismo figure and the first woman to preside over Venezuela’s National Assembly. Chavismo, which promotes socialism and anti-imperialist politics, is the political movement started by Chavez, Maduro’s mentor.
The indictment accuses Flores of joining Maduro’s cocaine importation conspiracy.
Other defendants
The indictment names four other people as Maduro’s coconspirators, namely Diosdado Cabello, Venezuela’s interior minister; Ramon Rodriguez Chacin, former Venezuelan interior minister; Nicolas Maduro Guerra, Maduro’s son and a Venezuelan politician; and Hector Rusthenford Guerrero Flores, the leader of Tren de Aragua, which was designated as a “foreign terrorist organization” by the US in February. But most experts do not define Tren de Aragua as a “terrorist organisation”.
It is not clear yet who will represent Maduro, Flores and the other defendants.
Who is the judge?
Hellerstein was born in 1933 in New York. He was appointed to the federal bench in 1998 by former President Bill Clinton.
He is likely on Monday to advise Maduro and Flores about their rights and ask them if they want to enter a plea.
What’s at stake?
Maduro’s freedom is primarily at stake. If convicted, he could face 30 years to life in prison.
“This is less about Maduro as it is about access to Venezuela’s oil deposits,” Ilias Bantekas, a professor of transnational law at Hamad Bin Khalifa University in Qatar, told Al Jazeera. “This is the number one target. Trump is not content with just allowing US oil firms to get concessions but to ‘run’ the country, which entails absolute and indefinite control over Venezuela’s resources.”
Venezuela’s oil reserves are concentrated primarily in the Orinoco Belt, a region in the eastern part of the country stretching across roughly 55,000sq km (21,235sq miles).
While the country is home to the world’s largest proven oil reserves – at an estimated 303 billion barrels as of 2023 – it earns only a fraction of the revenue it once did from exporting crude due to mismanagement and US sanctions.
Last month, Trump accused Venezuela in a post on his Truth Social platform of “stealing” US oil, land and other assets and using that oil to fund crime, “terrorism” and human trafficking.
Trump repeated his false claims after Maduro’s arrest. During a news conference on Saturday, Trump said the US would “run” Venezuela until a “safe, proper and judicious transition” could be carried out.
“Given the opposition of all South American states, save for Argentina, to US dominance in the region, Trump’s plan requires a vast military deployment. We need to see how countries like Brazil and Colombia react to this, including also BRICS,” said Bantekas from Hamad Bin Khalifa University.
In a joint statement released on Sunday, the governments of Spain, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico and Uruguay said the US actions in Venezuela “constitute an extremely dangerous precedent for peace and regional security and endanger the civilian population”.
Was Maduro’s abduction legal?
This case is unusual because there are questions about how Maduro was captured and whether it was legal. Russia, China and other Venezuelan allies have accused the US of violating international law.
“If there was an armed conflict between Venezuela and the USA and, given that Maduro is the head of his country’s armed forces, then he would be a legitimate target,” Bantekas said.
“However, under the circumstances there is no armed conflict between the two countries and in the absence of an armed attack by Venezuela against the US, the latter’s invasion in Venezuela violates article 2(4) of the UN Charter, as does the abduction of the country’s President. It is a blatant act of aggression.”
Article 2(4) of the UN Charter bars UN members from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state.
A United Nations Security Council meeting on Monday will determine the legality of the US abduction of Maduro.
“Given that Maduro is already in US custody and in the USA, it is in the interests of all parties that he appear before a court. At the very least, Maduro can challenge the legality of his arrest and the jurisdiction of the court,” Bantekas said.
“The court itself has an obligation to decide if it has jurisdiction and as a preliminary issue decide whether Maduro enjoys immunity from criminal prosecution. If these issues are dispensed the court nonetheless finds that it has jurisdiction and that Maduro does not enjoy immunity, then the prosecutor must prove its case.”
What’s next?
The Trump administration has not explicitly stated a clear plan for Venezuela, with analysts saying the administration has sent out confusing signals.
In an interview with the NBC news channels on Sunday, US Secretary of State Marco Rubio suggested that Washington will not govern Venezuela on a day-to-day basis besides enforcing an existing “oil quarantine”.
Rubio told ABC news on Sunday that the US had leverage over Venezuela and the US would “set the conditions” to ensure that Venezuela is no longer a “narco-trafficking paradise”.
But on Sunday, Trump told reporters that the US is ready to carry out a second military strike on Venezuela if its government refuses to cooperate with his plan to ‘resolve’ the situation there.
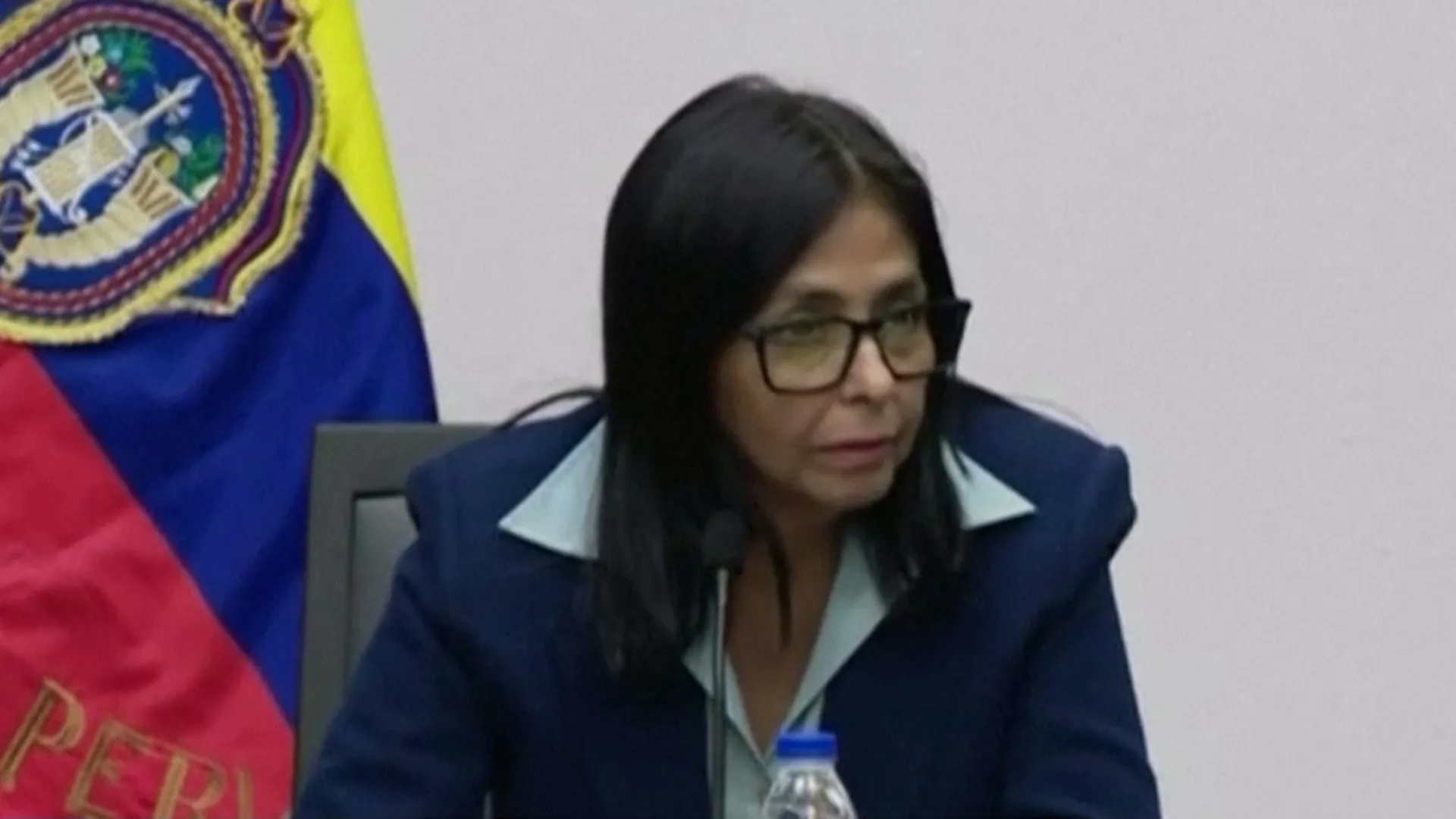
She could “pay a very big price” if she “does not do what’s right”, Trump said, refering Venezuela’s new leader, Delcy Rodriguez.
During his Saturday conference, Trump said that Rodriguez told Rubio that she will do what the US needs her to. “She really doesn’t have a choice,” Trump had said.
In his first press conference after Maduro’s illegal abduction on Saturday, Trump ruled out the possibility of working with opposition leader and Nobel Prize winner Maria Corina Machado, who was barred from running in the 2024 presidential elections.
Machado, a member of the Venezuelan National Assembly, is seen as the most credible adversary of Maduro’s leftist government.
On Monday, Rodriguez, the interim leader, offered to cooperate with Trump. In a statement posted on social media, she invited Trump to “collaborate” and sought “respectful relations”.
“President Donald Trump, our peoples and our region deserve peace and dialogue, not war,” she wrote.
Her conciliatory tone came a day after she appeared on state TV declaring that Maduro was still Venezuela’s sole legitimate president.