Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy says he plans to increase his armed forces’ lethality as part of a strategy to disarm Moscow and turn a deadlocked negotiating table.
“The task of Ukrainian units is to ensure a level of destruction of the occupier at which Russian losses exceed the number of reinforcements they can send to their forces each month,” he told military personnel on Monday.
Recommended Stories
list of 4 itemsend of list
“We are talking about 50,000 Russian losses per month, this is the optimal level,” he said.
Video analysis, Zelenskyy recently said, showed 35,000 confirmed kills in December 2025, up from 30,000 in November and 26,000 in October. But on Monday, he clarified that the 35,000 were “killed and badly wounded occupiers”, who would not be returning to the battlefield.
His commander in chief, Oleksandr Syrskii, conservatively estimated “more than 33,000” confirmed kills in December.
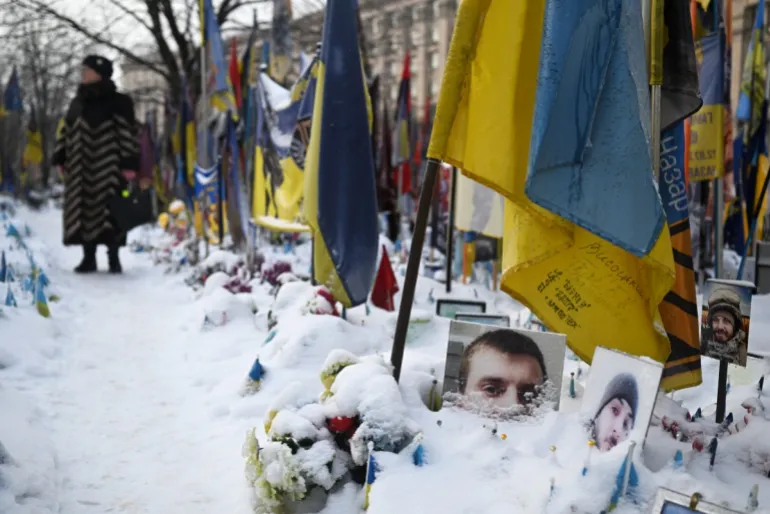
Ukraine believes it has killed or maimed 1.2 million Russians since Russia’s full-scale invasion in 2022.
The Center for Strategic and International Studies recently estimated that Russia had suffered 1.2mn casualties, including at least 325,000 deaths, and Ukraine up to 600,000 casualties, with as many as 140,000 deaths.
Al Jazeera cannot confirm casualty estimates from either side.

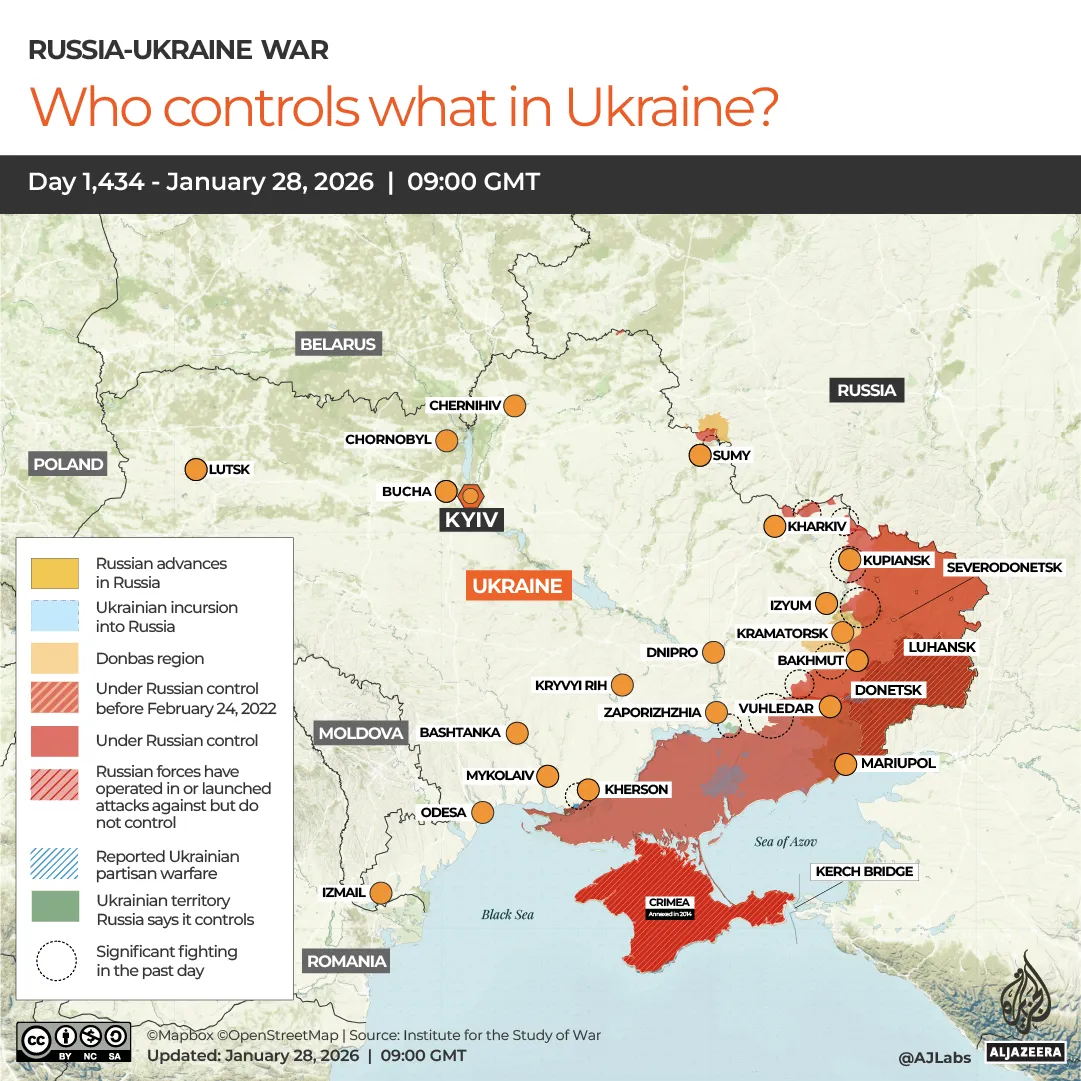
The war is currently stalemated, with Russia struggling to make meaningful territorial gains.
Russia held just more than a quarter of Ukraine a month into its full-scale war, in March 2022, according to geolocated footage.
The following month, Ukraine pushed Russian forces back from a string of northern cities – Kyiv, Kharkiv, Sumy and Chernihiv – leaving Russia in possession of one-fifth of the country.
In August and September 2022, then-ground forces commander Syrskii masterminded a campaign to push Russian forces east of the Oskil River in the northern Kharkiv region, and Russia itself withdrew east of the Dnipro River in the southern region of Kherson, leaving it with 17.8 percent of the country.
In the last three years, Russia increased that number to 19.3 percent.
For almost six months, Russia has struggled to seize two towns it has almost surrounded with 150,000 troops in Ukraine’s eastern Donetsk region.
“In Pokrovsk and Myrnohrad, the Ukrainian Defence Forces continue to contain the enemy, which is trying to infiltrate the northern districts of both cities in small groups,” Syrskii said last week.
Russia claimed it had captured the northern city of Kupiansk last month, but Russian military reporters say Ukrainian forces have retaken control of the town and surrounded the Russian assault force within it.
The engine of war
Zelenskyy’s strategy involves increasing domestic drone production and honing the skills of drone operators, because drones now hit 80 percent of targets on the battlefield.
“In just the past year alone, 819,737 targets were hit – hit by drones. And we clearly record every single hit,” he said on Monday.
The military has instituted a point system, rewarding drone operators for the number and precision of their hits.
That reflects a system put in place in April 2024, offering financial rewards to ground troops for destroying Russian battlefield equipment, culminating in $23,000 for capturing a battle tank.
Zelenskyy appointed Mykhailo Fedorov as defence minister this month, who previously served as digital transformation minister and deputy prime minister for innovation, education, science and technology.

Last week, Fedorov began to appoint his advisers. They include Serhiy Sternenko, who last year created Ukraine’s largest non-state supplier of military drones, to step up drone production. Fedorov’s former deputy at the digital transformation ministry, Valeriya Ionan, was put in charge of international collaborations, thanks to her experience with Silicon Valley giants like Google and Cisco. Fedorov also appointed Serhiy Beskrestnov as technological adviser. Beskrestnov is an expert on Russian drone and electronic warfare innovation.
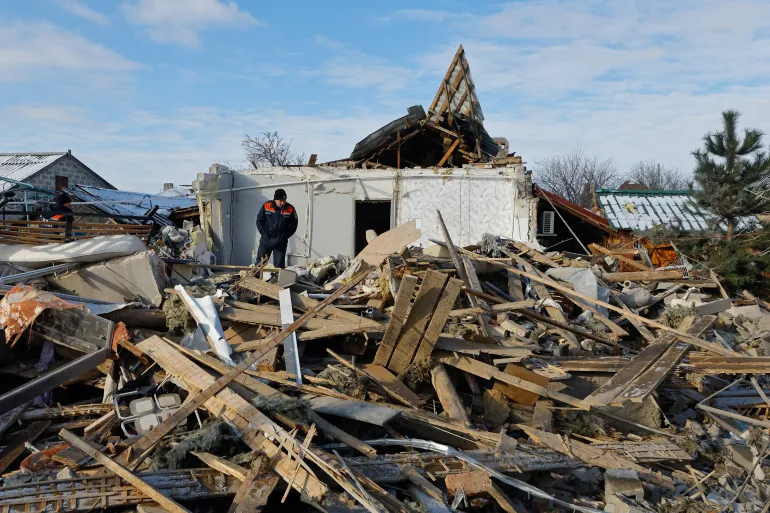
Russian assaults pound Ukraine
Zelenskyy’s war aims stem in part from the fact that Russia refuses to give up its campaign to seize more of Ukraine.
Despite US President Donald Trump’s efforts to bring about a ceasefire, talks remain deadlocked over the future of Donetsk.
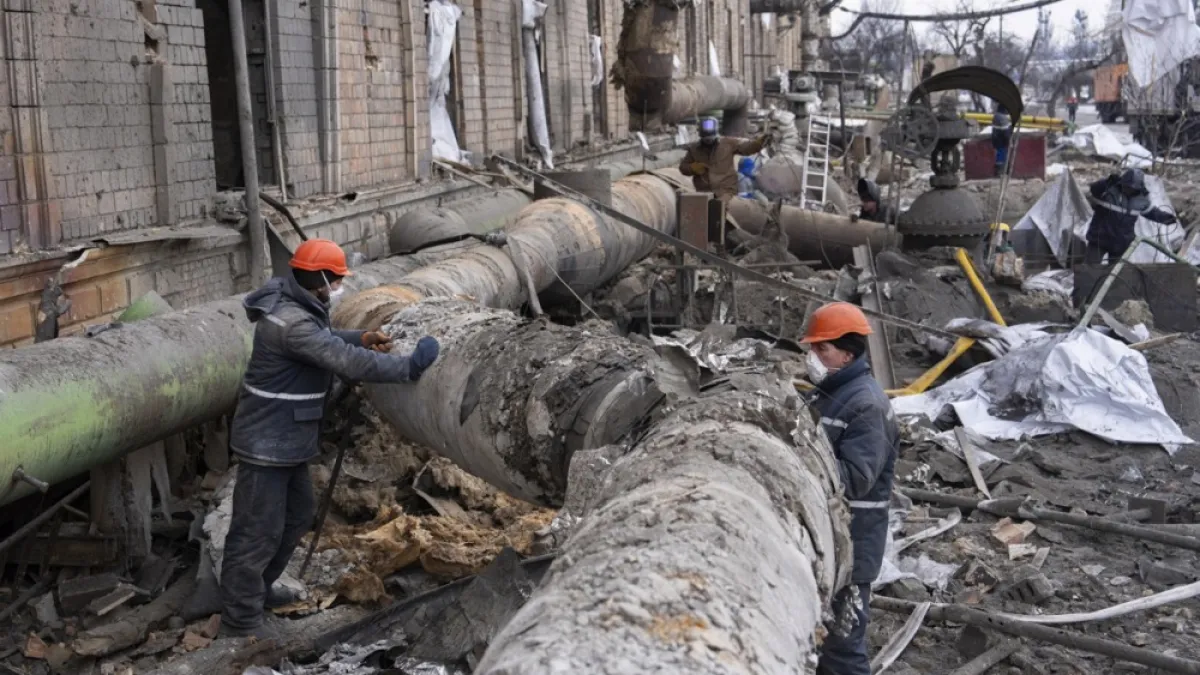
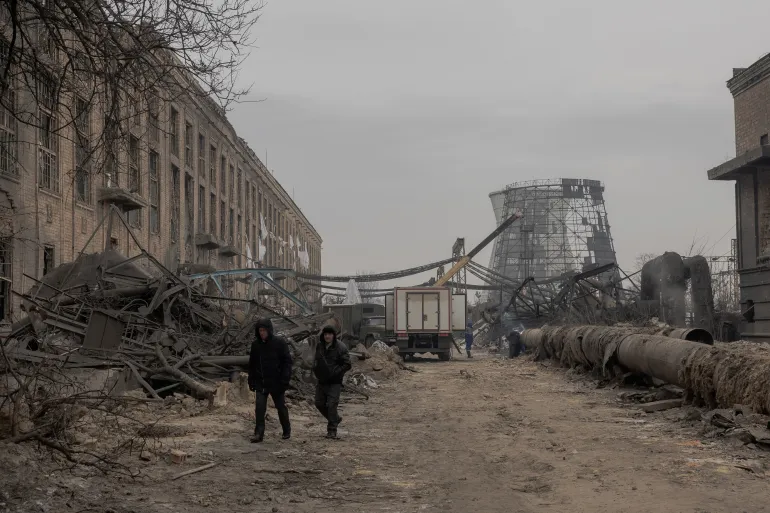
Russia’s worst attack against Ukrainian cities and energy facilities last week came on Saturday, involving 375 drones and 21 missiles, as Russian, US and Ukrainian delegations were negotiating a ceasefire in Abu Dhabi.
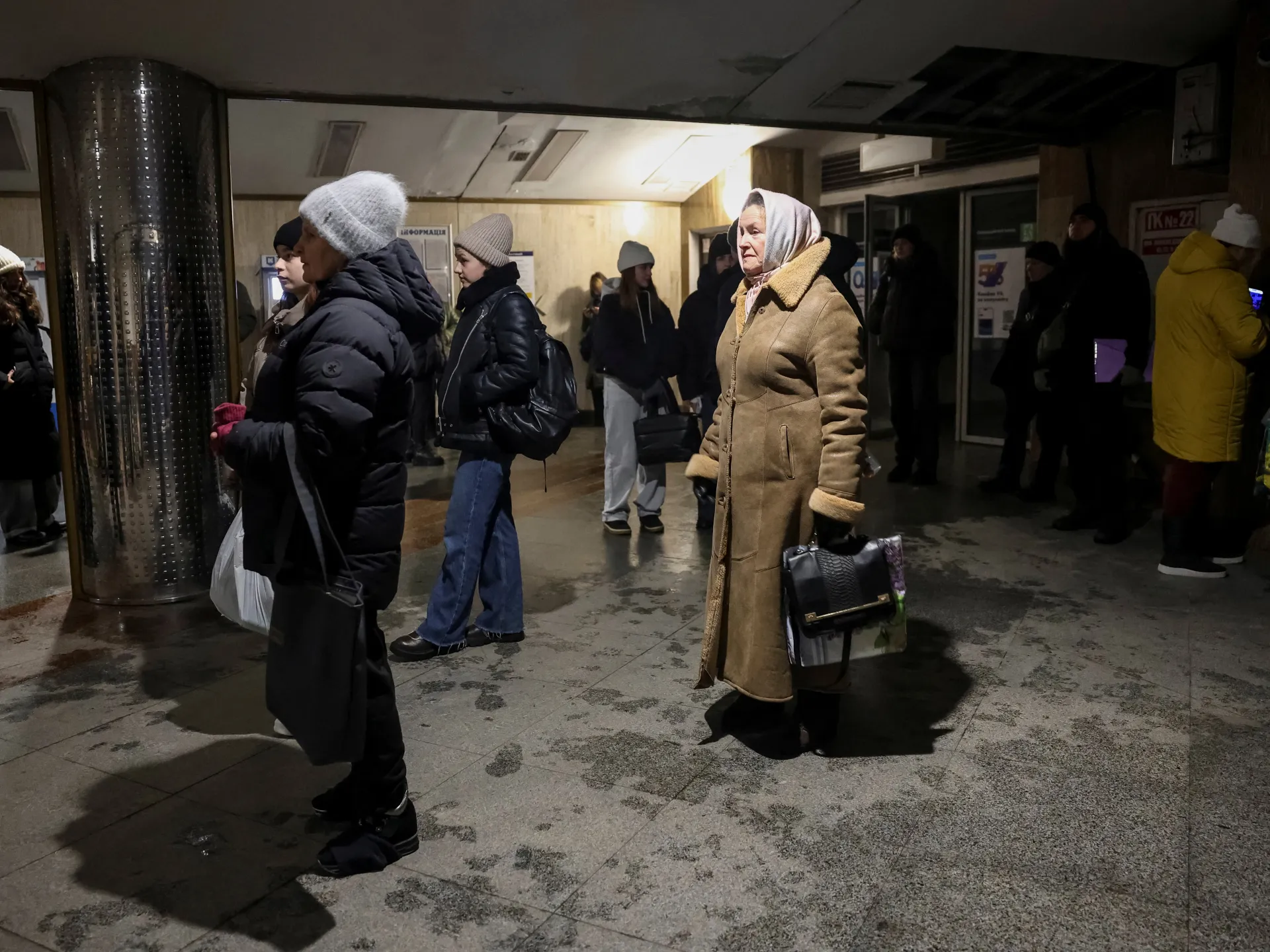
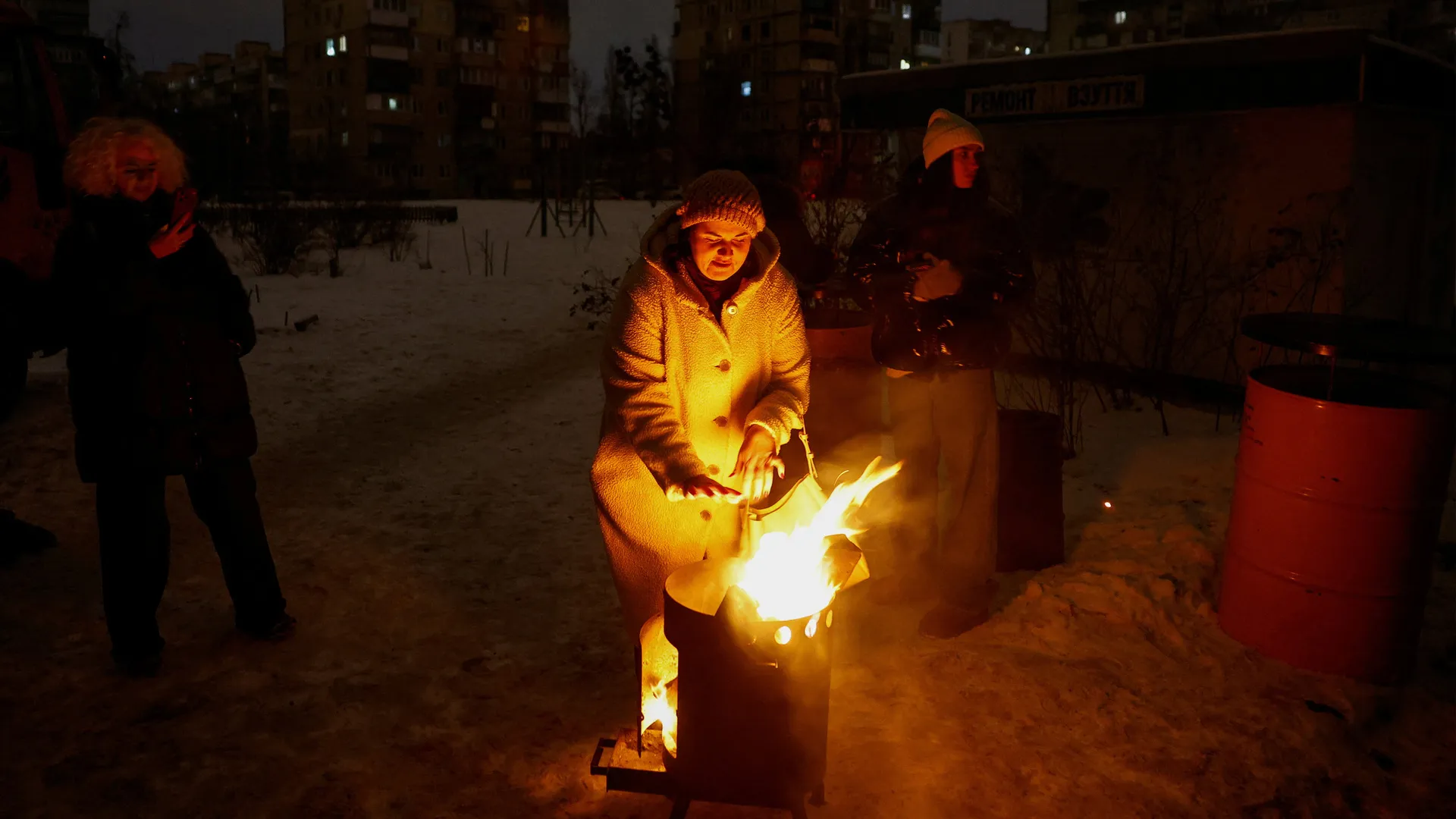
The strike left 1.2 million homes without power nationwide, including 6,000 in Kyiv.
Energy Minister Denys Shmyhal said 800,000 homes in Kyiv were still without power following three previous strikes this month. “Constant enemy attacks unfortunately keep the situation from being stabilised,” he wrote on social media.

Zelenskyy told Ukrainians in an evening video address that electricity supply problems were still widespread in Kyiv, Kryvyi Rih, Dnipro and in the Chernihiv and Sumy regions.
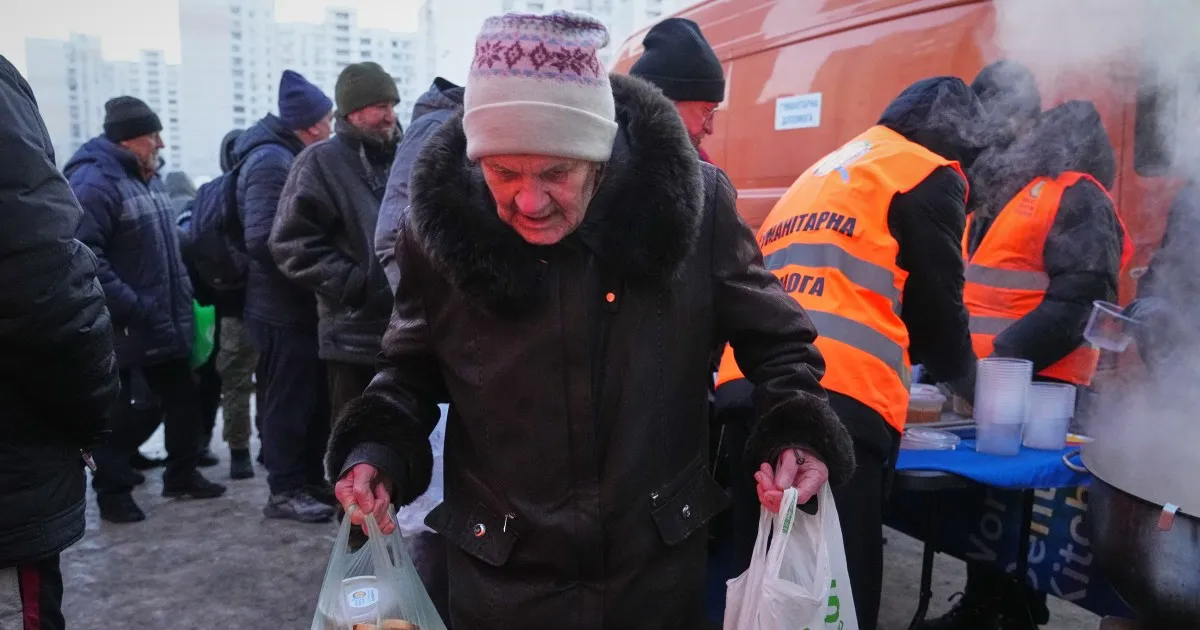
“We are scaling up assistance points and warming centers,” he said, adding that 174 [crews] were working to fix the damage in Kyiv alone. Shmyal said 710,000 people were still without power in Kyiv.
A Czech grassroots initiative fundraised $6m to buy hundreds of electric generators for Ukrainian households. On Friday, the European Commission said it was sending 447 generators to Ukraine.
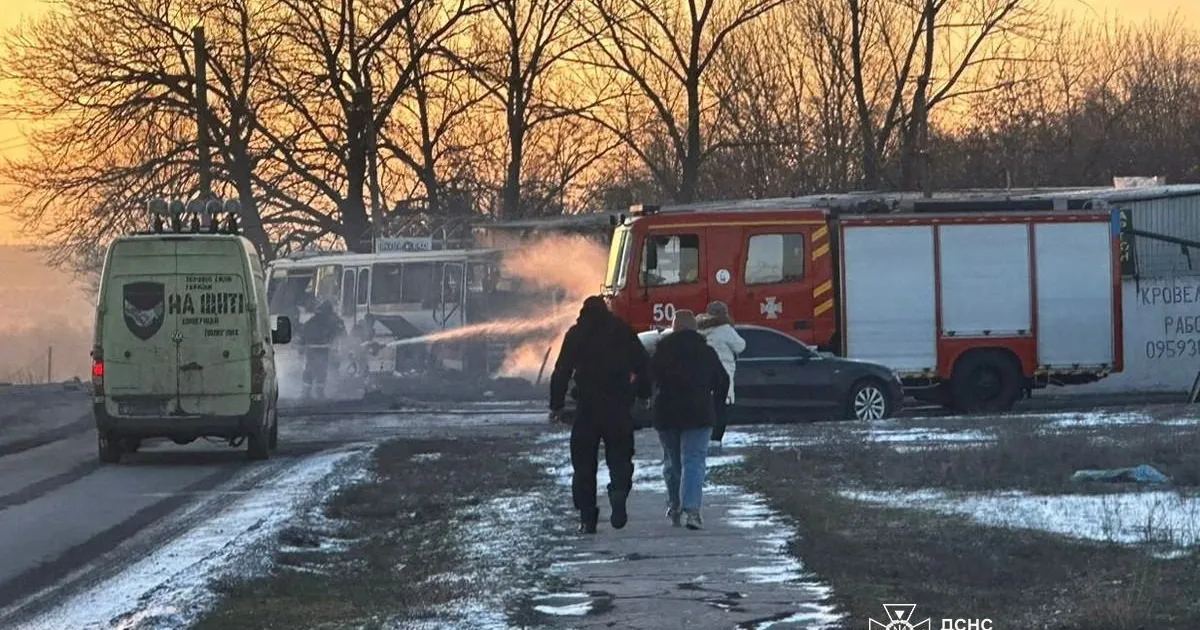
On Wednesday, Russian drones killed three people. Two of them were a young couple in Kyiv killed when a drone struck their apartment building. Rescuers found only their four-year-old daughter alive.
“When I carried her out, the girl started crying very hard, and then she began to shake violently,” said Marian Kushnir, a journalist who was a neighbour of the couple.
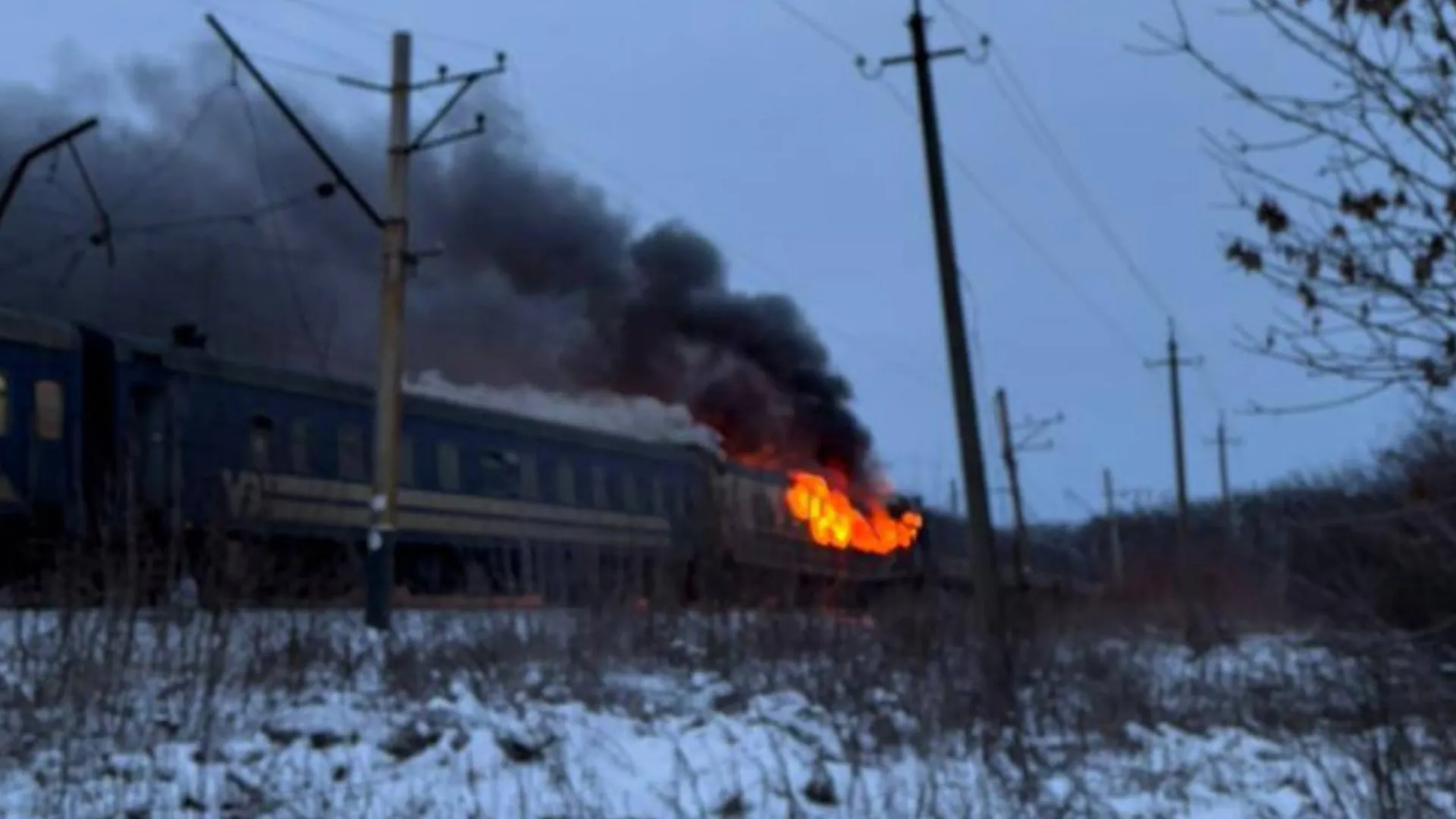
At least five more people died when a drone struck a passenger train in the northern Kharkiv region, and two children and a pregnant woman were wounded when 50 drones rained down on the southern port of Odesa.
Talks in Abu Dhabi ended without a ceasefire. Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov had said before they began that Russia was not willing to compromise on any of its territorial demands.
US Secretary of State Marco Rubio said talks were focusing on the nub of disagreement between the two sides, which is Ukraine’s refusal to hand over the remaining one-fifth of Donetsk that Moscow does not control.
Talks are scheduled to continue in Abu Dhabi on Sunday, officials said.
Unvarnished truth from Zelenskyy
In a scathing speech to the World Economic Forum in Davos, Zelenskyy accused his European allies of “wait-hoping” the Russian threat would disappear after almost four years of war in Ukraine.
“Europe relies only on the belief that if danger comes, NATO will act. But no one has really seen the Alliance in action. If Putin decides to take Lithuania or strike Poland, who will respond?” Zelenskyy asked.
US President Donald Trump’s threat to take Greenland by force on January 17, he said, revealed Europe’s lack of readiness when seven Nordic countries sent 40 soldiers to the island.
“If you send 30 or 40 soldiers to Greenland – what is that for? What message does it send? What’s the message to [Russian President Vladimir] Putin? To China? And even more importantly, what message does it send to Denmark – the most important – your close ally?”

In contrast, said Zelenskyy, Trump was willing to seize Russian tankers selling sanctioned oil, and put Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro on drug charges, while Putin, an indicted war criminal, remained free. “No security guarantees work without the US,” he said.
NATO Secretary-General Mark Rutte echoed those sentiments in a speech to the European Parliament on Monday [January 26].
“If anyone thinks here . . . that the European Union or Europe as a whole can defend itself without the US, keep on dreaming,” he said. “You can’t.”