‘Here Lies Love’ review: David Byrne’s musical made over at the Taper
Imelda Marcos’ fetish for fiendishly expensive shoes was a running gag in the 1980s. But did you know that she was also something of a disco queen?
The image of a jet-setting Marcos in her Beltrami pumps boogieing with arms dealers at fashionable New York nightspots is one of the inspirations of David Byrne’s musical about the notorious former first lady of the Philippines, who sang on the campaign trail for her husband, Ferdinand E. Marcos, and ruled with an iron fist alongside him after he declared martial law and plunged his nation into a brutal dictatorship.
“Here Lies Love,” which is having its Los Angeles premiere at the Mark Taper Forum, traces the political power couple’s rise and fall through a series of dance cuts that capture the irrational hold charismatic leaders can have on a public — at least while the music is blasting.
Byrne, the ingenious Talking Heads co-founder, conceived the show and wrote the music and lyrics. Fatboy Slim, a Grammy Award-winning DJ, musician and record producer, contributed to the music. The score, a mix of lush disco and synth pop with hints of island breezes and karaoke camp, brings a club-like energy to the stage.

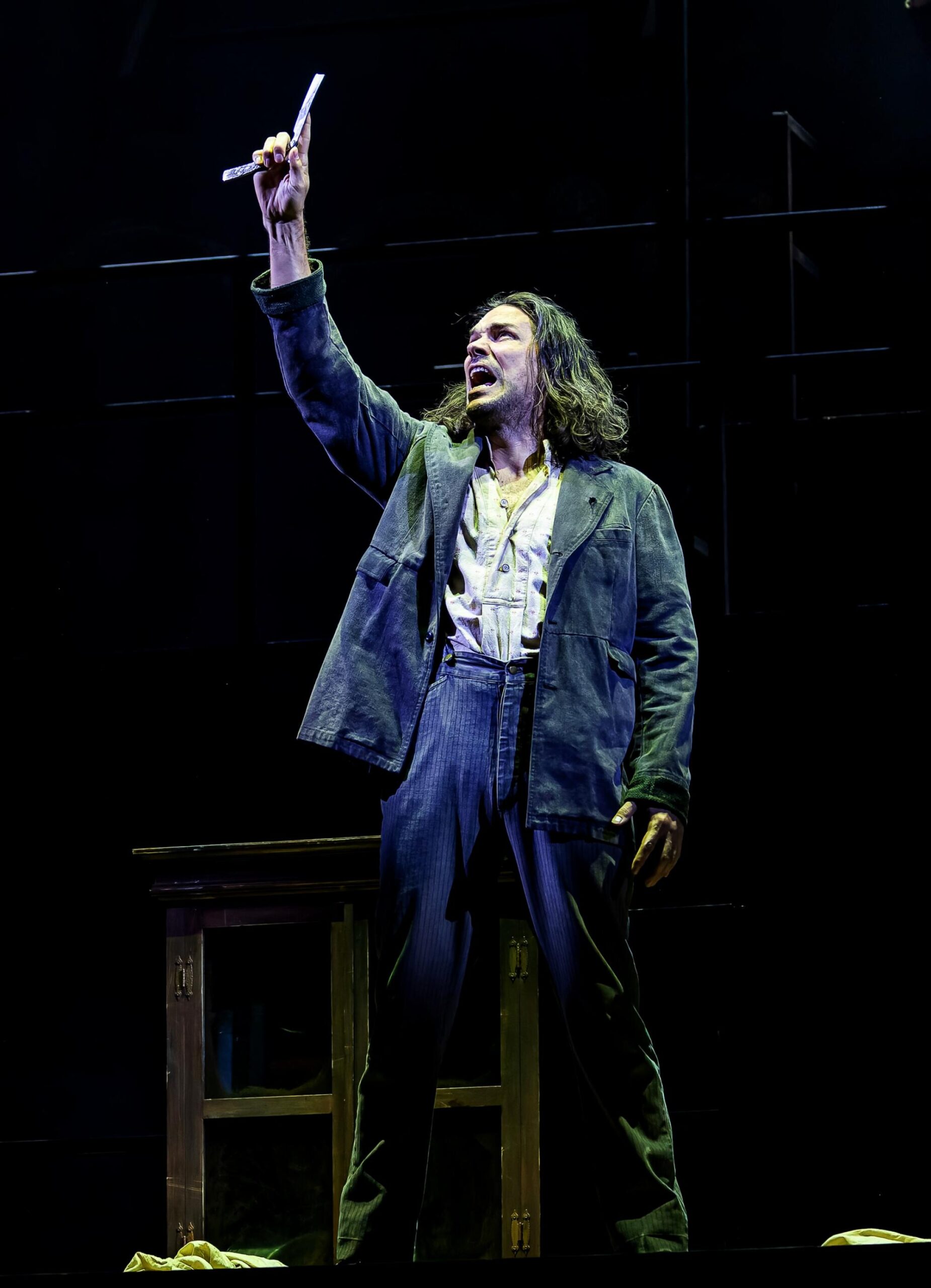
Aura Mayari and the company of “Here Lies Love” at the Mark Taper Forum.
(Jeff Lorch)
I first saw “Here Lies Love” at New York’s Public Theater in 2013, when the production, directed by Alex Timbers, was staged as an immersive dance party. Audience members moved along a shifting dance floor as the love story between Imelda, a beauty queen from the provinces, and Ferdinand, an ambitious senator accustomed to getting what he wants, sourly played out amid the backdrop of a traumatic national story.
This sung-through musical pulled off something of a coup of its own. As Ferdinand, now president and philandering husband, and Imelda, his embittered wife dripping in compensatory luxury, shore up their “conjugal dictatorship,” theatergoers discovered that, while partying to the seductive beat, a political dystopia was solidifying around them.
Imagine if, in “Evita,” audience members were invited to sing back up on the balcony as Eva Perón belts out “Don’t Cry for Me Argentina,” accompanying her in her last manipulative hurrah. “Here Lies Love” seemed to want its audience to leave with an aftertaste of cognitive dissonance.
Audiences don’t usually like being duped. But voters need to be continually reminded that when they go to bed with a strongman, they’ll likely wake up without healthcare or voting rights.
“Here Lies Love” at the Taper doesn’t follow the Public Theater’s staging or the similarly immersive Broadway production by Timbers that followed in 2023. It’s a more straightforward presentation that keeps audience members in their seats, except for a moment when uprising is in the air and a few theatergoers are conscripted to join the ecstatic rebellion.

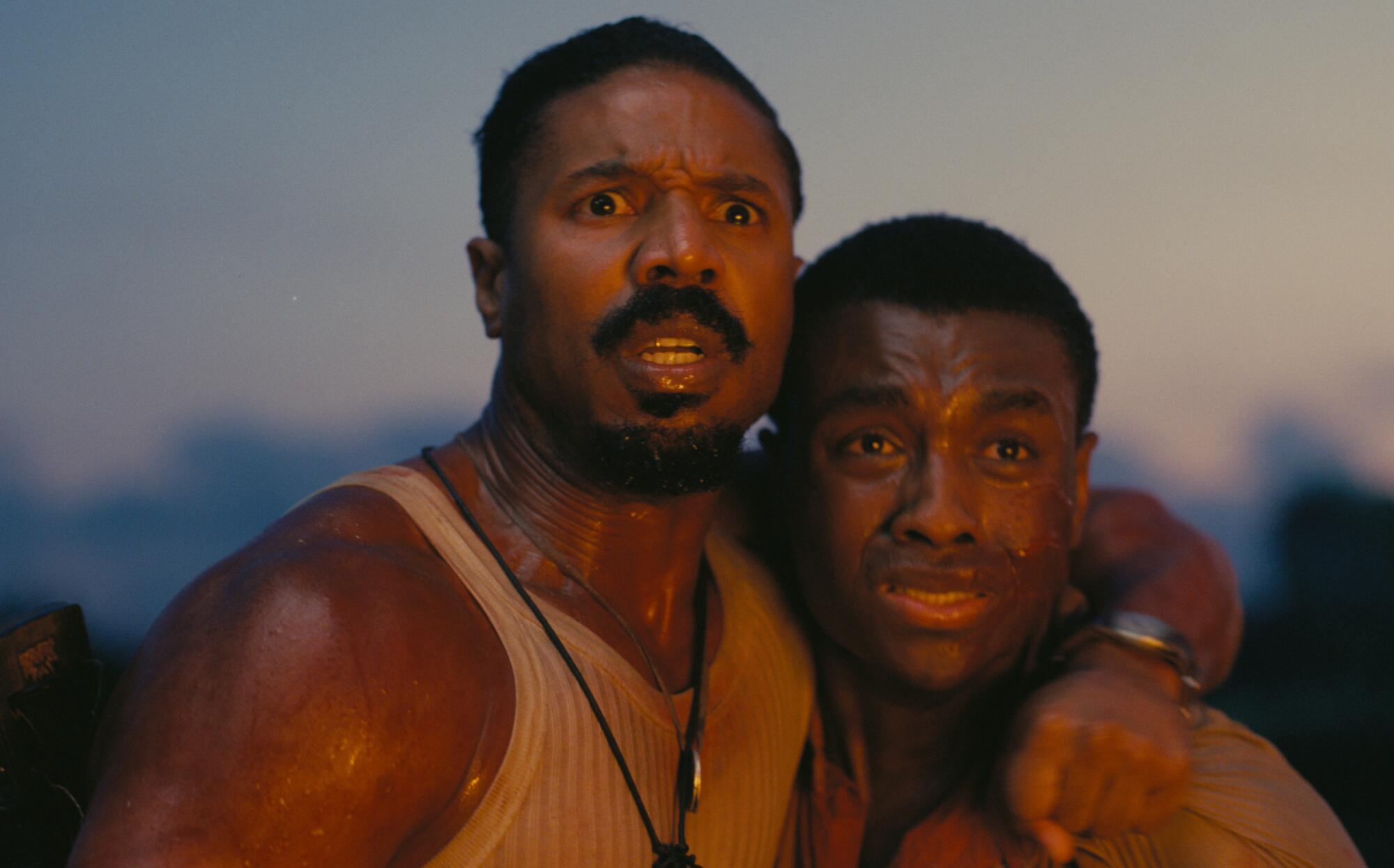
Jeff Lorenz Garrido, from left, Joshua Dela Cruz, and Garrick Goce Macatangay in “Here Lies Love” at the Mark Taper Forum.
(Jeff Lorch)
Snehal Desai’s direction is politically clear-eyed and scrupulous. Corruption, authoritarianism and censorship, as we’re learning firsthand, scandal after constitutional scandal, are no laughing matter. The question is whether “Here Lies Love” can bear the scrutiny of a more traditional musical.
There’s not a traditional libretto, so the story is transmitted mostly through song lyrics. But stump speeches, rallying cries and the theatrical guidance of Imeldific (Aura Mayari, alum of Season 15 of “RuPaul’s Drag Race”) help flesh out the chronicle.
This emcee figure, a Taper innovation, replaces the DJ role of previous productions and establishes the show’s metatheatrical frame. The opening number, “American Troglodyte,” underscores the American imperial role in the story and provides Imdeldific with a satiric banner that doesn’t let a smiling superpower off the hook.
William Carlos Angulo’s choreography is unfailingly kinetic, but participating in a party is more energizing than watching one at a remove. Yet the political case of Ferdinand and Imelda Marcos, a tale of celebrity and tyranny marching in lockstep, speaks so directly to our own time that I found myself gripped by the object lesson of this public saga, even if it’s not always easy to connect all the fragments, never mind distinguish between hard fact and fictional license.
I was particularly fascinated by the portrayal of Imelda (Reanne Acasio), whose political character seems to be shaped by personal disappointments and run-of-the-mill humiliations. Imelda is wounded not only by the philandering of Ferdinand (Chris Renfro) but by an even more painful injury inflicted by her first love, Ninoy Aquino (Joshua Dela Cruz), a politician determined to become the voice of his people.
Ninoy recognizes an essential incompatibility between them. Imelda lives for love while he has political work to do. He bids her adieu in the song “Opposite Attraction,” though fate will bring them together after Imelda and her husband gain power and Ninoy, as the leading opposition figure, becomes their prisoner and eventual victim of the chaos unleashed by their regime.

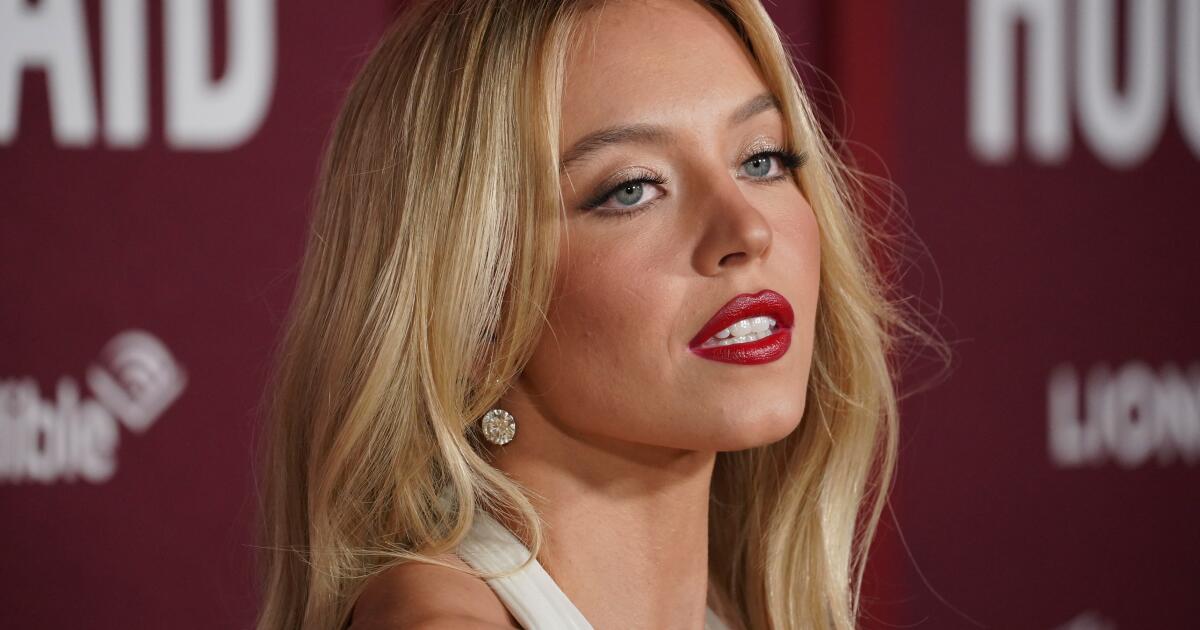
Joan Almedilla and the company of “Here Lies Love” at the Mark Taper Forum.
(Jeff Lorch)
Unfolding under the theatrical auspices of Imeldific, “Here Lies Love” retells the history of the Marcos years as a musical pageant. Imelda’s transformation, from shy, lowly country girl to “Iron Butterfly,” covering up her shame with jewelry from Tiffany and revealing a will every bit as hard as the diamonds she flaunts, is presented with music so catchy and compulsive that it has the force of historical inevitability
The grooves supplied by Byrne and Slim take not just the characters but the audience on a ride through a brutal anti-democratic period. Does the disco spectacle aesthetic treat this history too lightly?
The production seems wary of this criticism. A program note from dramaturg Ely Sonny Orquiza, attuned to the sensitivities of the large Filipino diaspora in Los Angeles, notes that the production, “featuring an all-Filipino cast and majority-AAPI creative team, is not intended as a definitive or comprehensive history, but as an entry point for dialogue and inquiry.”
The scale of damage perpetrated by the regime is still being collectively processed. One victim, Estrella Cumpas (Carol Angeli), makes the mistake of confronting Imelda, a childhood friend, and is taken into custody. She will have to stand in for thousands of others.
The design scheme certainly doesn’t want to spoil anyone’s good time. Arnel Sancianco’s sets, Marcella Barbeau’s lighting and the more glittering of Jaymee Ngernwichit’s costumes seem to place us in a retro Euro-style disco world, where fun is typically a function of the strength of the cocktails consumed.
But there’s a countermovement in the show, the People Power Revolution that gains momentum after the assassination of Nimoy. The funeral speech of his mother (Joan Almedilla) is turned into the galvanizing protest song, “Just Ask the Flowers,” in which something as basic as maternal love wakes the country to the madness around them. Desai, whose directorial work at the Taper thus far has brought together rave and rebellion, smoothly merges the Dionysian frenzy of the music with the nonviolent revolution that ended Ferdinand Marcos’ protracted dictatorship in 1986.
Dela Cruz’s stirring Ninoy standing tall against the patriarchal savagery of Renfro’s Ferdinand and the petty vindictiveness of Acasio’s well-drawn Imelda is a powerful call to action. Byrne and Slim’s score insists that not even death can stop the beat of this democratic spirit.
The production points out at the end that another Marcos, Ferdinand “Bongbong” Marcos Jr., Ferdinand and Imelda’s son, is now president. Perhaps the show’s final number can shed light: “God draws straight, but with crooked lines.”
‘Here Lies Love’
Where: Mark Taper Forum, 135 N. Grand Ave., L.A.
When: 7:30 p.m. Tuesdays-Thursdays, 8 p.m. Fridays, 2 and 8 p.m. Saturdays, 1 and 7 p.m. Sundays. (Check for exceptions.) Ends April 5
Tickets: Start at $40.25
Contact: (213) 628-2772 or centertheatregroup.org
Running time: 1 hour, 30 minutes (no intermission)