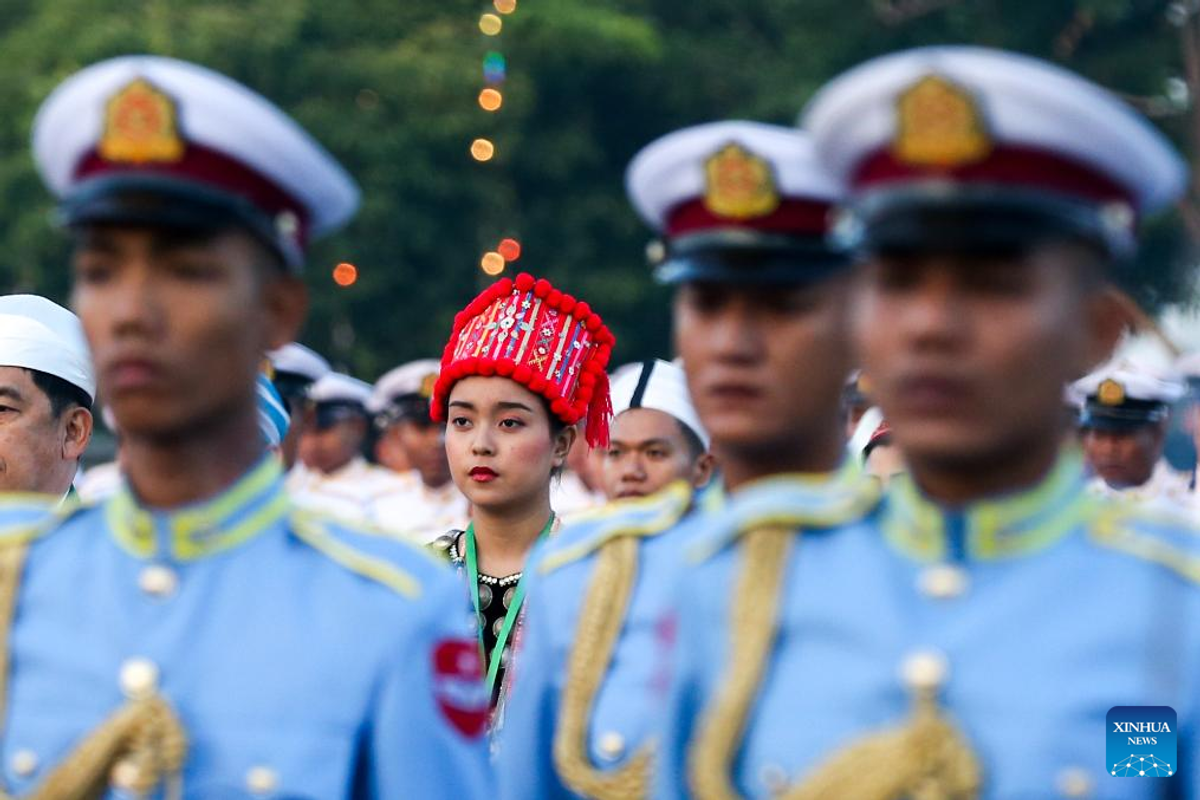
In 1886, Myanmar (then called Burma) came under British control, but the British made a distinction between how central Burma and the various outlying ethnic groups were ruled.
Following the end of the Second World War, General Aung San, head of the interim Burmese government and representatives from the Shan states, the Kachin hills and the Chin hills met in Panglong to determine the future of Burma.
They reached an agreement which was signed and passed on 12 February 1947. The agreement unified Burma and demanded that the British government restore independence to all of Burma. The Panglong agreement formed the basis for the creation of the Union of Burma. The deal also offered the ethnic leaders the possibility of seceding from the union if they were dissatisfied with the new nation.
The agreement was a key event in the history of Myanmar as it directly led to the creation of Burma as an independent state in January 1948.
While instrumental in the Panglong agreement, Aung San did not live to see Burma gains its independence in January 1948. He was assassinated on 19 July 1947.