Madagascar cyclone death toll hits 38, 12,000 displaced; Mozambique braces | Climate Crisis News
Gezani is forecast to return to cyclone status when it strikes southern Mozambique on Friday evening.
Nearly 40 people have been killed and more than 12,000 others displaced after Cyclone Gezani slammed into Madagascar’s second-largest city earlier this week, as Mozambique braced for the storm’s arrival.
Updating its tolls as assessments progressed, Madagascar’s National Office for Risk and Disaster Management (BNGRC) said on Thursday it had recorded 38 deaths, while six people remained missing and at least 374 were injured.
Recommended Stories
list of 3 itemsend of list
Gezani made landfall on Tuesday at the Indian Ocean island nation Madagascar’s eastern coastal city, Toamasina, bringing winds that reached 250km/h (155mph).
Madagascar’s new leader, Colonel Michael Randrianirina, has declared a national disaster and called for “international solidarity”, saying the cyclone had “ravaged up to 75 percent of Toamasina and surrounds”.
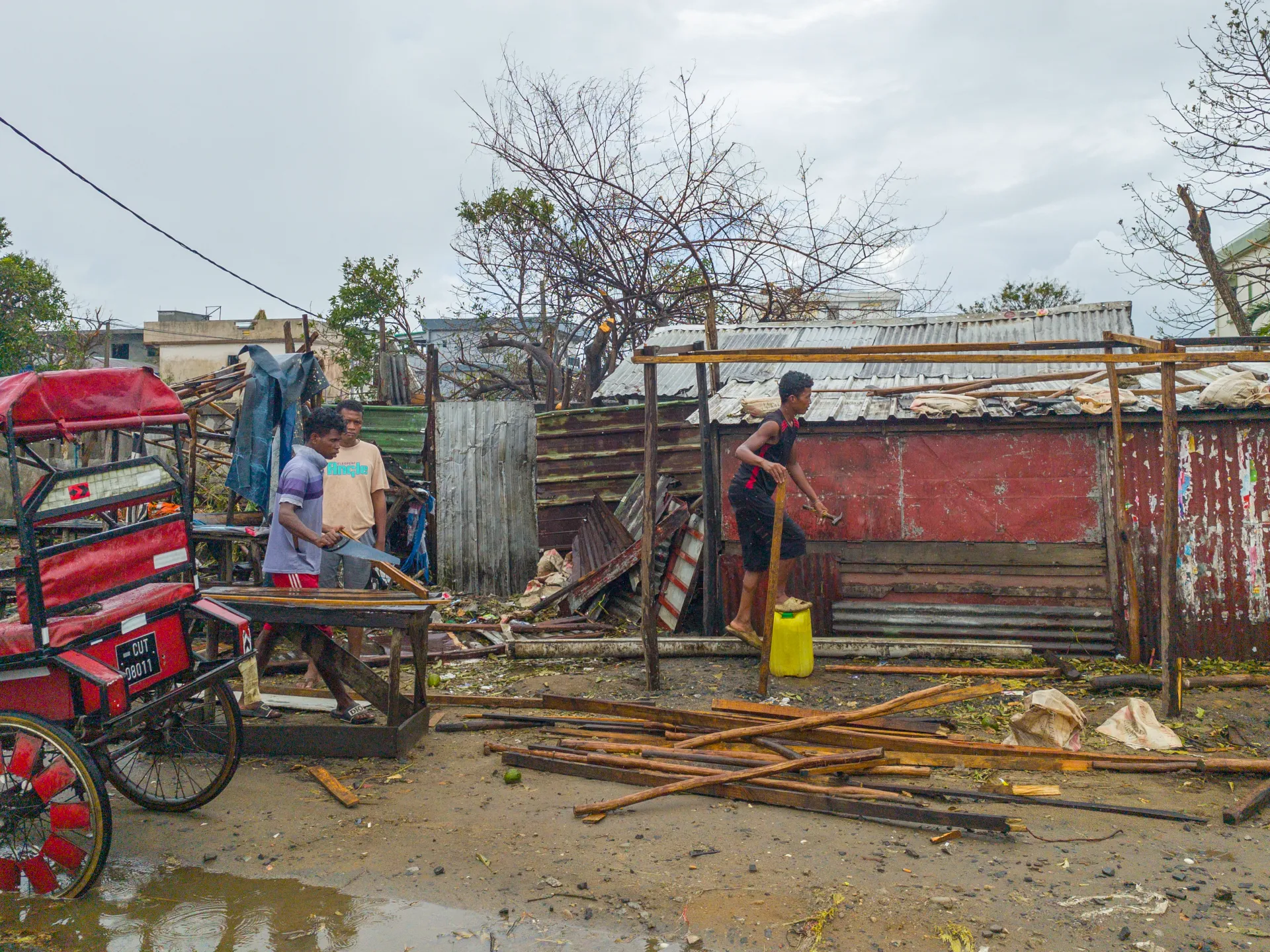
Images from the AFP news agency showed the battered city of 500,000 people littered with trees felled by strong winds and roofs blown off buildings.
Residents dug through piles of debris, planks and corrugated metal to repair their makeshift homes.
More than 18,000 homes were destroyed in the cyclone, according to the BNGRC, with at least 50,000 damaged or flooded. Authorities say many of the deaths were caused by building collapses, as many give inadequate shelter from strong storms.
The main road linking the city to the capital, Antananarivo, was cut off in several places, “blocking humanitarian convoys”, it said, while telecommunications were unstable.
The storm also caused major destruction in the Atsinanana region surrounding Toamasina, the disaster authority said, adding that assessments were still under way.
France announced the dispatch of food aid and rescue teams from its Reunion Island, about 1,000km (600 miles) away.
Thousands of people had been forced to leave their homes, said the United Nations’s International Organization for Migration (IOM), describing “widespread destruction and disruption”.
The cyclone’s landfall was likely one of the strongest recorded in the region during the satellite era, rivalling Geralda in February 1994, it said. That storm killed at least 200 people and affected half a million more.
Gezani weakened after landfall but continued to sweep across the island as a tropical storm until late on Wednesday.
It was forecast to return to cyclone status as it reaches the Mozambique Channel, according to the Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre La Reunion (CMRS), and could from Friday evening strike southern Mozambique.
Mozambican authorities issued warnings on Thursday about the approaching storm, saying it could cause violent winds and rough seas of 10-metre waves and urging people to leave the area of expected impact.
Both Madagascar and Mozambique are vulnerable to destructive storms that blow in off the Indian Ocean. Just last month, the northwestern part of Madagascar was hit by Cyclone Fytia, killing at least 14 people.
Mozambique has already faced devastating flooding from seasonal rainfall, with nearly 140 lives lost since October 1, according to the country’s National Disasters Management Institute.