The Al-Jaleel Society for Care and Community-based Rehabilitation has provided essential services to disabled Palestinians in Jenin refugee camp for decades. But now, after repeated Israeli attacks, the centre has been destroyed, and its staff have discovered that it sits in an Israeli-designated demolition zone.
Al-Jaleel’s staff have received no official notice, but in early June, the Israeli army published an aerial map showing several buildings in the area that were set to be destroyed, including the rehabilitation centre.
Zaid Am-Ali, senior advocacy officer for Palestine operations at Humanity and Inclusion, Al-Jaleel’s partner organisation, told Al Jazeera the reason the organisations were given was that the area was being secured for military and security purposes.
“This is not the first time the centre has been targeted, the Israeli military has destroyed parts of it during previous acts of demolition in the refugee camp and has breached and ransacked the centre and tampered with assistive devices meant for persons with disabilities,” Am-Ali said.
Al Jazeera has reached out to the Israeli military but has not received a response at the time of publication.
Supporting thousands of Palestinians
Al-Jaleel is a “critical lifeline”, Am-Ali said, describing how the demolition of the centre would deprive vulnerable communities in Jenin and the wider northern West Bank of its essential services.
It was established in 1991 as the Local Rehabilitation Committee, which became an independent NGO in 2010 under the name Al-Jaleel.
Since it first opened its doors, Al-Jaleel has provided thousands of Palestinians with a wide range of support and services, especially to those with mobility impairments resulting from injury, illness, or conflict-related trauma.
As well as prosthetics, orthotics and physical and occupational therapies, Al-Jaleel also offers psychological support for those affected by disability and continuing violent assaults perpetrated by the Israeli military, which has been attacking Jenin on a regular basis for years, but has intensified operations since the start of 2025.
“This is the same area that has been subject to an ongoing Israeli military operation for years now, causing a lot of casualties and damage to civilian infrastructure,” Am-Ali said.
Al-Jaleel’s ability to function and provide care was severely compromised in April when an Israeli attack damaged the building.
Although staff have since relocated and started operating from another location due to their displacement from the camp, they have not yet been permitted to re-enter the organisation’s original building to retrieve any equipment that was spared during the April attack.
Staff were told they would be allowed to evacuate their equipment on July 12, but were then not allowed to do so by the Israeli military.
It is unclear when or if staff will be able to collect Al-Jaleel’s belongings before the demolition takes place. With the area now declared a closed military zone, Al-Jaleel’s staff are being denied information about the building’s status.
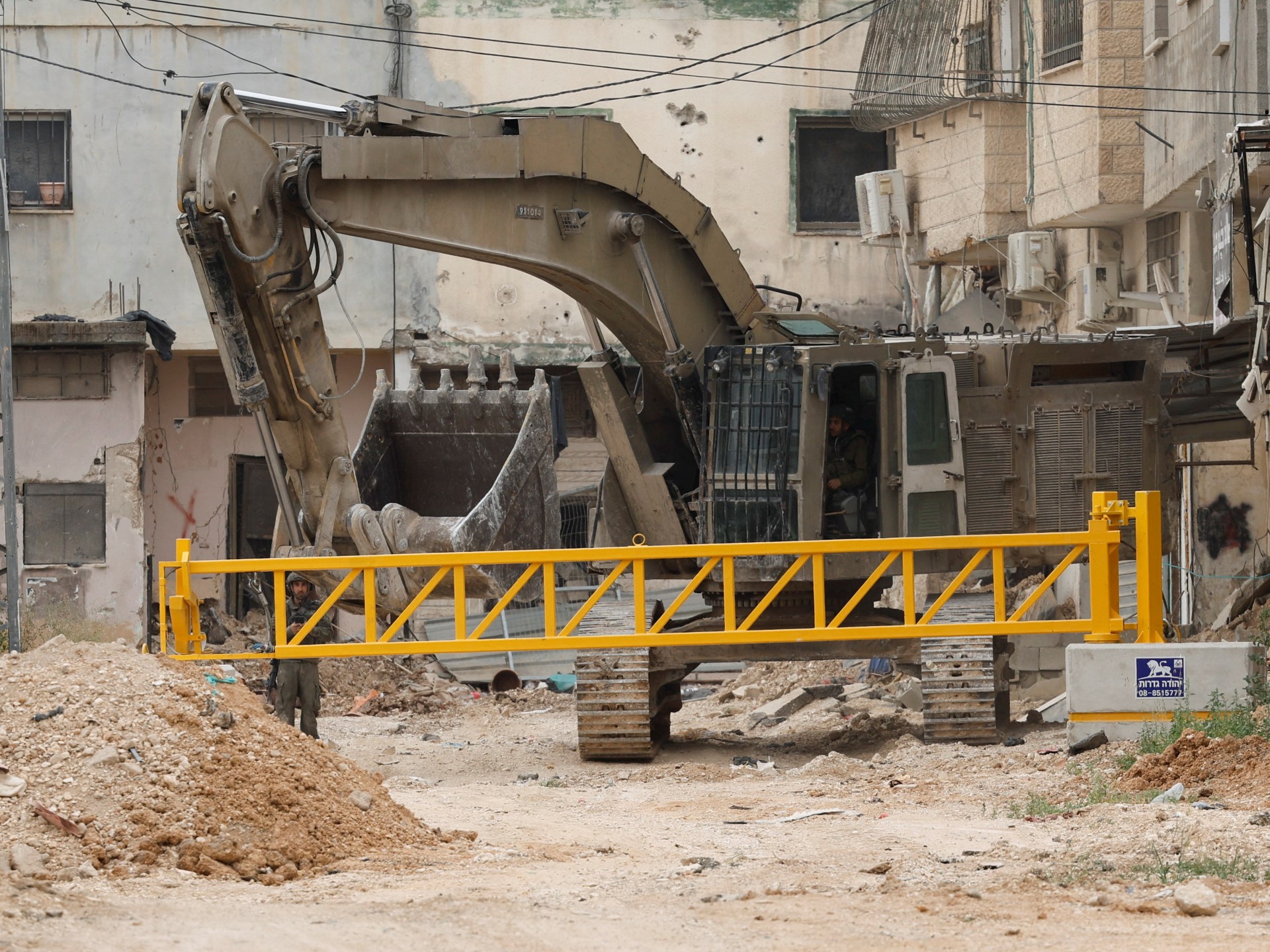
At the time of writing, the centre has not been demolished, but other buildings in its vicinity have been torn down.
Violence in Jenin
Violence in Jenin has escalated significantly since January 21, when the Israeli military launched “Operation Iron Wall” in the city and the nearby refugee camp.
According to Israeli forces, the operation is an “antiterrorism” offensive, attempting to crush Palestinian resistance efforts in the area.
The Israeli military has for years attempted to root out any form of armed resistance in the occupied West Bank, conducting raids that have escalated in severity since the beginning of Israel’s war on Gaza in October 2023. At least 1,000 Palestinians have been killed by Israeli forces or settlers in that period.
“Operation Iron Wall” – targeting Palestinian fighters in the northern West Bank – started in Jenin, but has since spread to Tulkarem, Nur Shams, and al-Fara refugee camps.
On March 22, just 60 days after the beginning of the offensive, the UN agency for Palestinian refugees (UNRWA) reported that 40,000 Palestinian refugees had been displaced from refugee camps in the northern West Bank.
In addition, earlier this year, Israeli authorities announced that they planned to wipe out the Jenin refugee camp completely.
Since then, Israeli bulldozers have been tearing down commercial buildings and homes at an alarming rate.
Wafa, the Palestinian news agency, reported on June 30 that more than 600 homes and 15 roads in Jenin camp had been demolished.
On June 17, the Israeli Supreme Court rejected a petition filed by Adalah, a legal centre for Palestinian minority rights in Israel, on June 12 to halt the demolition of Jenin refugee camp.
The Supreme Court authorised the Israeli military to proceed with the destruction of nearly 90 civilian buildings that housed hundreds of Palestinian families.
“The Israeli Supreme Court’s decision to uphold these operations, including its 7 May 2025 rejection of Adalah’s petition against the mass demolitions in Nur Shams and Tulkarem refugee camps, provides a false legal cover for policies of forced displacement and entrenched impunity,” said Adalah.
Bigger picture
The potential demolition of Al-Jaleel fits into a wider pattern of Israeli attacks on Palestinian healthcare institutions.
The targeting of health facilities, medical personnel and patients has been widespread during Israel’s war on Gaza. These actions are considered war crimes under the 1949 Geneva Convention. Israel has justified the attacks as being part of its fight against Hamas and other armed groups, accusing them, without any overwhelming evidence, of using health facilities as cover for their bases and operations.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), at least 94 percent of all hospitals in Gaza are damaged or destroyed.
Between October 7, 2023, and July 2, 2025, WHO recorded 863 attacks on healthcare in the West Bank. These attacks affected 203 institutions and 589 health transports
In a statement to Al Jazeera, WHO reported that, of the 476 government health service delivery units assessed by WHO and partners in the West Bank in June 2025, only 345 are fully functional, 112 are partially functional, nine are non-functional, and 1 has been destroyed.
That, Am-Ali believes, is being overlooked amid the understandable focus on Gaza, where Israel has killed more than 58,000 Palestinians. And it is allowing Israel to get away with its devastation of Palestinian life in the West Bank, and its destruction of vital centres like Al-Jaleel.
“These developments are not isolated incidents and are in clear violation of international law, including the prohibition on the acquisition of territory by force under the UN Charter and the Fourth Geneva Convention,” he said.