Could Biden undo Trump’s actions in Israel, West Bank?
WASHINGTON — If he wins the presidential election, Joe Biden will find a Middle East quite different from the one at the end of the Obama administration.
Nuclear threats may once again be on the horizon in Iran. Militant groups are on the ascendance in Lebanon and Yemen. And Israelis and Palestinians stand further away from settling their conflict than they have in a long time.
Biden says his first task will be repairing much of what he and his supporters consider to be the damage done by President Trump, who demolished long-standing norms and decades of U.S. policy regarding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
“Joe Biden will benefit just by not being President Trump,” Biden’s top foreign policy advisor Tony Blinken said in a recent interview. “That is the opening opportunity.”
More difficult will be deciding whether to reverse some of Trump’s controversial actions and, if so, which ones.
The Palestinian Authority leadership boycotted administration-led peace talks after Trump recognized Jerusalem as the capital of Israel and moved the U.S. Embassy from Tel Aviv to the disputed holy city.
Palestinians claim the eastern part of the city — which Israel seized during the 1967 Middle East War — as their capital. For decades the U.S. avoided recognizing either side’s claim in Jerusalem pending a final peace agreement.
Biden’s advisors say he will not return the U.S. Embassy to Tel Aviv, but it is likely he would reopen a U.S. Consulate in East Jerusalem that would cater to Palestinians and allow a Palestinian de facto embassy in Washington.
Regaining Palestinian trust will be a major challenge. The Biden team has released careful, measured policies for the decades-old conflict, a clear rebuke to Trump, but disappointing to many progressives.
Unlike Trump, Biden supports the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel.
“There will be a very important statement about the intention to pursue a two-state solution,” said Jeremy Ben-Ami, president of J Street, a pro-Israel advocacy organization in Washington and informal advisor to the campaign. “Those signals will be sent early.”
And Biden said he plans to revive U.S. financial aid to support Palestinians that was cut off by Trump as punishment for what he termed their lack of cooperation.
His hands will be partly tied by Congress. The 2018 Taylor Force Act prohibits U.S. aid from going to some Palestinian entities as long as the Palestinian Authority gives stipends to families of Palestinians killed in attacks on Israelis. It will be easier to resume funding to the United Nations Relief and Works Agency, which supports hundreds of thousands of Palestinian refugees, and to hospitals in Palestinian-dominated parts of East Jerusalem, all cut off by Trump.
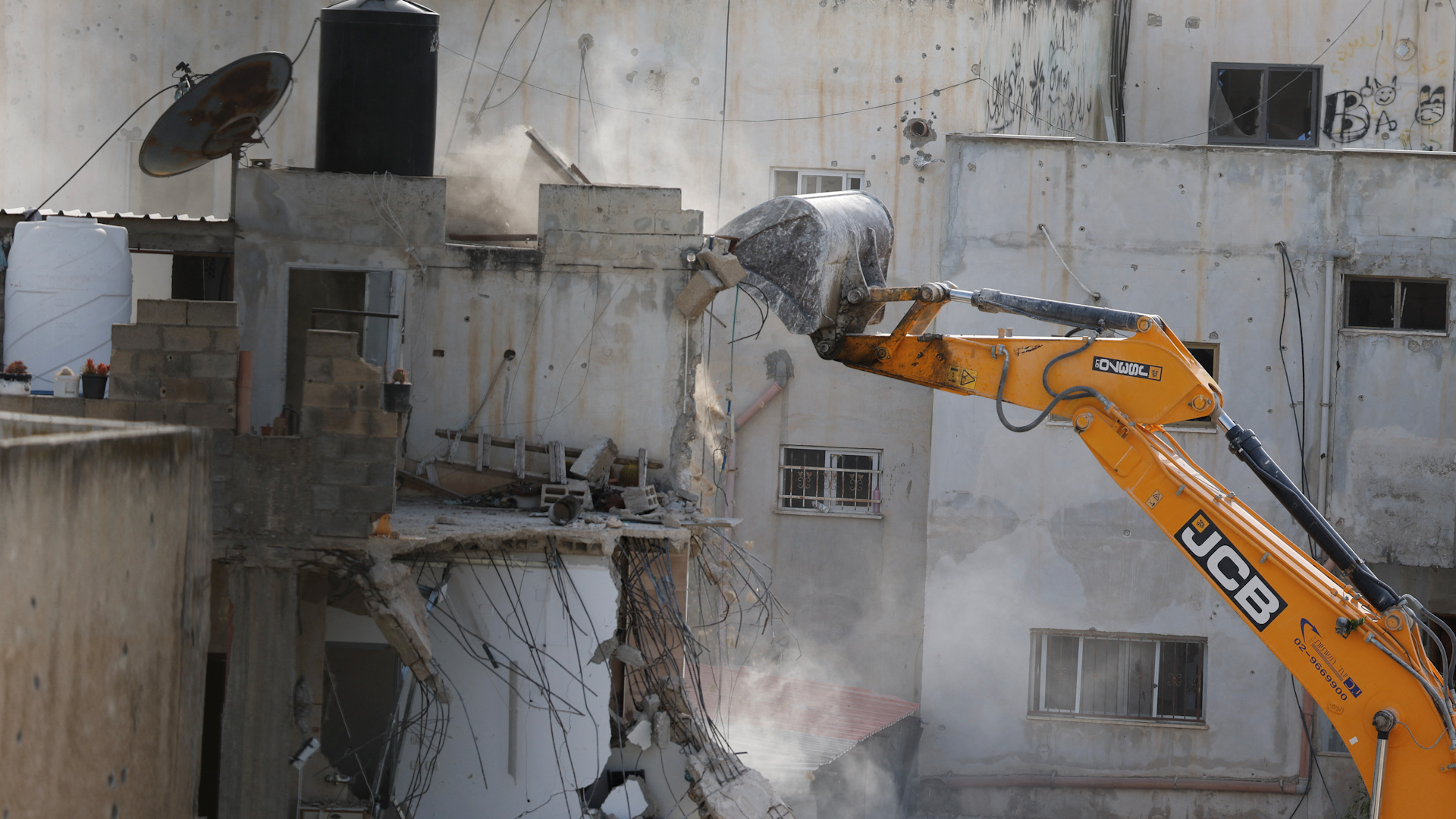
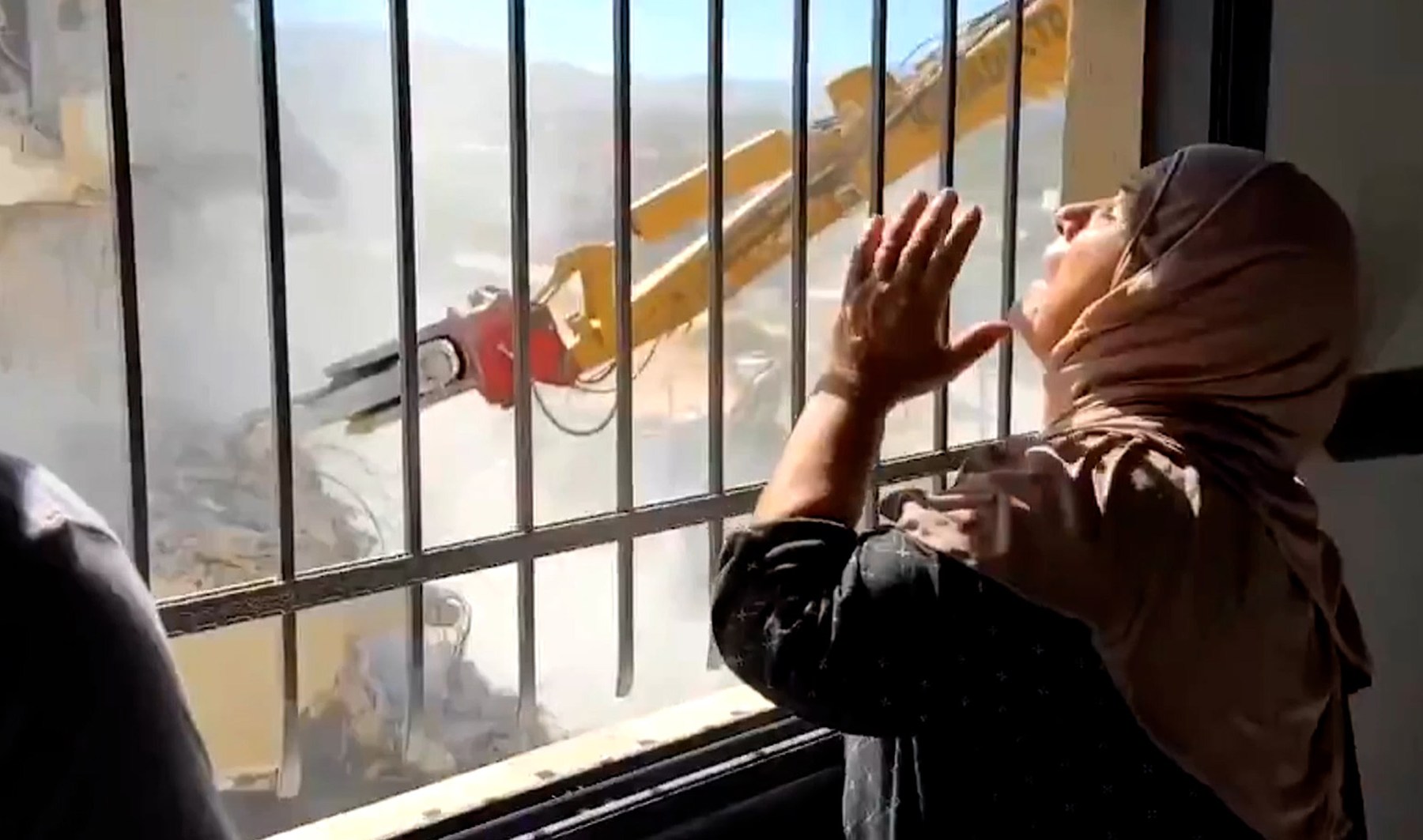
Biden is likely to frown on any Israeli annexation of West Bank land it seized during the 1967 war and that Palestinians have claimed for their state. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s annexation plan was tacitly approved by Trump, but has since been put on hold, partly out of concern about hurting Trump in November and partly because of a pending agreement to normalize diplomatic relations with United Arab Emirates.
How strongly Biden might act to block annexation remains to be seen. He has been careful not to say that U.S. aid to Israel would be conditioned on Israeli behavior.
Much of what Biden could do might be mired in U.S. domestic politics. Any action risks antagonizing either the pro-Israel lobby or the progressive wing of his party.
“I think the best we can hope for from a Biden government is undoing a lot of the damage and doing no more harm, while giving the Palestinians space to get their own house in order,” said Khaled Elgindy, a senior fellow at the Middle East Institute, a Washington think tank, and director of the Palestine and Israeli-Palestinian affairs program.
Elgindy and others predicted there would be no bold initiatives on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict at the beginning of a Biden administration. There will be more-pressing crises, his advisors say, and the environment is not ripe for new negotiations.
Netanyahu got nearly everything he wanted with no concessions from Trump, so he has little incentive now to negotiate.
Palestinians, long skeptical about whether the U.S. could be a neutral broker in peace talks, gave up any hope of that after Trump. Members of the governing Palestinian Authority are biding their time, Elgindy and others said, hoping that a Biden victory at least returns the troubled U.S-Palestinian relationship back to a better footing.
“Have we given up on the U.S.? Yes,” said Diana Buttu, a Palestinian attorney and former legal advisor to the Palestinian Authority headed by President Mahmoud Abbas. At most, she predicted, “we will see that Biden will reach out to Abbas, but won’t do much other than that.”
She said that in addition to failing to condemn the U.S. Embassy relocation, Democratic Party leadership declined to include a reference in its platform to the “ongoing occupation” of Palestinian territories by Israel.
Another of Trump’s surprising breaks from years of U.S. policy came when he recognized Israeli sovereignty over the Golan Heights, a large, fertile plateau that Israel seized from Syria in the 1967 war. It is unclear whether such a move can be easily reversed, and there appears to be little precedent for it. On the other hand, recognition did not lead to any concrete U.S. action and put the United States in conflict with the rest of the international community, which views Israel’s control over Golan as a violation of international law.
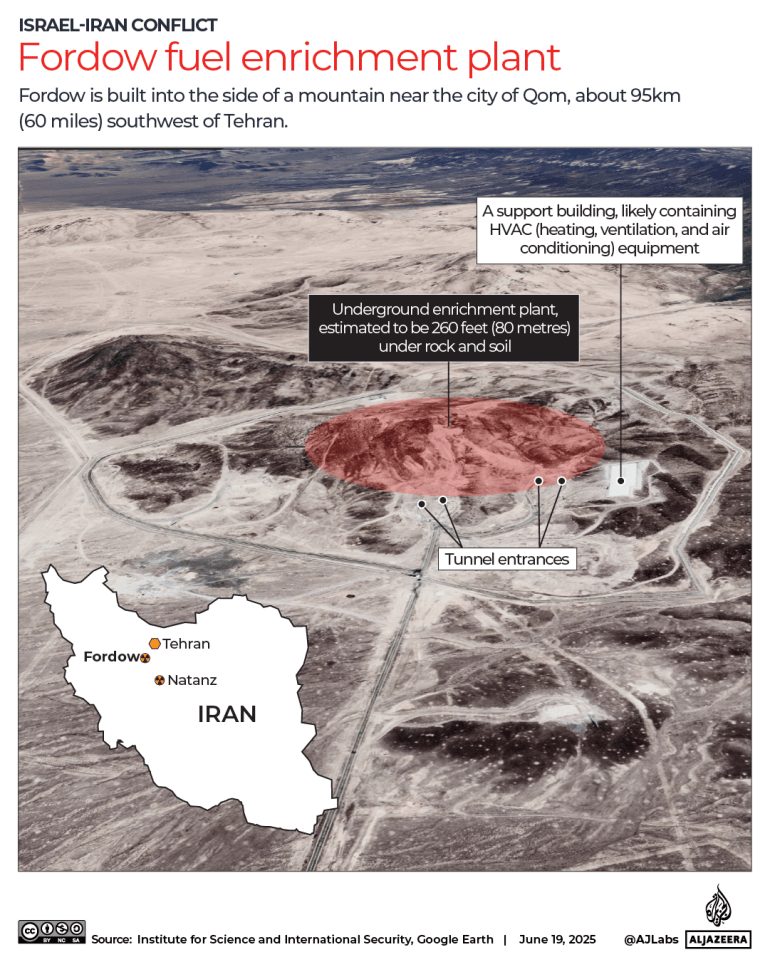
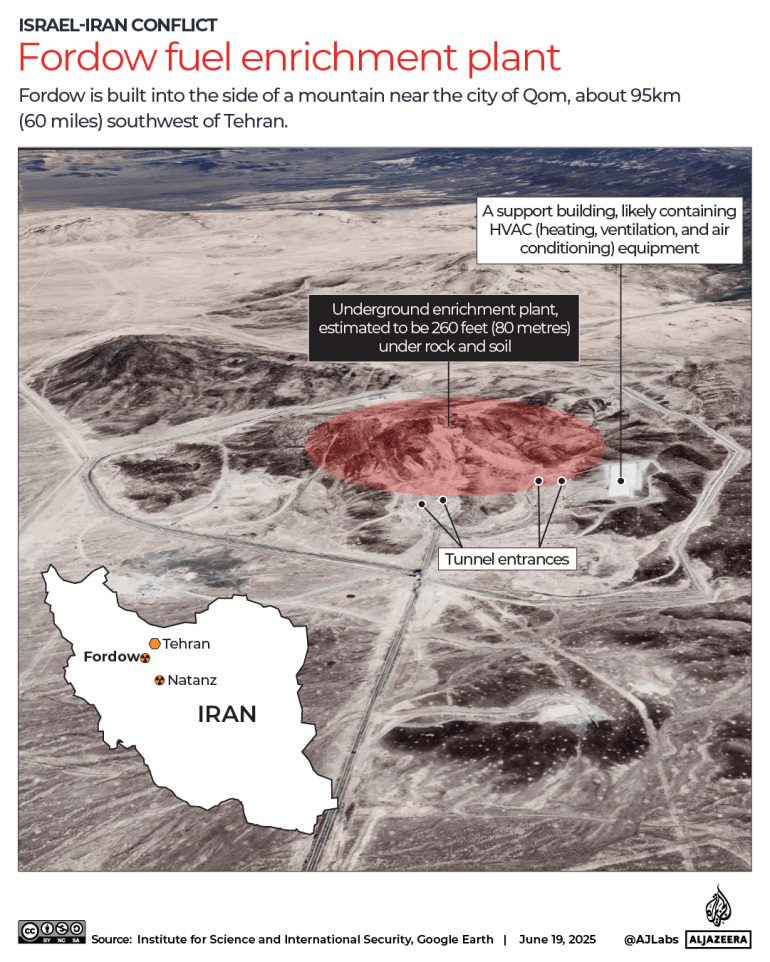
On Iran, Biden is expected to chart a dramatically different course, and one that Netanyahu won’t like.
Trump unilaterally withdrew the U.S. from the landmark 2015 Iran nuclear deal, which forced the Islamic Republic to dismantle most of its infrastructure that could be used to produce nuclear weapons, in exchange for the lifting of economic sanctions on Tehran and release of its assets frozen in banks all over the world.
Trump — prodded by Netanyahu — contended the deal was flawed because it failed to limit other Iranian activities such as its support for the region’s militant groups, including Hezbollah in Lebanon and Houthi rebels in Yemen. In recent months, the Trump administration has piled on new sanctions and other punishment to increase pressure on Iran in hopes of destroying the deal once and for all.
Biden wants to revive it by first bringing Iran back into compliance, and then reenlisting the United States.
“Assuming the deal is still on life support when he takes office, [Biden] would move toward mutual reentry,” said Colin Kahl, who served as national security advisor to the then-vice president and now consults with the campaign.
Biden said this year that once the deal is revived, he would work with European allies to “strengthen and extend it, while more effectively pushing back against Iran’s other destabilizing activities.”
Israel’s government, which views Iran as an existential threat, has been working to undermine the nuclear agreement since before it was signed.
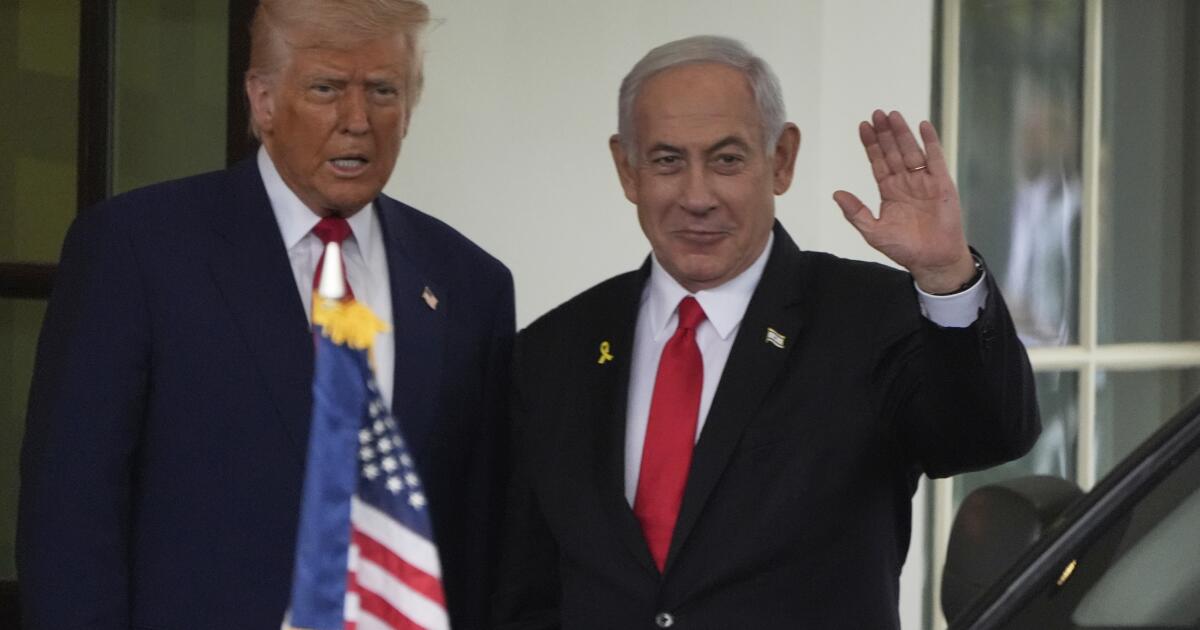
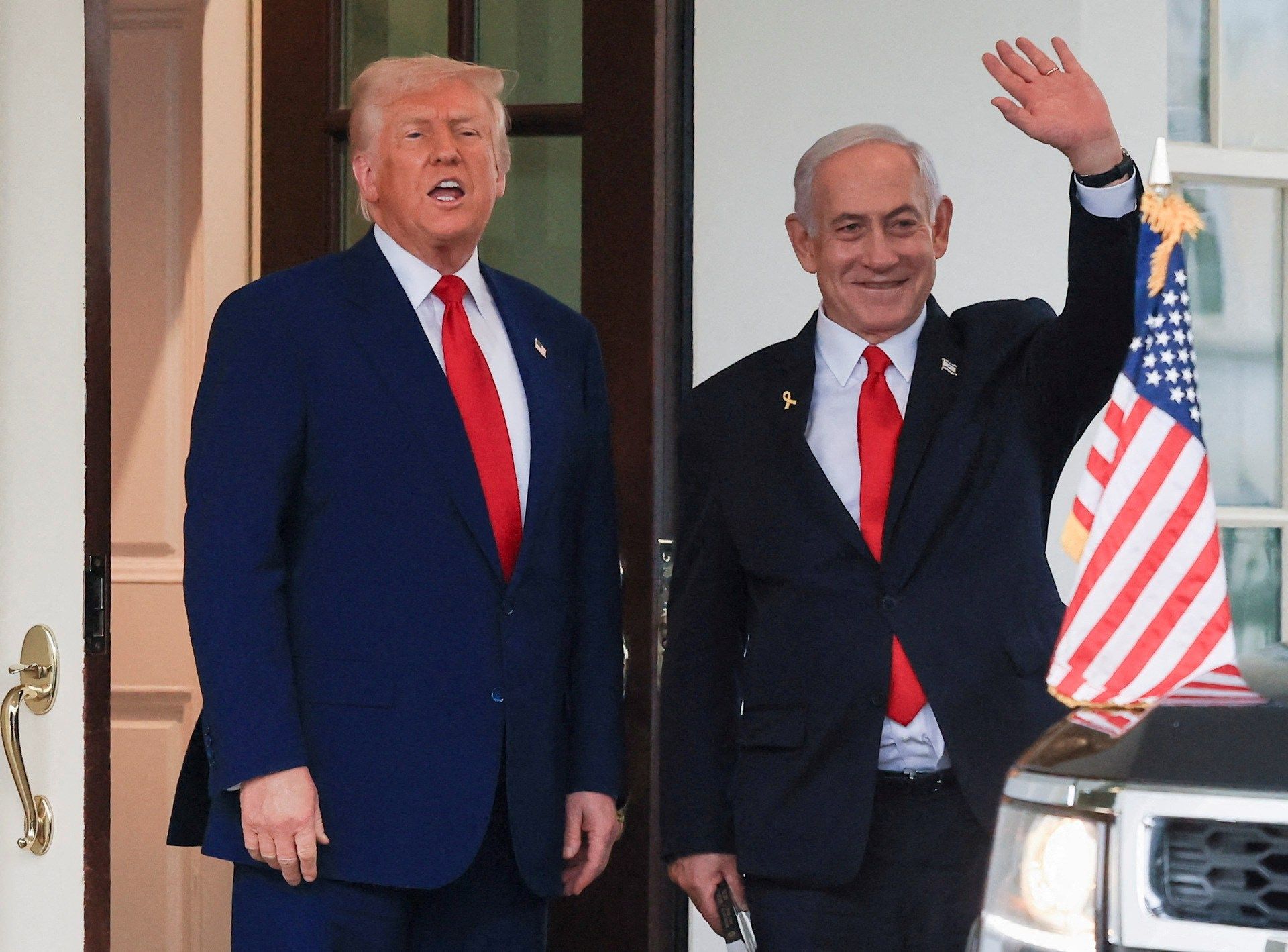
Another unknown will be the relationship between Biden and Netanyahu.
Trump and Netanyahu had one of the warmest relationships between any U.S. and Israeli leaders. That’s a hard act for Biden to follow, particularly since he’s associated with the Obama administration, which repeatedly and bitterly clashed with Netanyahu.
But Biden has known Netanyahu for decades, including during the years the Israeli leader spent in the United States. According to aides, the pair enjoy an amiable if sometimes prickly friendship.