‘Avignon warmed our bones and fed our souls’: readers’ favourite early spring trips to southern Europe | Europe holidays
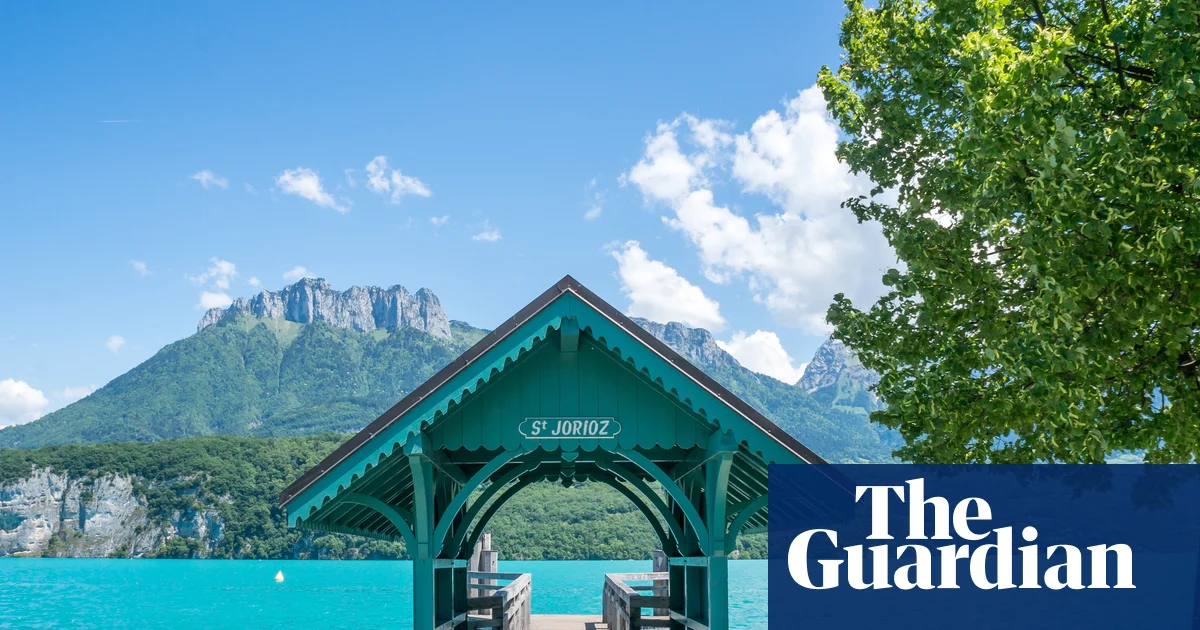
Winning tip: cycle the greenways of Annecy
Saint-Jorioz in Haute-Savoie will provide a springtime lift for your spirits. On the shore of Lake Annecy, it’s a short bus ride from the city of Annecy, but less busy and with superior lake and mountain views. Hike to the surrounding peaks, towards the lesser-known Col de l’Arpettaz, or cycle on the excellent greenways. Relax by the cool blue alpine water. Behind you lies the underrated Les Bauges Unesco Geopark. The department only joined France in 1860, and has its own Italian-influenced regional cuisine.
Brian Lowry
Naples is best in early spring
Although not the most traditionally beautiful city in Italy, Naples offers a glimpse of warmth in early spring. A world apart from Florence or Turin, Naples is a fascinating, lived-in city with a long history and a rich culinary tradition. The Spaccanapoli, which runs right through the core of the city, is a bustling place to walk along and experience Neapolitan life. The world-class sites of Pompeii and Herculaneum are nearby, as are Mount Vesuvius, Sorrento and the wonderful islands of Capri, Ischia and Procida. You can get to Naples by train from London via Paris and Turin or Milan in about 15 hours.
Michael Kuipers
Take the ferry to Corsica
Eurostar from London via an easy connection at Lille or a change in Paris takes between six and eight hours to arrive in Marseille. After a shower at the station, refresh in Vieux Port before arriving for breakfast in Bastia, Corsica, via a comfortable night-ferry. From Bastia, catch the scenic mountain railway into this remarkably unspoiled island to explore its wild interior and coastal regions. Mid to late spring is best for southern Europe, when snow-melt replenishes streams and waterfalls that dry up in summer. The weather is sunny yet exceedingly pleasant, hillsides blanketed with wildflowers, wild animals nurturing their young and locals refreshed in mood.
Jake
Profile
Readers’ tips: send a tip for a chance to win a £200 voucher for a Coolstays break
Show
Guardian Travel readers’ tips
Every week we ask our readers for recommendations from their travels. A selection of tips will be featured online and may appear in print. To enter the latest competition visit the readers’ tips homepage
–
Germany’s greenest, sunniest city
Take the Eurostar to Paris and continue east via Strasbourg by high-speed train through the rolling hills and vineyards of Alsace to Freiburg – Germany’s warmest, sunniest and greenest city. (Some routes go via Brussels and Cologne.) Feast on Swabian classics such as käsespätzle (cheesy egg noodles with caramelised onion), enjoy tacos at YepaYepa or drop into Hausbrauerei Feierling’s lively beer garden for a drink. From Freiburg, explore the Black Forest’s highlights, from Triberg’s cuckoo clocks and waterfalls to the treetop walk in Bad Wildbad. Opt to stay at a participating town and you’ll receive a Konus guest card, giving you free transport around the region for your entire stay.
George
Tiny beaches near Nice
I’ve spent many happy spring breaks in Villefranche-sur-Mer, just a few miles east of Nice. The charm of its historic heart, the beauty of its deepwater bay, the proximity to spectacular coast and mountains, plus excellent cafes and restaurants make it hard to beat. Take the TGV to Nice, then it’s just a few minutes on the local train (easy for day trips to Cannes and Menton, too). It should be warm enough for a dip at the tiny, secluded Plage de la Darse, or Plage de la Fosse on swanky Cap Ferrat …
Gill R
Lemons and light on the Côte d’Azur
My sister and I spent a beautiful sunny few days in Menton on the Côte d’Azur in early April. We spent our time meandering the cobbled streets with their pastel-coloured buildings, eating a mix of French and Italian meals (it’s the last French town before the Italian border) and paddling in the calm blue bay. We trekked in the hills north of the town, past stunning houses, pine trees and spring flowers to explore Maison Gannac, a citrus farm that grows the Menton lemon, which is renowned for its flavour and aroma.
Katie
A boat trip along the Moselle in Germany
The Moselle valley in April was stunning. Starting in the old Roman city of Trier, with its amazing Porta Nigra gate, we followed the river 30 miles north-west to enjoy the panoramic views from Burg Landshut. We took boat trips, including to Cochem, to take the chairlift opposite the castle up to the Pinnerkreuz viewpoint. Early April means wildflower-strewn meadows and fewer visitors. Castles, boats and cable cars kept the children entertained; the fresh Moselle valley rieslings kept the adults happy. We finished our trip in Koblenz, with its selection of traditional breweries where späzle and schnitzel pair well with any beer.
Kirsten Lowery
Coastal paths near Perpignan
Go south by train and resist the rush. Take the Eurostar to Paris, then a fast TGV to Perpignan in six hours, before a final 25-minute local train to Port-Vendres – about nine hours from London, end to end. Early spring suits this working harbour: many places are shut, the fish market is not. Lunch at its no-nonsense restaurant, then walk the coastal paths to Collioure, brighter and busier by comparison. The Pyréneés-Orientales coast is one of France’s sunniest areas, and even out of season the light does much of the work.
Becky
The hazily golden city of Avignon
En route to Sicily via ferry from Genoa, we stopped in Avignon. We got off the train in the early evening to find a hazily golden city with winding medieval streets full of small independent shops, the amazing Palais des Papes (Popes’ Palace), a beautiful shining Rhône river – and we explored the remaining four arches and gatehouse of the 12th-century Pont Saint-Bénézet. Everywhere was walkable, from the very comfortable and reasonably- priced Bristol Hotel. Warm in the evening, plenty of traditional restaurants, no crowds. In the off-season, Avignon relaxed us, warmed our bones and fed our souls.
Hilary