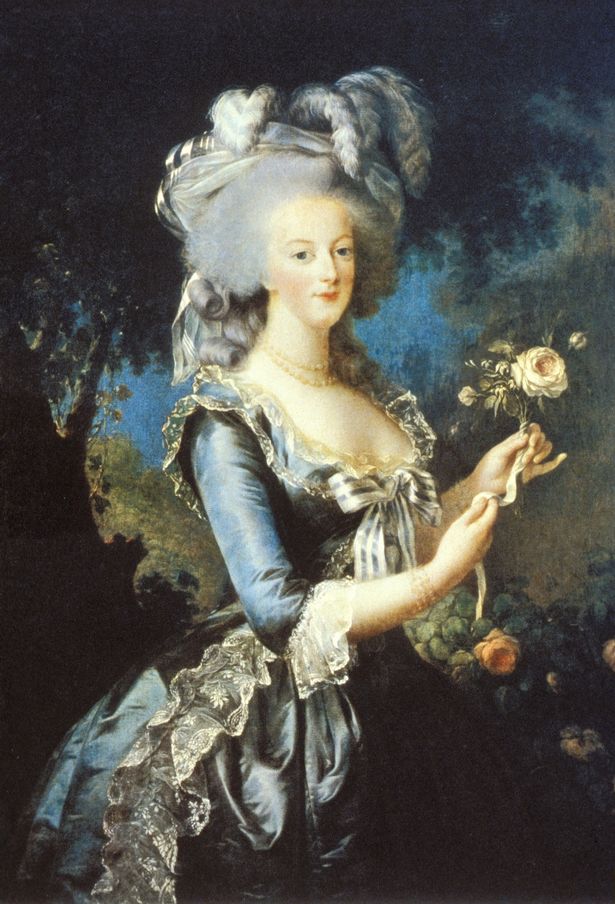TikTok sensation Katie Kennedy – aka The History Gossip – is bringing history to life in her new Sky TV show History Crush after going viral with her bawdy social media videos
Queen Elizabeth I was “fuggers”, Henry VIII “clapped” and it’s debatable whether Anne Of Cleeves was a “minger”.
Katie Kennedy, better known as The History Gossip, uses this colourful language to bring alive famous historical characters in her bawdy social media posts, which have earned millions of likes on TikTok. Most people take years to get noticed, but Katie became famous practically overnight.
One minute she was writing her 12,000-word dissertation on Women in Pompeii in her final year at Durham University, the next she’d posted a few quirky history videos on TikTok and gone viral.
Like most students, she’d happily wile away hours of study time on social media, but for Katie, it led to greater things. “I was on TikTok all the time anyway, so I posted some stuff about the Tudors and I got a couple of thousand followers Then I did a video with the caption – why were the Tudes clapped?” she says.
READ MORE: ‘I visited the pitiful never-before-seen room where Jane Austen took her last breath’
Seeing my blank expression, she translates: “Why were they really ugly? That did really well. It got onto this really big meme page called Great British Memes and they’ve got loads of followers. People were screenshotting it and asking, ‘Is that you?”
Earthy and funny, Katie’s history videos are the right side of sweary, with a sprinkling of Gen Z language. “Some of the slang that I’ve picked up through the years was originally just to get around TikTok guidelines,” she explains.
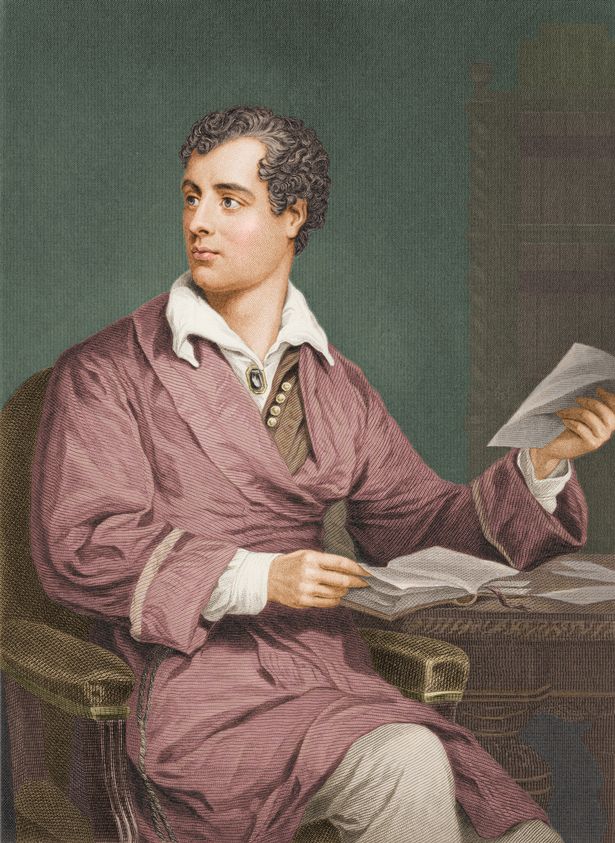
Half a million followers later, Katie got a book deal and published The History Gossip – Was Anne Of Cleeves A Minger? And she will now be appearing on our screens on Sky TV’s History Crush, where she’ll be rummaging through the underwear drawers of historical figures like Lord Byron, Charles Dickens or Marie-Antoinette – and asking the big questions like was Henry VIII clapped? “Yes he was,” she giggles. And was Lord Byron a crush or a burn? “Definitely a crush.”
The speed at which Katie got a book deal will have many seasoned writers gnashing at the bit. “I had a message from my now agent in February last year when things were going off,” she says. “And she was like, ‘Have you ever thought about writing a book?’ And I thought, ‘Yeah maybe in the future.’ But as soon as I handed in my dissertation, I started writing it and finished it during Freshers Week at Oxford – when I was hungover!
“We got it out for November for Christmas, because it was more of a gifty book. It’s still really weird seeing it in the book shops.”
When we meet outside on a sunny afternoon in pretty Vaults and Gardens Cafe by Radcliffe Camera in Oxford, where 25-year-old Katie’s now studying for her masters, I have to ask, “Was Anne of Cleeves a minger?”
“Well I don’t think so,” she replies. “Henry VIII gave her a castle and they had a brother and sister type of relationship. Of all his wives, she came out of it quite well. She wasn’t really minging, like her portraits said, but she was ‘mid’.”
What about Elizabeth 1? “Her teeth were fuggers because she ate so much sugar,” says Katie. “And it’s so funny that even when she looks a bit minging in her portrait, that’s probably her best photoshopped version.”
READ MORE: Luxury Brit cruise liner sent to brutal war – with astonishing comparison to Titanic
Katie has just returned from a holiday abroad, but her skin remains the colour of porcelain. “I don’t like to sit in the sun because I get scared of getting sunburned,” she says in her sing-song Geordie accent.
“I’ve lived in Durham my whole life. I grew up there, went to a local comprehensive school, did sixth form. And then a journalism apprenticeship with BBC,” she says.
This explains why Katie’s so good at finding a hook in a story – and she has a journalism certificate to prove it. “In my posts, I have to get a three second intro to get people interested – that takes a lot of research,” she explains. “I don’t really script them though, I just press record!”
The secret of Katie’s success is clearly an authentic voice on the platform, which is backed up by years of hard academic study.
“I did journalism for two years, but I felt like I’d missed out on university, so I applied to Durham to do Ancient History and Archeology – and got in!” she says.
While she seems surprised by her ‘luck,’ it strikes me that both Durham and Oxford are lucky to have someone with such a knack for bringing history to life.
Although she has a bit of imposter syndrome, the university social life has made up for it. “I loved being at Durham – all the traditions and stuff and that’s partly why I wanted to come to Oxford,” she admits. “It’s fun and you don’t get that in every university.”
A quick peek at her socials and you can see Katie has settled in well since arriving last September. She laughs: “Yeah the balls are so nice. I love wearing the gowns. I went to a Balioll College ball last week. I can’t lie – the balls here are better than Durham!”
Katie’s first taste of history came when her parents dragged her around National Trust properties every Sunday. “I remember when I was seven being like, I don’t want to go to Wellington and Cragside, I just want to sit on my little Nintendo,’” she admits.
But the experience left an impression, because she fell in love with immersive history – even becoming part of a Beamish Living Museum of the North exhibit.
“It’s just down the road from where I liv,e so I did work experience there twice,” she recalls. “Once dressed up as a Victorian school child and then as a Second World War evacuée and I had my little cardboard gas mask box.
“Did you know during rationing, instead of ice lollies little kids would have frozen carrots?”
Inspired by TV historians such as Lucy Worsley and Ruth Goodman, Katie admits that Horrible Histories – which has probably done more to make history popular than all the dusty old academic institutions put together – inspired her.
“Horrible Histories doesn’t make you feel like you’re learning. The author of the books, Terry Deary, is from Sunderland, which is not far from where I’m from,” she adds proudly.
“I used to love Ruth when she would do Victorian Farm on TV and she would be like, ‘I’m going to make bread from scratch.’ She doesn’t make you feel you’re being lectured to – she’s living history and talking about normal people, who I think get overlooked sometimes.
“It definitely sparked the way I like to present history in a fun, doesn’t-feel-like-you’re-learning type of way.”
I do wonder what Katie’s more traditional tutors think of her style of bringing history to the masses. “When I first started on TikTok, I blocked everyone at Durham and friends and family, because I was embarrassed about posting a video that might get three views,” she reveals. “It was only later when I did a series on the Victorians, that I stopped caring what people thought.
“My supervisor at Oxford’s really supportive. I told him it’s like Horrible History but for adults, and he thinks it’s great that I’m making history more accessible.”
Social media burn out is real for influencers. I ask how she’s managing her time with so much on her plate. “My masters is on British and European 18th-century history, and I’m doing my dissertation on the fan-making industry and how women used fans. But I’ve gone part-time now, so I’ve got another year to get my arse in gear and sort it”: she says.
READ MORE: Brits urged to ditch cheese and onion for insect crisps as health benefits are amazing
“I used to post every single day on TikTok, but I’ve learned to take a step back from it and know that if I don’t post today, it’s not like the end of everything.”
And history clearly attracts a decent social media crowd. “I just get Americans not being able to understand my accent, or they’re like ‘what’s a minger?’” she laughs.
In Durham she lives with her mum, dad and brother, who’s just started studying politics at university. “He was debating history or politics, but he likes arguments, so it’s politics,” she says.
While she’s keen to ask if historical figures are worth dating, she sidesteps when asked if she’s single. “Depends on who’s asking?” she smiles.
But she gushes when talking about one of her great loves back in Durham. “We’ve just got a King Charles Spaniel puppy called Millie – I love to sit and cuddle her in the garden,” she says. “I miss her so much when I’m not there.”
Devoting a lot of time to studying women in history Katie continues: “I especially like the Brontes and also Mary Antoinette, because I feel like she was very misunderstood.”
The arts have been losing out in the push for more maths and engineering, but Katie is making history cool again and reminds us the importance of knowing about our past.
“History keeps repeating itself,” she says. “People aren’t so different to us today. The Tudors put belladonna in their eyes to make them sparkle. Victorian women would eat arsenic wafers to give their skin a pale complexion and wore dresses dyed with a green pigment made from arsenic. Women died wearing them.”
So, forget Brazilian butt lifts, or excessive tanning – when it comes to dying for beauty, the Tudors and Victorians got there first.
• HISTORY CRUSH, presented by Katie Kennedy (aka History Gossip), will be available on Sky HISTORY on demand via Sky and Virgin Media from May 29. More at www.history.co.uk/shows/history-crush #HISTORYCRUSH @HISTORYUK
READ MORE: Claudia Winkleman-loved brand launches Bank holiday sale including ‘holy grail’ spray