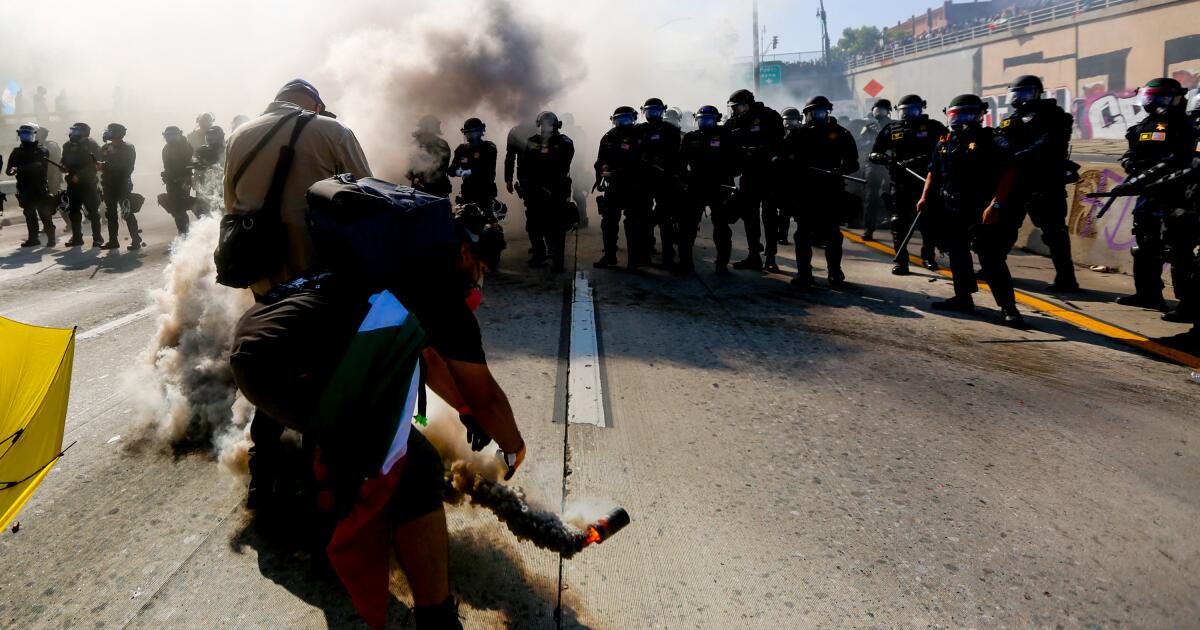
Contributor: California’s long history of National Guard overreaction to peaceful protesters
American history has the receipts. As we approach the 250th anniversary of this nation’s birth, it ought to be common knowledge that putting the National Guard into the center of turmoil is not to be taken at all lightly. Federalizing the California Guard to quell a supposed insurrection on the streets of greater Los Angeles is a bold move of presidential showmanship and look-tough opportunism. It is also risky on many fronts.
We have been here before, and we would be wise to heed history’s caution. In the spring of 1894, a nationwide railroad strike, spreading out from the outskirts of Chicago, paralyzed freight and passenger rail traffic up and down California. Strikers took to the streets, occupied railroad depots, often with their families, waved signs, and erected tents and hastily constructed shanties. In Oakland, strikers who had “killed” a locomotive covered it in black crepe.
Political leaders and railroad officials insisted that the strikers were insurrectionists ripping at the fabric of the republic. But the public did not necessarily see things the same way. Strikers who were hunkered down in Northern California depots took in provisions from farmers loyal to their cause. A U.S. marshal sent to Sacramento to clear them out and get the trains moving was beaten up and insisted later that the local police force was sympathetic to the strikers.
Judging the Sacramento situation as an insurrection, Gov. H.H. Markham of Pasadena called up the National Guard, which mustered first in San Francisco on July 3. Some elderly Civil War veterans volunteered for duty but were politely turned away. Instead, young California guardsmen, each given 20 rounds of ammunition, marched to the Bay amid a jeering crowd, took a ferry to Oakland and tried to get to Sacramento by train.
But all train service had been interrupted by the strike, and skilled rail operators did not want to cross the picket lines. After nine hours, the exhausted guardsmen arrived in Sacramento early on the morning of July 4 — having taken a train through a circuitous route to avoid trouble. They marched to the city armory, then on to the occupied depot, where they were met by Sacramento members of the National Guard who were already deployed. Guardsmen — about 1,000 weekend warriors — stood in the hot sun, rifles at the ready alongside the Gatling gun they brought, facing the railroad strikers camped out in the depot with their wives and children. One Guardsman’s gun went off accidentally, killing a bystander. Officers ordered their men to fix their bayonets and, if ordered to shoot, to “aim to kill.”
One Sacramento unit reported that its men would not fire on their friends and relatives. Other Guardsmen wore their sympathies on their sleeves and lapels: pro-striker buttons. The strikers and their families began to mingle with the phalanx of guardsmen. “Frank, if you kill me you make your sister a widow,” one striker informed her brother-in-law in the Guard. Some guardsmen removed the ammunition from their weapons; others lowered them and just wandered away — toward the lemonade and ice that the protesters themselves provided. The strikers stayed in the depot for weeks. The whole thing was a chaotic farce.
Matters were hardly any less tense in Southern California. People lined the streets of downtown Los Angeles, chanting and cheering for the strikers, many of whom wore American flag lapels. Photographs of goings on in Sacramento and the Bay Area got passed from one Angeleno to another in the crowd. Guardsmen in L.A. expressed the same kind of trepidation about bringing militarized force to bear on the strikers. “If we had to fight Indians or some common enemy,” one guardsman offered in a revelatory admission, “we might have some fun and excitement. But this idea of shooting down American citizens simply because they are on strike for what they consider their rights is a horse of another color. All of the boys are against it from first to last, and many are in sympathy with the strikers.”
In hindsight, the federal and state response to the rail strike of 1894 appears to have lacked some consideration of unintended consequences. Calling in the Guard only created chaos, emboldened the strikers and, for a time at least, sustained much of the public’s support. The federal government, with some seeing 1894 as “the greatest crisis in our history,” allied with the rail corporations in a set of legal maneuverings that led to the deployment of federal troops across the country. As the strike dissipated, each side tried to take the high ground of intention and behavior: The crisis was lawlessness or it was unwarranted government overreach.
Though it is too soon to know how things will play out here in L.A. this time, nothing looks good from the rough scenes in downtown and the adjacent freeway exits and entrances.
Mark Twain said that “history never repeats itself, but it does often rhyme.” Here we have that rhyme written in the latest Los Angeles verse of our tense world. The administration’s move to federalize the Guard in the name of quelling a domestic insurrection has poured more gasoline onto the tinder of our times here in the Southland.
Deverell is a professor of history at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts & Sciences.
Insights
L.A. Times Insights delivers AI-generated analysis on Voices content to offer all points of view. Insights does not appear on any news articles.
Viewpoint
Perspectives
The following AI-generated content is powered by Perplexity. The Los Angeles Times editorial staff does not create or edit the content.
Ideas expressed in the piece
- The article argues that historical deployments of the National Guard during labor disputes, such as the 1894 railroad strike, often escalated tensions rather than resolving them. Governor Markham’s decision to mobilize the Guard in Sacramento led to accidental violence, internal dissent among troops, and public sympathy for strikers, undermining the state’s authority[1][3].
- It emphasizes the Guard’s reluctance to use force against civilians, citing instances where soldiers removed ammunition, mingled with protesters, or openly sympathized with strikers. One Guardsman expressed discomfort with targeting fellow citizens, framing the conflict as a moral dilemma rather than a law enforcement issue[3].
- The author draws parallels between 1894 and contemporary Los Angeles, warning that federalizing the Guard risks repeating past mistakes by inflaming protests and polarizing public opinion. He critiques the framing of labor actions as “insurrections,” arguing this justification enables disproportionate militarized responses[3].
Different views on the topic
- Contemporary government and railroad officials in 1894 viewed the strike as an existential threat to commerce and lawfulness. U.S. Marshals and military leaders prioritized restoring rail operations, with Colonel Shafter’s Regular Army troops swiftly securing railroad property in Los Angeles to ensure mail delivery and freight movement[1][3].
- Legal authorities insisted the strikers’ occupation of depots and disruption of rail services constituted unlawful obstruction. Marshal Baldwin’s failed attempt to clear Sacramento’s depot without military support was cited as evidence of the need for Guard intervention to enforce court orders[1][3].
- Proponents of military deployment argued that the strike’s nationwide scale—paralyzing over 20,000 miles of track—required decisive action to prevent economic collapse. The Pullman Strike’s disruption of interstate commerce was framed as a crisis justifying federal troop involvement under constitutional authority[2][4].