‘Hoppers’ review: A robotic beaver and a threatened glade in Pixar’s triumph
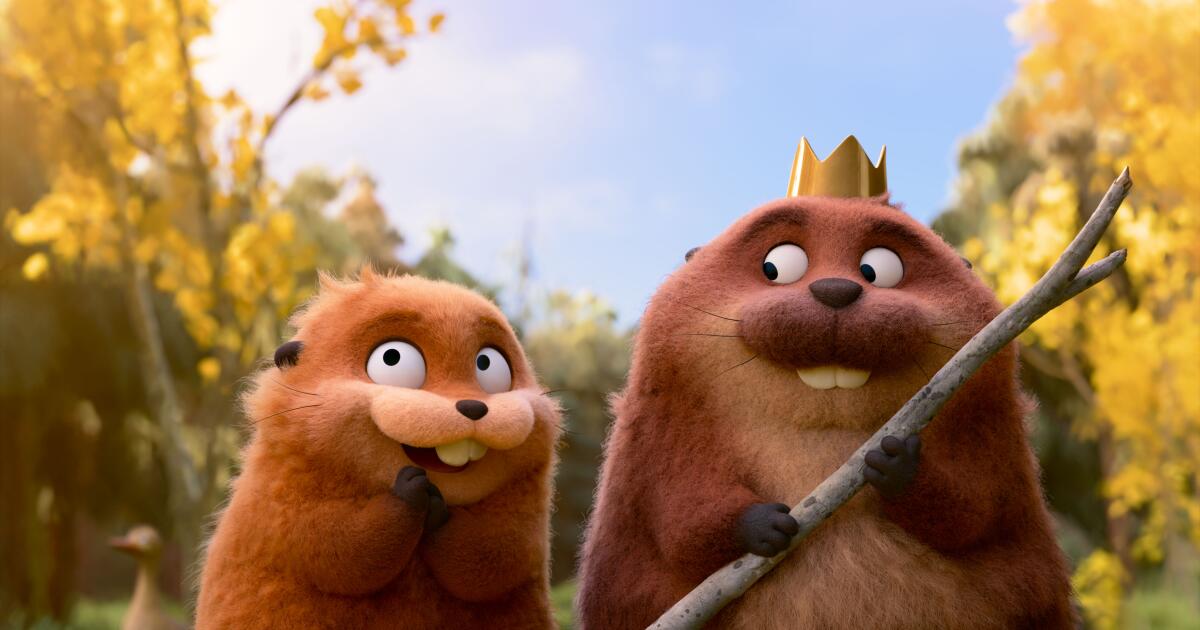
“Pond rules” dictate that if an animal is hungry, the creature that’s about to become a meal should accept its fate. That’s the first lesson that Mabel (voiced by Piper Curda), an idealistic university student whose mind is transferred into the body of a robotic beaver, learns while interacting with wildlife as one of their own in Pixar’s inventive “Hoppers.” In typical human fashion (we love to meddle with nature), Mabel ends up breaking that directive by saving a “fellow” beaver, the slumberous Loaf (Eduardo Franco), attracting unwanted attention that leads her to a wacky group of characters who will transform her rigid young worldview.
For his second feature, Daniel Chong, best known for creating the popular “We Bare Bears” series for Cartoon Network, has unleashed a hilariously unexpected and outrageous crowd-pleaser with “Hoppers.” Recently, I bemoaned that a movie like Sony’s “Goat” stood as further proof that talking-animal animated films had mostly run their course. Chong and screenwriter Jesse Andrews swiftly push back on that read with this environmentalist tale in defense of people who stand up for something, even when it seems no one is willing to stand beside them.
“Hoppers” is Pixar by way of a creator, Chong, whose career isn’t exclusively tied to the studio. That’s likely why his movie is more daring in its humor and tone, bringing a refreshing infusion of mischief to Pixar while maintaining the genuine emotional gravitas that has endeared the company to audiences for over 30 years.
Why is Mabel’s psyche roaming around inside a fake beaver à la “Avatar”? After discovering that this technology has been developed by one of her professors, Mabel thinks it could be the answer to saving the local forest glade where self-aggrandizing mayor Jerry (Jon Hamm) wants to build a highway. Mabel’s grandmother instilled in her an appreciation for nature as a reminder that she’s part of something greater than herself. Collecting signatures isn’t yielding results to stop construction, so, to the dismay of the scientists in charge, Mabel hops into the human-made mammal to learn from the creatures themselves why they’ve left the glade, giving Jerry carte blanche to destroy their home.
The poignancy-to-comedy ratio is precisely calibrated. Sharp gags, whether visual or in superbly timed lines of dialogue often laced with irony, work on multiple levels. A few moments like an accidental death or the wild introduction of an aquatic character are so wonderfully out of left field they make one’s head spin. That also goes for instances late in Mabel’s adventure in which “Hoppers” steps into amusingly creepy terrain, paying homage to the horror genre. These impish touches involve a wicked caterpillar (Dave Franco) whose mother, the Insect Queen, is voiced by acting royalty Meryl Streep. Each group of animals has its own ruler.
Since most scenes occur in the forest glade, the artists at Pixar have created strikingly rendered settings which, while aiming for photorealism, also have a fantastical glow to them, highlighting the inherent magic of nature. That such a seemingly commonplace location is elevated to feel mesmerizing speaks to how animation can make the mundane anew. That’s on top of how the rotund beavers in “Hoppers” have been conceived for maximum cuteness. One of them, Mabel’s guide through this ecosystem, is the disarmingly adorable King George (Bobby Moynihan), who wears a tiny crown (Where did he get it? No one knows) and rules over all mammals with a gentle hand.
Mabel’s friendship with King George, who doesn’t know she is human, becomes the movie’s heartstring-pulling core. The jovial royal believes he can persuade Jerry to change course. Mabel, conversely, doesn’t think Jerry will listen. Her cynicism and King George’s sincere faith in others clash. Among Mabel’s non-furry pals, Tom Lizard (Tom Law) becomes a scene-stealer. (The crazy-eyed, eloquent reptile first became an online sensation as part of a post-credits scene in “Elio.”)
Chong and his team include a minuscule but brilliant detail that illustrates how character design can have major narrative impact: When the animals are speaking among themselves, their eyes are large and expressive, full of life. But when the film takes the perspective of a human looking at the forest dwellers, their eyes appear small and dark, almost nondescript. It’s a subtly visual symbol for how we often fail to gaze at others with understanding.
There are many heavy hitters still to come, but “Hoppers” feels like the first great animated movie of the year. At a time when our right to protest is under siege, this sci-fi yarn exalts the way an individual’s conviction can plant seeds of change, leading to a stronger sense of community. Neither simplistically optimistic nor preachy, “Hoppers” smuggles timely ideas inside a rodent body. Pond rules would probably call that a beaver victory.
‘Hoppers’
Rated: PG, for action/peril, some scary images and mild language
Running time: 1 hour, 45 minutes
Playing: Opens Friday, March 6 in wide release