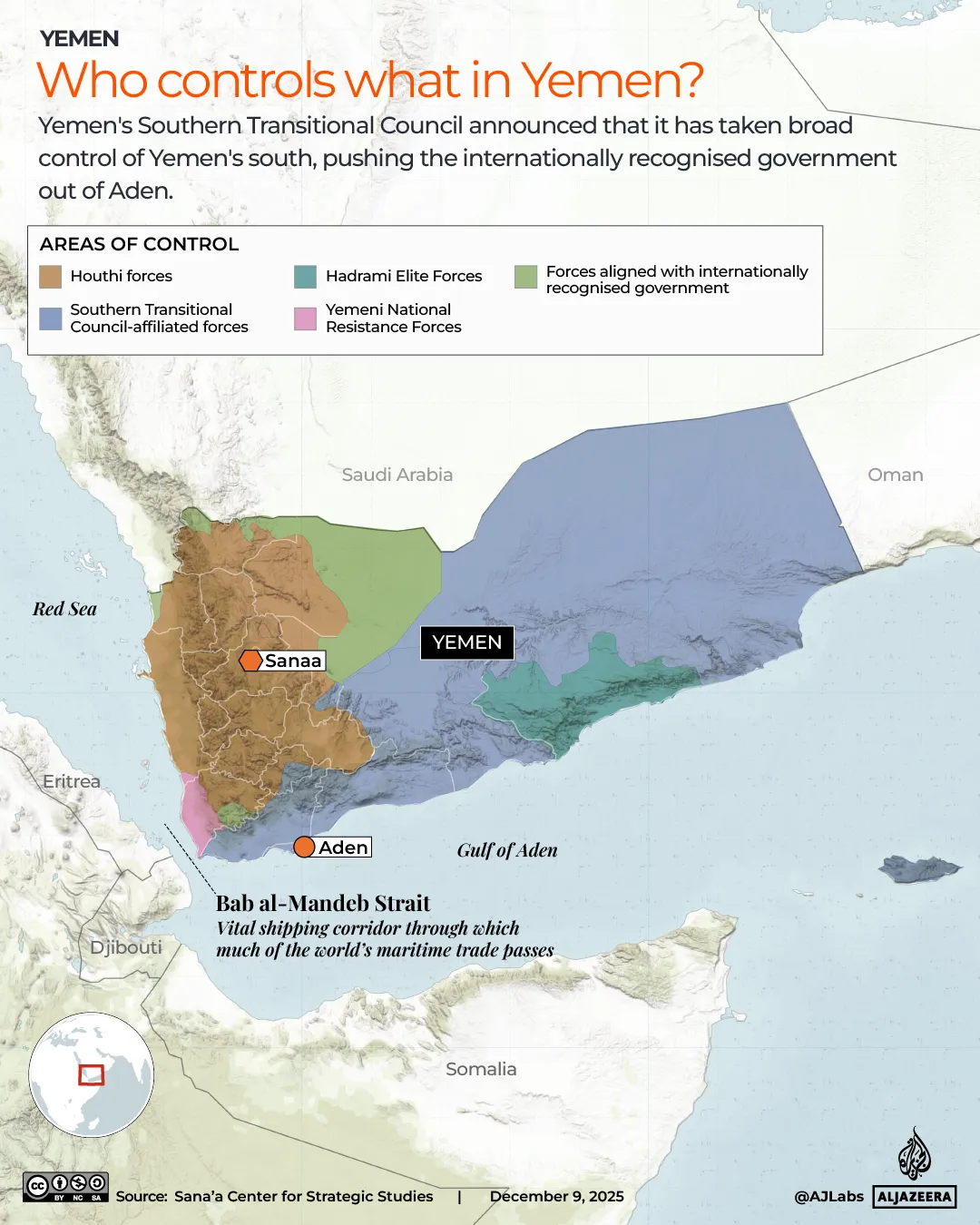
Trump says he wants to free up Venezuelan oil flow. What was blocking it? | US-Venezuela Tensions News
United States President Donald Trump and Secretary of State Marco Rubio say they want to free up the flow of Venezuelan oil to benefit Venezuelans after US forces abducted President Nicolas Maduro from Caracas.
“We’re going to rebuild the oil infrastructure, which requires billions of dollars that will be paid for by the oil companies directly,” Trump said at a media briefing at his Mar-a-Lago estate in Florida hours after Maduro was seized on Saturday. “They will be reimbursed for what they’re doing, but it’s going to be paid, and we’re going to get the oil flowing.”
Then, on Tuesday, the US president said he wanted to use proceeds from the sale of Venezuelan oil “to benefit the people of Venezuela and the United States”. Rubio has echoed Trump in his comments in recent days.
But what has been holding back the flow of Venezuelan oil, preventing the country from attracting investments and driving the country into poverty?
A key reason is one that Trump and Rubio have been silent about: Washington’s own efforts to strangle Venezuela’s oil industry and economy through sanctions, which also have set off a refugee crisis.
What has Trump said about Venezuelan oil?
In a post on his Truth Social platform on Tuesday night, Trump said Venezuela will turn over 30 million to 50 million barrels of sanctioned oil to the US.
Trump wrote: “This Oil will be sold at its Market Price, and that money will be controlled by me, as President of the United States of America, to ensure it is used to benefit the people of Venezuela and the United States!”
Trump added that he had directed his energy secretary, Chris Wright, to execute the plan “immediately”.
“It will be taken by storage ships, and brought directly to unloading docks in the United States,” Trump wrote.
During the news conference on Saturday, Trump said US oil companies would fix Venezuela’s “broken infrastructure” and “start making money for the country”.
Earlier Trump had accused Venezuela in a Truth Social post of “stealing” US oil, land and other assets and using that oil to fund crime, “terrorism” and human trafficking. Top Trump adviser Stephen Miller has made similar claims in recent days.
What does it mean for the US to take Venezuelan oil?
Oil is trading at roughly $56 per barrel.
Based on this price, 30 million barrels of oil would be worth $1.68bn and 50 million barrels of oil would be worth $2.8bn.
“Trump’s statement about oil in Venezuela is beyond an act of war; it is an act of colonisation. That is also illegal based on the UN Charter,” Vijay Prashad, the director of the Tricontinental Institute for Social Research based in Argentina, Brazil, India, and South Africa, told Al Jazeera.
Ilias Bantekas, a professor of transnational law at Hamad Bin Khalifa University in Qatar, told Al Jazeera that the US involvement in Venezuela was “less about Maduro as it is about access to Venezuela’s oil deposits”.
“This [oil] is the number one target. Trump is not content with just allowing US oil firms to get concessions but to ‘run’ the country, which entails absolute and indefinite control over Venezuela’s resources.”
According to the website of the US Energy Information Administration, the US consumed an average of 20.25 million barrels of petroleum per day in 2023.
What has Rubio said about Venezuelan oil?
In an interview on the NBC TV network’s Meet the Press programme that aired on Sunday, Rubio said: “We are at war against drug trafficking organisations. That’s not a war against Venezuela.”
“No more drug trafficking … and no more using the oil industry to enrich all our adversaries around the world and not benefitting the people of Venezuela or, frankly, benefitting the United States and the region,” Rubio said.
Rubio said in the interview that since 2014, about eight million Venezuelans have fled the country, which he attributed to theft and corruption by Maduro and his allies. According to a report by the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees from May, nearly 7.9 million people have indeed left Venezuela.
But he was silent on the US’s own role in creating that crisis.
What are the US sanctions against Venezuela’s oil?
Venezuela nationalised its oil industry in 1976 under then-President Carlos Andres Perez during an oil boom. He established the state-owned Petroleos de Venezuela SA (PDVSA) to control all oil resources.
Venezuela continued to be a major oil exporter to the US for some years, supplying 1.5 million to 2 million barrels per day in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
After President Hugo Chavez took office in 1998, he nationalised all oil assets, seized foreign-owned assets, restructured the PDVSA and prioritised using oil revenue for social programmes in Venezuela.
From 2003 to 2007, Venezuela under Chavez managed to cut its poverty rate in half – from 57 percent to 27.5 percent. Extreme poverty fell even more sharply, by 70 percent.
But exports declined, and government authorities were accused of mismanagement.
The US first imposed sanctions on Venezuela’s oil in retaliation for nationalising US oil assets in 2005.
Under US sanctions, many senior Venezuelan government officials and companies have been barred from accessing any property or financial assets held in the US. They cannot access US bank accounts, sell property or access their money if it passes through the US financial system.
Critically, any US companies or citizens doing business with any sanctioned individual or company will be penalised and risk becoming subject to enforcement actions.
Maduro took over as president in 2013 after Chavez’s death. In 2017, Trump, during his first term in office, imposed more sanctions and tightened them again in 2019. This further restricted sales to the US and access for Venezuelan companies to the global financial system. As a result, oil exports to the US nearly stopped, and Venezuela shifted its trade mainly to China with some sales to India and Cuba.
Last month, the Trump administration imposed yet more sanctions – this time on Maduro family members and Venezuelan tankers carrying sanctioned oil.
Today, the PDVSA controls the petroleum industry in Venezuela, and US involvement in Venezuelan oil drilling is limited. Houston-based Chevron is the only US company that still operates in Venezuela.
How have sanctions hurt Venezuela’s oil flows?
Trump might today be interested in getting Venezuelan oil flowing, but it is US sanctions that blocked that flow in the first place.
Venezuela’s oil reserves are concentrated primarily in the Orinoco Belt, a region in the eastern part of the country stretching across roughly 55,000sq km (21,235sq miles).
While the country is home to the world’s largest proven oil reserves – at an estimated 303 billion barrels – it earns only a fraction of the revenue it once did from exporting crude.
[BELOW: The sentence above promises statistics that will show how much oil exports have dropped, but the next graf doesn’t deliver. We should add that figure]
According to data from the Observatory of Economic Complexity, Venezuela exported $4.05bn of crude oil in 2023. This is far below other major exporters, including Saudi Arabia ($181bn), the US ($125bn) and Russia ($122bn).
How have US sanctions hurt Venezuelans and the country’s oil infrastructure?
The US sanctions on Venezuelan oil prevent US and non-US companies from doing business with the PDVSA. Because the US is a market no one wants to lose, firms, including banks, are wary of taking any steps that could invite Washington’s sanctions.
In effect, that has meant Venezuela’s oil industry has been almost entirely deprived of international financial investment.
The sanctions additionally restrict Venezuela from accessing oilfield equipment, specialised software, drilling services and refinery components from Western companies.
This has resulted in years of underinvestment in the PDVSA’s infrastructure, leading to chronic breakdowns, shutdowns and accidents.
The sanctions have also resulted in broader economic turmoil.
The country’s gross domestic product per capita stood at about $4,200 in 2024, according to World Bank data, down from more than $13,600 in 2010.
From about 2012, the economy went into a sharp decline, driven by domestic economic policies, a slump that was later deepened by US sanctions. The resulting hardships have pushed millions of Venezuelans to leave the country – the same people who Trump and Rubio now argue should benefit from Venezuela’s oil revenues.
Does the US have any claim to Venezuelan oil?
US companies began drilling for oil in Venezuela in the early 1900s.
In 1922, vast petroleum reserves were initially discovered by Royal Dutch Shell in Lake Maracaibo in Zulia state in northwestern Venezuela.
At this point, US companies ramped up their investments in the extraction and development of Venezuelan oil reserves. Companies such as Standard Oil led development under concession agreements, propelling Venezuela to a position as a key global supplier, especially for the US.
Venezuela was a founding member of OPEC, joining at its creation on September 14, 1960. OPEC is a group of major oil-exporting countries that work together to manage supply and influence global oil prices.
But the claims by Trump and Miller that Venezuela somehow “stole” US oil are baseless under international law, experts said.
The principle of permanent sovereignty over natural resources, adopted by the UN General Assembly in a resolution in 1962, is clear that sovereign states have the inherent right to control, use and dispose of their resources for their own development.
In other words, Venezuela alone owns its oil.