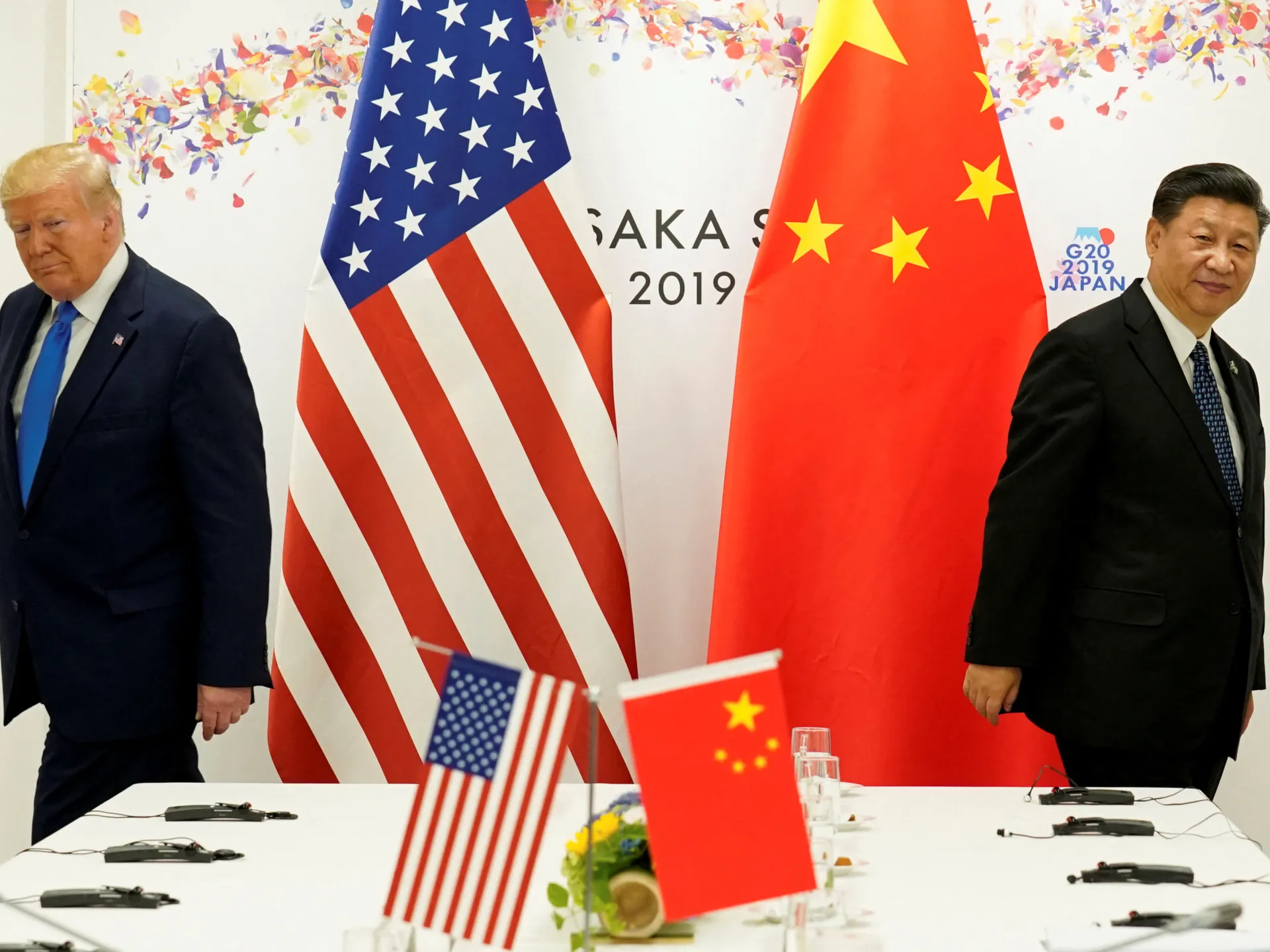
China has accused the United States of “double standards” after US President Donald Trump threatened to impose an additional 100 percent tariff on Chinese goods in response to Beijing’s curbs on exports of rare earth minerals.
China says its export control measures announced last week were in response to the US restrictions on its entities and targeting of Beijing’s maritime, logistics and shipbuilding industries.
Recommended Stories
list of 4 itemsend of list
Trump’s tariff threats, which come weeks ahead of the likely meeting between the US president and his Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping, have the potential to reignite a trade war months after Washington lowered the China tariffs from 125 to 30 percent.
The actions by the world’s two largest economies threaten to ignite a new trade war, adding further uncertainty to global trade. So what’s the recent history of US trade measures against China, and will the two countries be able to resolve their differences?
Why did China tighten export controls on rare earths?
On October 9, China expanded export controls to cover 12 out of 17 rare-earth metals and certain refining equipment, effective December 1, after accusing Washington of harming China’s interests and undermining “the atmosphere of bilateral economic and trade talks”.
China also placed restrictions on the export of specialist technological equipment used to refine rare-earth metals on Thursday.
Beijing justified its measures, accusing Washington of imposing a series of trade curbs on Chinese entities despite the two sides being engaged in trade talks, with the last one taking place in Madrid, Spain last month.
Foreign companies now need Beijing’s approval to export products containing Chinese rare earths, and must disclose their intended use. China said the heightened restrictions come as a result of national security interests.
China has a near monopoly over rare earths, critical for the manufacture of technology such as electric cars, smartphones, semiconductors and weapons.
The US is a major consumer of Chinese rare earths, which are crucial for the US defence industry.
At the end of this month, Trump and Xi are expected to meet in South Korea, and experts speculate that Beijing’s move was to gain bargaining advantage in trade negotiations with Washington.
China’s tightening of restrictions on rare earths is “pre-meeting choreography” before Trump’s meeting with Xi, Kristin Vekasi, the Mansfield chair of Japan and Indo-Pacific Affairs at the University of Montana, told Al Jazeera.
How did Trump respond?
On October 10, Trump announced the imposition of a 100 percent tariff on China, effective from November 1.
“Based on the fact that China has taken this unprecedented position … the United States of America will impose a Tariff of 100 percent on China, over and above any Tariff that they are currently paying,” Trump wrote in a post on his Truth Social platform.
He added that this would come into effect on November 1 or before that. Trump added that the US would also impose export controls on “any and all critical software”.
Earlier on October 10, Trump accused China of “trade hostility” and even said he might scrap his meeting with Xi. It is unclear at this point whether the meeting will take place.
“What the United States has is we have a lot of leverage, and my hope, and I know the president’s hope, is that we don’t have to use that leverage,” US Vice President JD Vance told Fox News on Sunday.
How did China respond to that?
China deemed the US retaliation a “double standard”, according to remarks by the Chinese Ministry of Commerce spokesperson on Sunday.
China said that Washington had “overstretched the concept of national security, abused export control measures” and “adopted discriminatory practices against China”.
“We are living in an era of deeper intertwining of security and economic policies. Both the US and China have expanded their conceptions of national security, encompassing a range of economic activities,” Manoj Kewalramani, chairperson of the Indo-Pacific Studies Programme at the Takshashila Institution in Bangalore, India, told Al Jazeera.
“Both have also weaponised economic interdependence with each other and third parties. There are, in other words, no saints in this game.”
Kewalramani said that China started expanding the idea of “national security” much earlier than others, especially with its “comprehensive national security concept” introduced in 2014.
Through this, China began to include many different areas, such as economics, technology, and society, under the term “national security”. This shows that China was ahead of other countries in broadening what counts as a national security issue.
China threatened additional measures if Trump went ahead with his pledge.
“Willful threats of high tariffs are not the right way to get along with China. China’s position on the trade war is consistent: we do not want it, but we are not afraid of it,” the Chinese Commerce Ministry spokesperson said in a statement.
“Should the US persist in its course, China will resolutely take corresponding measures to safeguard its legitimate rights and interests,” the statement said.
What trade measures has the US taken against China in recent history?
2025: Trump unleashes tariff war
A month after taking office for his second term, Trump signed an executive order imposing a 10 percent tariff on all imports from China, citing a trade deficit in favour of China. In this order, he also imposed tariffs on Mexico and Canada. China levied countermeasures, imposing duties on US products in retaliation.
In March, the US president doubled the tariff on all Chinese products to 20 percent as of March 4. China imposed a 15 percent tariff on a range of US farm exports in retaliation; these took effect on March 10.
Trump announced his “reciprocal tariffs,” imposing a 34 percent tariff on Chinese products. China retaliated, also announcing a 34 percent tariff on US products. This was the first time China announced export controls on rare earths.
Hours after the reciprocal tariffs went into effect, Trump paused them for all his tariff targets except China. The US and China continued to hike tit-for-tat levies on each other.
Trump slapped 145 percent tariffs on Chinese imports, prompting China to hit back with 125 percent tariffs. Washington and Beijing later cut tariffs to 30 percent and 10 percent, respectively, in May, then agreed to a 90-day truce in August for trade talks. The truce has been extended twice.
December 2024: The microchip controls are tightened
In December 2024, Trump’s predecessor, former US President Joe Biden, tightened controls on the sale of microchips first introduced on October 2022.
Under the new controls, 140 companies from China, Japan, South Korea and Singapore were added to a list of restricted entities. The US also banned more advanced chip-making equipment to certain countries. Even products manufactured abroad with US technology were restricted.
April 2024: Biden signs the TikTok ban
Biden signed a bill into law that would ban TikTok unless it was sold to a non-Chinese buyer within a year. The US government alleged that TikTok’s Chinese parent company ByteDance was linked to the Chinese government, making the app a threat to national security.
ByteDance sued the US federal government over this bill in May 2024.
In September this year, Trump announced that a deal was finalised to find a new owner of TikTok.
October 2023: Biden introduces more restrictions on chips
In October 2023, Biden restricted US exports of advanced computer chips, especially those made by Nvidia, to China and other countries.
The goal of this measure was to limit China’s access to “advanced semiconductors that could fuel breakthroughs in artificial intelligence and sophisticated computers that are critical to [Chinese] military applications,” Gina Raimondo, who was secretary of the US Department of Commerce during the Biden administration, told reporters.
Prior to this, Biden signed an executive order in August 2023, creating a programme that limits US investments in certain high-tech areas, including semiconductors, quantum computing, and artificial intelligence, in countries deemed to be a security risk, like China.
October 2022: Biden restricts Chinese access to semiconductors
Biden restricted China’s access to US semiconductors in October 2022. The rules further expanded restrictions on chipmaking tools to include industries that support the semiconductor supply chain, blocking both access to American expertise and the essential components used in manufacturing the tools that produce microchips.
Semiconductors are used in the manufacturing of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. The US government placed these restrictions back then to limit China’s ability to acquire the ability to produce semiconductors and advance in the technological race.
The restrictions made it compulsory for entities within China to apply for licences to acquire American semiconductors. Analysis by the US-based Carnegie Endowment for International Peace described these licences as “hard to get” back then.
Recently, some US lawmakers are calling for even more restrictions, warning that China could quickly reverse-engineer advanced semiconductor technologies on its own, outpace the US in the sector, and gain a military edge.
May 2020: Trump cracks down on Huawei
In May 2020, the US Bureau of Industry and Security intensified rules to stop Huawei, the Chinese tech giant, from using American technology and software to design and make semiconductors in other countries.
The new rules said that semiconductors are designed for Huawei using US technology or equipment, anywhere in the world, would need US government approval before being sent to Huawei.
May 2019: Trump bans Huawei
Trump signed an executive order blocking Chinese telecommunications companies like Huawei from selling equipment in the US. The Shenzhen-based Huawei is the world’s largest provider of 5G networks, according to analysis by the New York City-based think tank the Council on Foreign Relations (CFR).
Under this order, Huawei and 114 related entities were added to a list that requires US companies to get special permission (a licence) before selling certain technologies to them.
The rationale behind this order was the allegation that Huawei threatened US national security, had stolen intellectual property and could commit cyber espionage. Some US lawmakers alleged that the Chinese government was using Huawei to spy on Americans. The US did not publicise any evidence to back these allegations.
Other Western countries had also cooperated with the US.
March 2018: Trump imposes tariffs on China
During his first administration, Trump imposed sweeping 25 percent tariffs on Chinese goods worth as much as $60bn. In June of 2018, Trump announced more tariffs.
China retaliated by imposing tariffs on US products. Beijing deemed Trump’s trade policies “trade bullyism practices”, according to an official white paper, as reported by Xinhua news agency.
In September 2018, Trump issued another round of 10 percent tariffs on Chinese products, which were hiked to 25 percent in May 2019.
During the Obama administration (2009-2017)
In 2011, during US President Barack Obama’s tenure, the US-China trade deficit reached an all-time high of $295.5bn, up from $273.1bn in the previous year.
In March 2012, the US, European Union, and Japan formally complained to China at the World Trade Organization (WTO) about China’s limits on selling rare earth metals to other countries. This move was deemed “rash and unfair” by China.
In its ruling, the world trade body said China’s export restraints were breaching the WTO rules.
In 2014, the US indicted five Chinese nationals with alleged ties to China’s People’s Liberation Army. They were charged with stealing trade technology from American companies.
What’s next for the US-China trade war?
Trump and Xi are expected to meet in South Korea on the sidelines of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), which is set to begin on October 31.
But the latest trade dispute has clouded the Xi-Trump meeting.
On Sunday, Trump posted on his Truth Social platform, downplaying the threat: “Don’t worry about China, it will all be fine! Highly respected President Xi just had a bad moment. He doesn’t want Depression for his country, and neither do I. The U.S.A. wants to help China, not hurt it!!!”
In an interview with Fox Business Network on Monday, US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said, “President Trump said that the tariffs would not go into effect until November 1. He will be meeting with [Communist] Party Chair Xi in [South] Korea. I believe that meeting will still be on.”
When it comes to which of the two players is more affected by the trade war, Kewalramani said that he thinks “what matters is who is willing to bear greater pain, endure greater cost”.
“This is the crucial question. I would wager that Beijing is probably better placed because Washington has alienated allies and partners with its policies since January. But then, China’s growing export controls are not simply aimed at the US. They impact every country. So Beijing has not also endeared itself to anyone,” Kewalramani said, pointing out how Trump’s tariffs and China’s rare earth restrictions target multiple countries.
“The ones affected the most are countries caught in the midst of great power competition.”
On Sunday, US VP Vance told Fox News about China: “If they respond in a highly aggressive manner, I guarantee you, the president of the United States has far more cards than the People’s Republic of China.”
Kewalramani said that so far, Beijing has been more organised, prepared and strategic than the US in its policies.
“That said, it has overreached with the latest round of export controls. US policy, meanwhile, has lacked strategic coherence. The US still is the dominant global power and has several cards to play. What matters, however, is whether it can get its house in order.”