From Floodplains to Fault Lines: The Illusion of Growth in a Drowning Nation
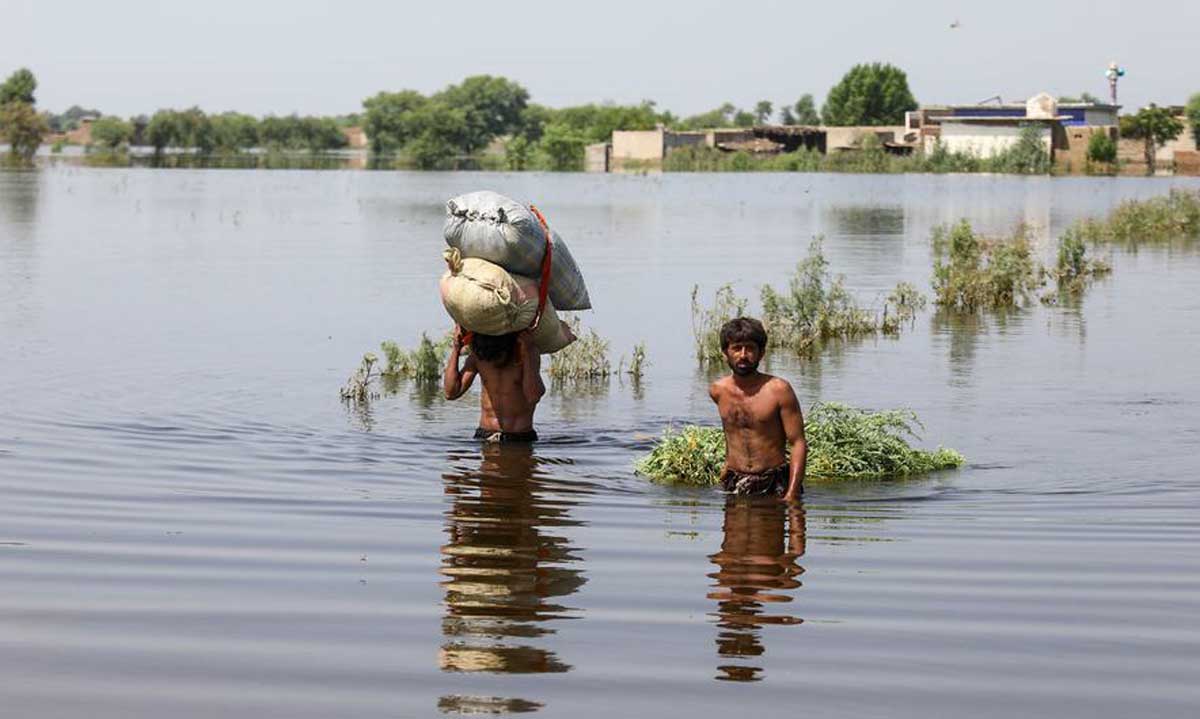
Pakistan’s infrastructure narrative over the past few years has been painfully instructive. Investments meant to connect markets and power industry have sometimes deepened vulnerability because climate risk and ecological limits were treated as afterthoughts. The scale of recent shocks is no longer anecdote. The catastrophic 2022 floods affected roughly 33 million people and left millions homeless, and the country is again reeling from extraordinary monsoon events in 2025 that, by mid-September, had displaced millions, damaged vast tracts of farmland (2.5 million acres in Punjab alone) and killed hundreds, with some reports putting the affected population in the millions and death tolls approaching the high hundreds. These are not distant statistics but the reality behind submerged villages, broken irrigation, and shattered livelihoods across Punjab, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Sindh.
These floods are compounded by mountain hazards: glacial-lake outburst floods (GLOFs) this summer in Gilgit-Baltistan destroyed scores of homes in several villages and briefly formed large, newly emergent lakes that severed roads and tourism circuits in fragile mountain economies. The visible loss of homes, guesthouses and the thin economic base of high-altitude communities illustrates how poorly planned transport and tourism infrastructure can multiply the harm of climate-driven glacier changes.
The thermal extremes of 2025 added a second front. Heatwaves pushed many urban centres and rural plains into temperature ranges far above seasonal norms, April 2025 was the second-hottest April in 65 years, with national mean temperature about 3.37°C above historical standard, daytime highs exceeding norms by 4.66°C, and Shaheed Benazirabad reaching 49°C. Heat stress has direct impacts on labour productivity, public health and the viability of energy systems, spiking demand at exactly the moment supply is least secure. The return of La Niña this winter poses another test of Pakistan’s resilience, as shifting temperature and rainfall patterns will once again reveal how exposed communities, ecosystems, and infrastructure remain to a changing climate. In short, Pakistan is experiencing compound hazards, heat stress, glacial instability, and unusually intense rainfall that together convert ordinary infrastructure failures into humanitarian catastrophes.
Why do these predictable collisions between people, nature and climate still happen? Why are the same infrastructure fail-points recurring? What good is growth if it washes away each year? Why villages again suffer loss, why roads wash away, why power systems falter and why communities bear the worst harm? The patterns are familiar: inadequate spatial planning that ignores biodiversity and hydrology, weak enforcement of EIAs and social safeguards, faulty compensation and resettlement processes that leave families poorer and more exposed, and infrastructure designed to historical standards rather than future climates.
Since most of the infrastructure is still built with the old climate baseline in mind, monsoon design storms, flood embankments, drainage systems calibrated for decades-old rainfall intensities. As rainfall intensifies, drainage and bridges collapse; hydraulic structures (culverts, flood bypasses) are undersized. Embankments along rivers like the Chenab, Ravi and Sutlej are overtopped or breached because they were not upgraded to accommodate altered flow regimes, upstream glacial melt, or enhanced rainfall due to La Niña cycles. Recent floods showed how urban drainage systems and river embankments, often built or altered without integrated watershed assessments, were overwhelmed. Releases from upstream reservoirs and poorly coordinated transboundary water management also amplified downstream impacts. Building dams and roads without resilience is no longer progress; it is policy myopia. Where accountability is thin and safeguards are procedural rather than substantive, projects proceed on convenience rather than resilience, and the poorest pay the price.
There is, however, a pragmatic path forward if we align tools, policy and practice. Practical screening tools, the Climate Risk Screening Tool (CRST) to assess exposure and vulnerability across sectors and regions, the Pakistan Climate Information Portal (PCIP) for localized climate projections and hazard mapping, and the Climate Public Expenditure and Institutional Review (CPEIR) to track and align financial flows with climate priorities, must be institutionalized into corridor-level planning and project appraisal so that environmental risk is not an advisory footnote but a gating criterion. Infrastructure corridors must be routed to avoid ecological risk zones, embankments upgraded, drainage scaled for extreme rainfall. Finance and contracts must include enforceable safeguards and compensation for those displaced or harmed. Integrating these tools within Pakistan’s emerging climate governance framework, guided by URAAN’s Environment & Climate Change pillar, will ensure assessments translate into actionable, accountable, and climate-aligned planning.
China’s role in Pakistan’s infrastructure landscape is already shifting the technical terms of that conversation. Recent investments and technology transfers have supplied cheap solar modules, wind equipment and battery storage that are rapidly changing Pakistan’s energy mix. Solar already supplied a substantial share, 25% of Pakistan’s utility-supplied electricity, of grid electricity in early 2025. Some road and hydropower projects are now being planned with higher flood levels in mind, more robust drainage, and designs that anticipate glacial-lake outburst risks. Chinese firms are also financing and building large transmission and storage projects that, if governed with green conditionality, can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and improve energy resilience. The leverage here is policy: using preferential finance and partnership to insist on climate-proof designs, environmental management plans, local content for green jobs, and decommissioning/redesign clauses that prevent stranded assets under accelerating climate change. Evidence of large Chinese-backed renewables, storage pilots and green energy deals suggests opportunity, but success will depend on domestic governance and procurement rules that prioritize sustainability over short-term cost savings.
Social and regulatory failures compound the damage. If Pakistan is to move from reactive disaster response to proactive resilience, we must redesign how infrastructure is conceived: SEAs and EIAs must be strategic and enforceable, not pro forma; decision-making criteria should explicitly value ecosystem services, social equity and future climate scenarios; and corridor planning should integrate nature-based solutions, wetland restoration for flood attenuation, reforestation for slope stability, and mangrove expansions to protect coasts, alongside hard infrastructure. Equally important is finance architecture that links green bonds, concessional Chinese and multilateral finance, and private investment to verifiable environmental and social performance. These are practical reforms, not theoretical ideals: they change engineering specifications, procurement clauses and contract supervision in ways that reduce risk and cost over the asset’s life.