Saudi Arabia ‘struggles to build ski resort’ in middle of desert for winter games as part of £373bn blood-soaked NEOM
UNCERTAINTY looms over Saudi Arabia’s plans to build a high-tech mountain ski resort in the middle of the desert.
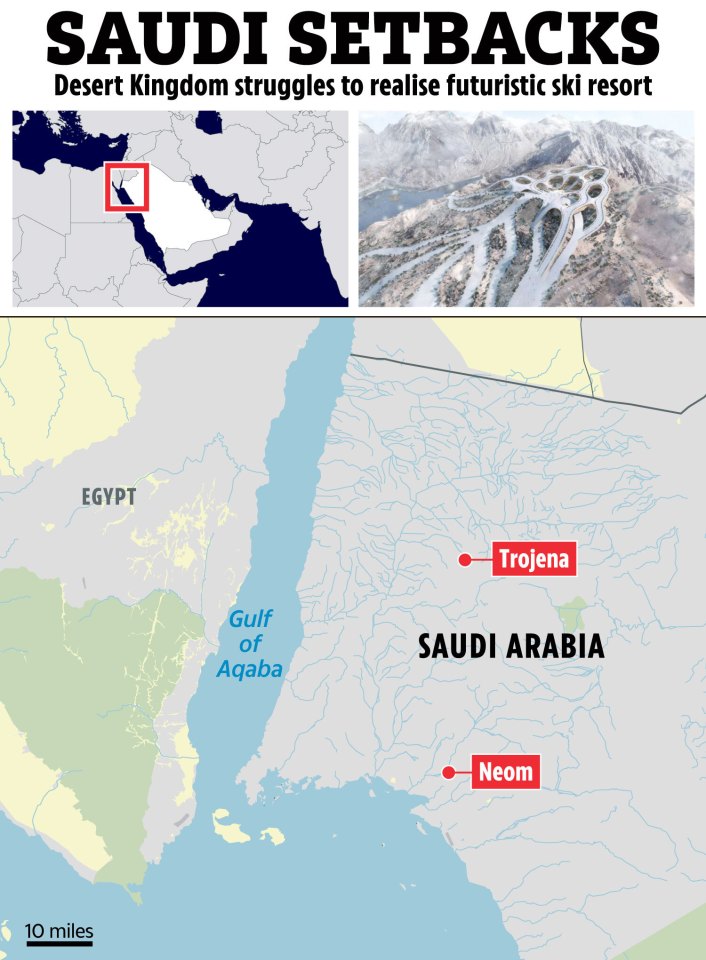
The project has met such substantial woes that the country is even reportedly in talks to relocate the 2029 Asian Winter Games.
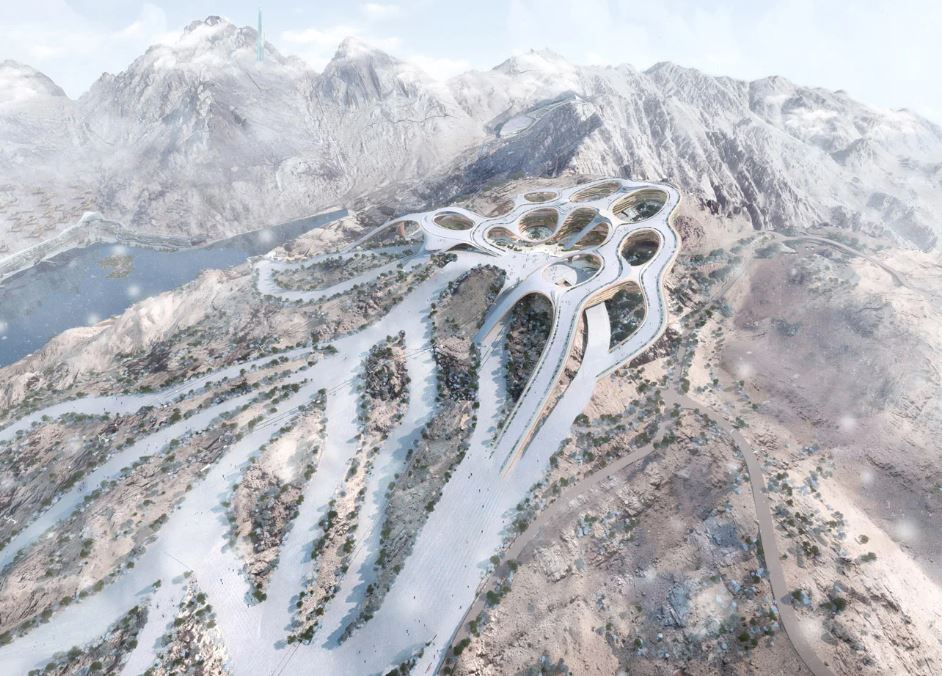
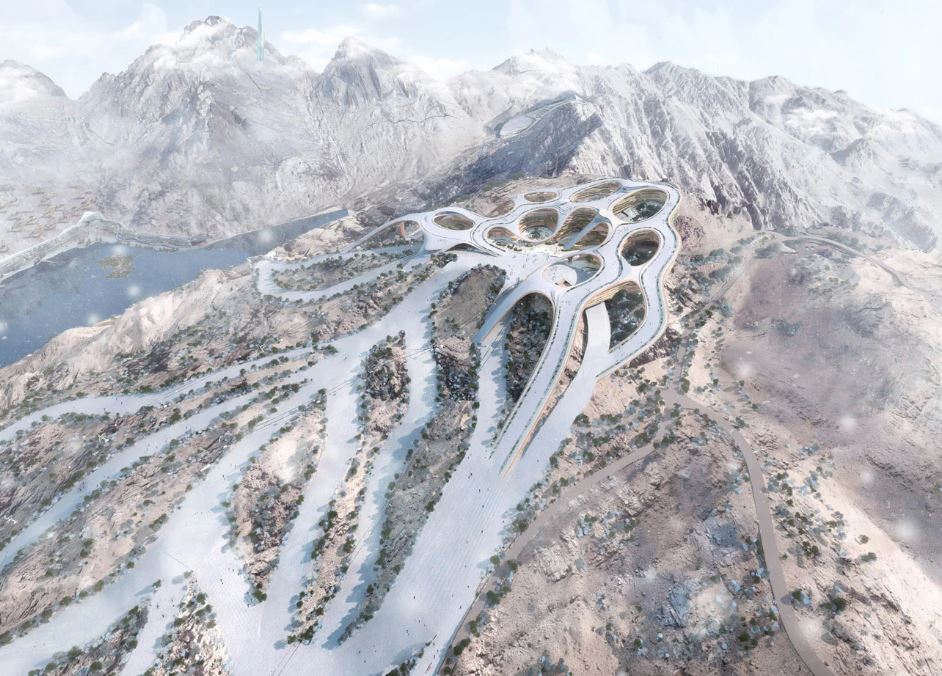
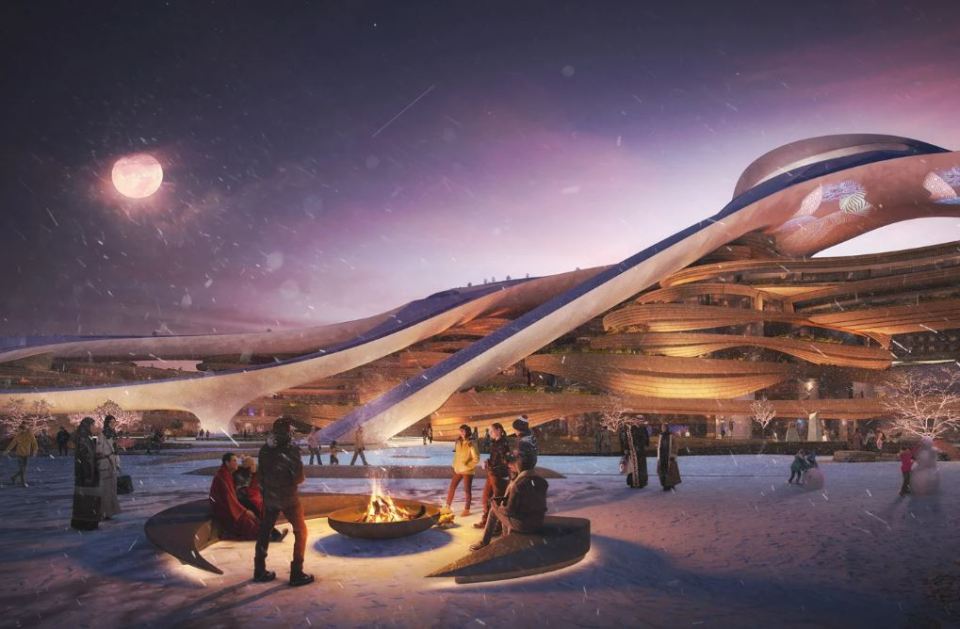
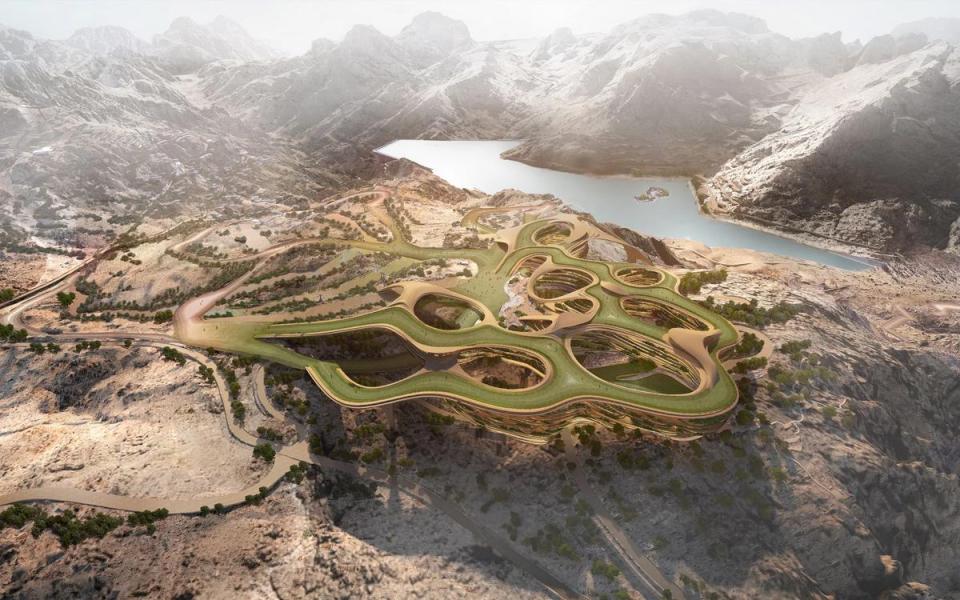
These games had been expected to take place in Trojena – in the futuristic city of NEOM in the north of Saudi Arabia.
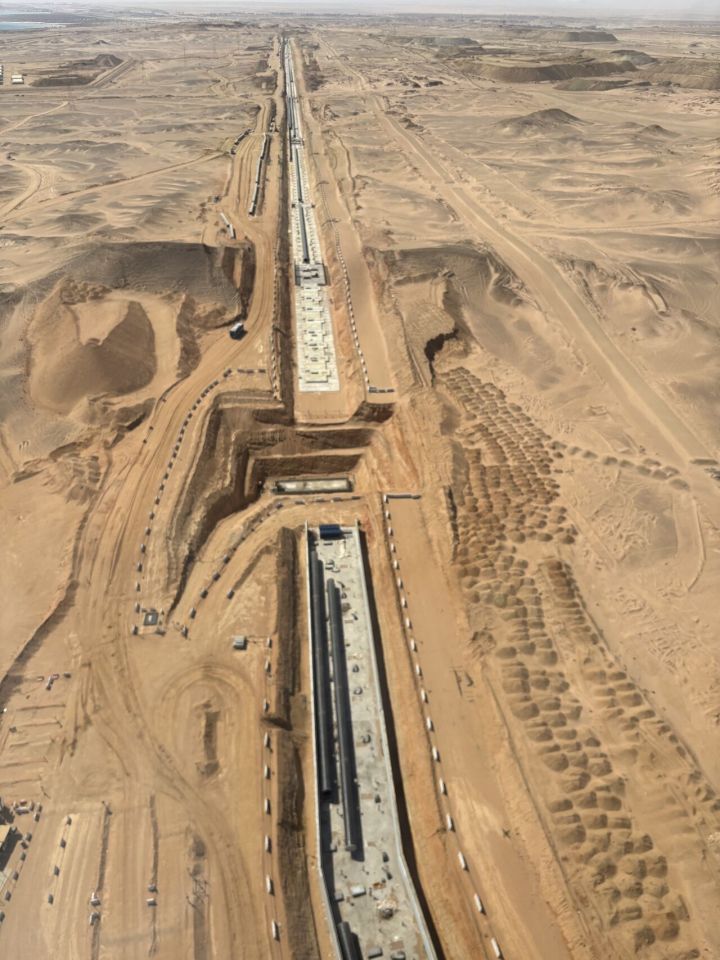
But the project has faced substantial difficulties as the desert Kingdom scrambles to complete the resort in time, the FT has reported.
Trojena is planned to feature 30km of ski-runs – which will include the Asian Games’ 400m slope.
Snow for the ski slopes would be artificial, and would be pumped from the Gulf of Aqaba 200km away.
“Trojena will become one of the most dazzling destinations in NEOM and across the world,” says a NEOM spokesperson.
But for all the promise of a glittering, high tech future, NEOM’s many projects have been bogged down with delays and setbacks, with Trojena being no exception.
Amid construction woes, South Korea and China are reportedly being considered as alternate venues for the games.
But a source familiar with the project told the Telegraph: “The difficulties have been magnified by the schedule imposed on the project.”
Another said: “The Saudis are really committed to building something there.
“Maybe not on the scale that they have imagined in the first place.”
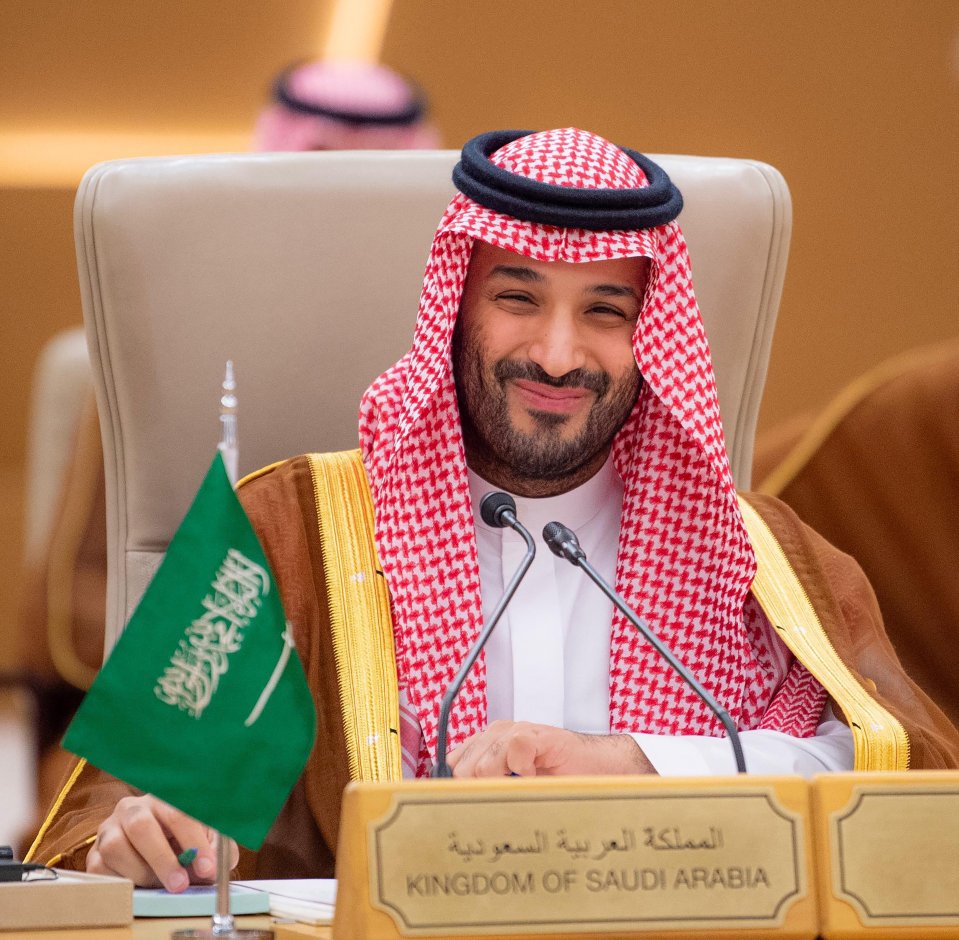
NEOM was announced as part of Saudi Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman’s Project 2030 in 2017.
It came as part of a major push to wean the oil-rich nation’s economy off its reliance on fossil fuels.
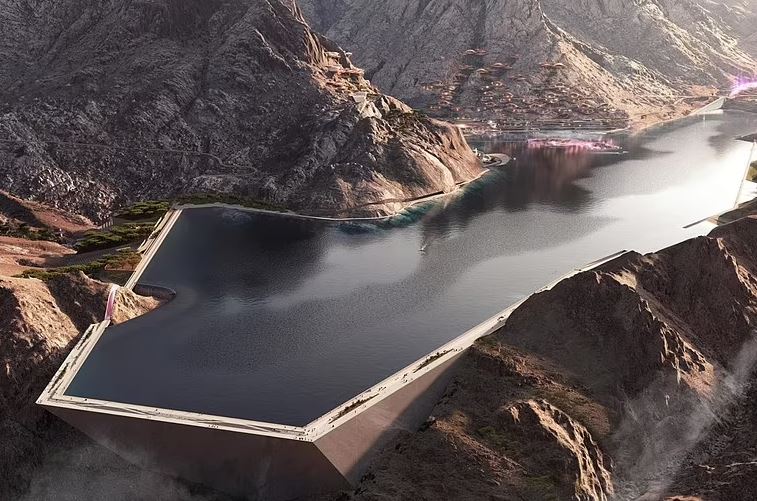
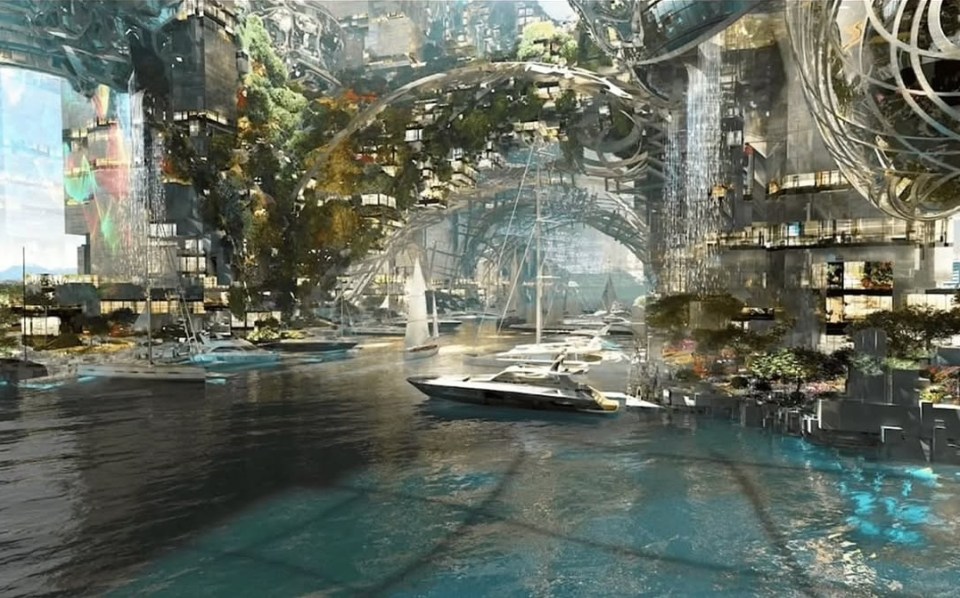
As well as the ski slopes, it is expected to include The Line, Oxagon, Trojena, Sindalah and the Gulf of Aqaba Projects.
Yet human rights abuses and brutal conditions for workers looming over NEOM.
As many as 21,000 are reported to have died during construction, but Saudi authorities have disputed this figure.
Human Rights Watch researcher Joey Shea previously told the Sun: “Unfortunately migrant workers in Saudi Arabia continue to face widespread abuses, some of which may amount to situations of forced labour, including at high profile gigaprojects.
“On NEOM, Human Rights Watch has found that ambitious targets set by Saudi authorities have tight and unrealistic deadlines which can lead employers to demand that workers continue to work under dangerous conditions.
“Migrant workers in Saudi Arabia experience illegal and exorbitant Recruitment Fees, limits to job mobility, obstacles exiting the country, as well as serious health and safety risks.”
One NEOM worker previously told The Sun that the project’s management has “overspent quite a bit” since its announcement.
He said: “They were focusing on way too many things at the same time.
“They just wanted everything at the highest level possible. The biggest entertainment complex in the world. The biggest media studio in the region.
“No matter how much money you throw at the thing, it takes more than just money to make it work.”
Top 5 blunders plaguing NEOM project
BY Juliana Cruz Lima, Foreign News Reporter
Saudi Arabia’s NEOM project, despite its ambitious vision, has been criticized for several major blunders that have raised concerns about its feasibility, ethics, and overall execution.
Here are the top five major blunders associated with the project:
Forced Displacement of Indigenous Communities: One of the most significant controversies surrounding NEOM is the forced displacement of the Huwaitat tribe.
This indigenous community, which has lived in the area for centuries, was forcibly removed from their ancestral lands to make way for the development of the mega-city.
The Saudi government’s crackdown on those who resisted, including the killing of a tribal leader, Abdul Rahim al-Howeiti, has drawn widespread condemnation from human rights organisations.
This blunder not only sparked international outrage but also tainted NEOM’s image as a forward-thinking, humane project.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Concerns: NEOM has been marketed as an environmentally sustainable city, but the environmental impact of such a massive development is a major concern.
The project’s scale—covering over 26,500 square kilometers—poses significant risks to local ecosystems, particularly in the Red Sea, which is home to rich marine biodiversity.
Critics argue that the construction of artificial islands and extensive urbanisation could lead to irreversible ecological damage.
The enormous water and energy demands required to maintain a green city in the desert also raise questions about the project’s sustainability.
Economic Viability and Cost Overruns: NEOM is one of the most expensive development projects in history.
But there are serious doubts about its economic viability. Critics question whether the project can attract the necessary foreign investment and whether it will generate sufficient returns to justify the enormous expenditure.
The economic risks are further compounded by potential cost overruns and delays, which are common in megaprojects of this scale.
This financial gamble has led some to worry that NEOM could become a costly white elephant if it fails to meet its ambitious goals.
Technological Overreach and Ethical Concerns: NEOM is envisioned as a high-tech city, heavily reliant on artificial intelligence, robotics, and extensive surveillance systems.
While this technological ambition is central to NEOM’s identity, it also raises significant ethical concerns. The level of surveillance planned for the city could lead to unprecedented control over residents’ lives, sparking fears about privacy and civil liberties.
The lack of transparency about how AI will be used, coupled with concerns about job displacement, has also led to criticism that NEOM’s technological vision may be more dystopian than utopian.
Cultural and Social Disconnect: NEOM’s vision of a futuristic, liberalized society clashes sharply with Saudi Arabia’s deeply conservative cultural norms.
The project plans to introduce mixed-gender sports, entertainment events, and other liberal lifestyle elements that are rare in the kingdom.
This cultural shift has raised concerns about a potential clash between NEOM’s globalised vision and the traditional values of Saudi society.
The disconnect between the project’s ambitions and the broader cultural context has led to skepticism about whether NEOM can truly integrate into Saudi Arabia’s social fabric without causing significant friction.