Iran’s legal case for striking the Gulf collapses under scrutiny | Israel-Iran conflict
The Gulf states have spent years trying to broker peace between Iran and the West: Qatar brokered nuclear talks, Oman provided back-channel diplomacy, and Saudi Arabia maintained direct dialogue with Iran through 2024 and into 2025. Iran attacked them anyway. The idea that the Gulf states have a responsibility, a moral one, to protect Iran from the consequences of its actions because of good neighbourliness is now grotesque in context. Iran did not return good neighbourliness. Iran returned ballistic missiles.
Iran’s position is based on three propositions. First, that Iran acted in lawful self-defence pursuant to Article 51 of the UN Charter; that host countries relinquished territorial sovereignty by allowing US military bases on their territory; and that the definition of aggression in Resolution 3314 justifies the attack on those bases as lawful military objectives. Each of these propositions is legally flawed, factually skewed, and tactically wrong. Collectively, they add up to a legal argument that, if accepted, would ensure that the Gulf is permanently destabilised, the basic principles of international law are destroyed, and, in a curious twist, the very security threats that Iran is reacting to are reinforced.
The self-defence claim does not meet the required legal threshold
The UN Charter, in Article 51, permits the use of force only in self-defence against an “armed attack”, and this term is not defined by reference to the state invoking it. The International Court of Justice, in cases such as Military and Paramilitary Activities in and against Nicaragua (Nicaragua v. United States) (1986) and Oil Platforms (Iran v. United States) (2003), has interpreted the requirement of an “armed attack” under Article 51 of the UN Charter restrictively. The Court distinguished between the most grave forms of the use of force, which qualify as armed attacks triggering the right of self-defence, and less grave uses of force that do not. Accordingly, not every use of force, such as minor incidents or limited military activities, amounts to an armed attack. In this light, the mere presence of foreign military bases in Gulf states, maintained for decades under defence agreements with host governments, would not in itself constitute an armed attack against Iran.
Necessity and proportionality are also part of customary international law, requiring that self-defence be necessary and proportional. Iran has not demonstrated either. Targeting the territory of other sovereign Arab states in response to the policy decisions of the United States is neither necessary, since diplomatic and United Nations avenues are still available, nor proportional, since it imposes military consequences on states that are not a party to any conflict with Iran.
Critically, Article 51 also has a mandatory procedural element, in that any state employing self-defence is immediately required to notify the Security Council. Iran has consistently evaded this requirement in each of its escalatory actions. While this may seem to be a minor element, it is in fact the means by which the international community is able to verify and check self-defence claims. A state that evades this requirement is not employing Article 51. It is exploiting the language of Article 51.
Iran’s reading of Resolution 3314 is a fundamental distortion
The provision of Article 3(f) of the Annex to United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3314 (XXIX) (1974) states that an act of aggression includes the “action of a State in allowing its territory, which it has placed at the disposal of another State, to be used by that other State for perpetrating an act of aggression against a third State”. Iran could rely on this provision to hold the Gulf states that host United States military bases liable for any act of aggression committed from their territories against Iran. Nevertheless, the mere presence of military bases is not sufficient to hold them to be lawful military objectives; this will depend on their actual contribution to military activities against Iran based on the rules of international humanitarian law.
Thus, such an Iranian reading would be wrong on three distinct legal grounds.
First, Resolution 3314 is definitional in nature. The resolution was adopted to assist the Security Council in determining when aggression has taken place, not to confer upon states the unilateral power to punish states deemed to have committed aggression through the use of force. The resolution itself, in Article 2, asserts the power of the Security Council to make the determination of what constitutes aggression. The self-application of Article 3(f) of the resolution is therefore bypassed altogether.
Second, Article 3(f) speaks of the active launching of an attack, not the passive hosting of a military base. The legal distinction is fundamental. A state, in signing a defence treaty with another and hosting the latter’s troops on its soil, is engaging in a measure of sovereignty. A state, actively launching, coordinating, or enabling military strikes against a third party, is engaged in a different matter altogether. Iran has not credibly shown this latter case. The presence of US troops or bases in the Gulf has been a fact for decades, and this has not constituted armed aggression against Iran under any legal standard.
Third, even if Article 3(f) were applicable, the appropriate course would be to bring the matter to the Security Council, not to launch unilateral military strikes. General Assembly resolutions do not override the Charter. Iran cannot rely upon a non-binding resolution defining terms to override the Chapter VII requirements for the use of force or the clear criteria of Article 51.
Sovereignty cannot be dictated by a neighbour’s strategic preferences
Iran, in invoking the principle of good neighbourliness, asks the Arab Gulf states to deny the United States basing rights. Good neighbourliness is a two-way principle, and it does not allow for interference in the internal affairs of other states, certainly not interference in the decisions of other states simply because they are deemed inconvenient to the interfering state. All UN states possess the inherent right to conclude defence treaties with whomever they choose, and this is so regardless of the opinion of their neighbours.
The asymmetry of Iran’s position is striking and self-disqualifying. Iran itself has active military relationships with Russia and China. Iran arms, finances, trains, and supports the activities of non-state military actors in Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, and Yemen. The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Quds Force operates openly in various states, and this has been extensively documented in United Nations Panels of Experts reports, as well as other international monitoring reports. According to the standards that Iran applies to the Gulf states, any state that hosts the activities of the IRGC, the transfer of Iranian arms, or the coordination of Iranian proxies on its soil would be engaging in aggression against third parties. Iran will not accept this principle when it is applied to itself. A legal principle that is unacceptable to the party to whom it would be applied is not a legal principle at all; it is a political tool.
A doctrine that defeats Iran’s own strategic interests
From the perspective of international relations theory, Iran’s position follows the logic of offensive realism, which seeks to remove the external balancing architecture of regional neighbours by claiming it to be hostile in nature. However, this approach is empirically self-defeating.
Under balance of threat theory, states react to offensive capability, geographic proximity, and aggressive intentions. Iran’s doctrine, in asserting the right to strike any state that hosts forces it perceives as a threat, drives each and every threat variable to maximum levels for each and every state in the region. The obvious consequence, evident in the data, is that the states in the region and external powers are becoming more, rather than less, securely integrated. The Fifth Fleet’s permanent base in Bahrain, the UAE’s negotiations over F-35s, Saudi Arabia’s deployments of THAADs, and Qatar’s expansion of the Al Udeid base are reactions to Iran’s escalation, not causes of it.
From the perspective of constructivism, the legitimacy of a legal argument is also partly based on the normative credibility of the state that presents the argument. The record of Iran’s compliance with IAEA regulations, including the enrichment of uranium to a purity level of 60 percent or more in 2023–2024, interference with inspections, the removal of monitoring cameras, and the overall violation of the non-proliferation regime, has undermined the credibility of the state significantly. A state that is itself a violator of the legal regime cannot claim the role of a law-abiding state seeking protection under the norms of the legal regime.
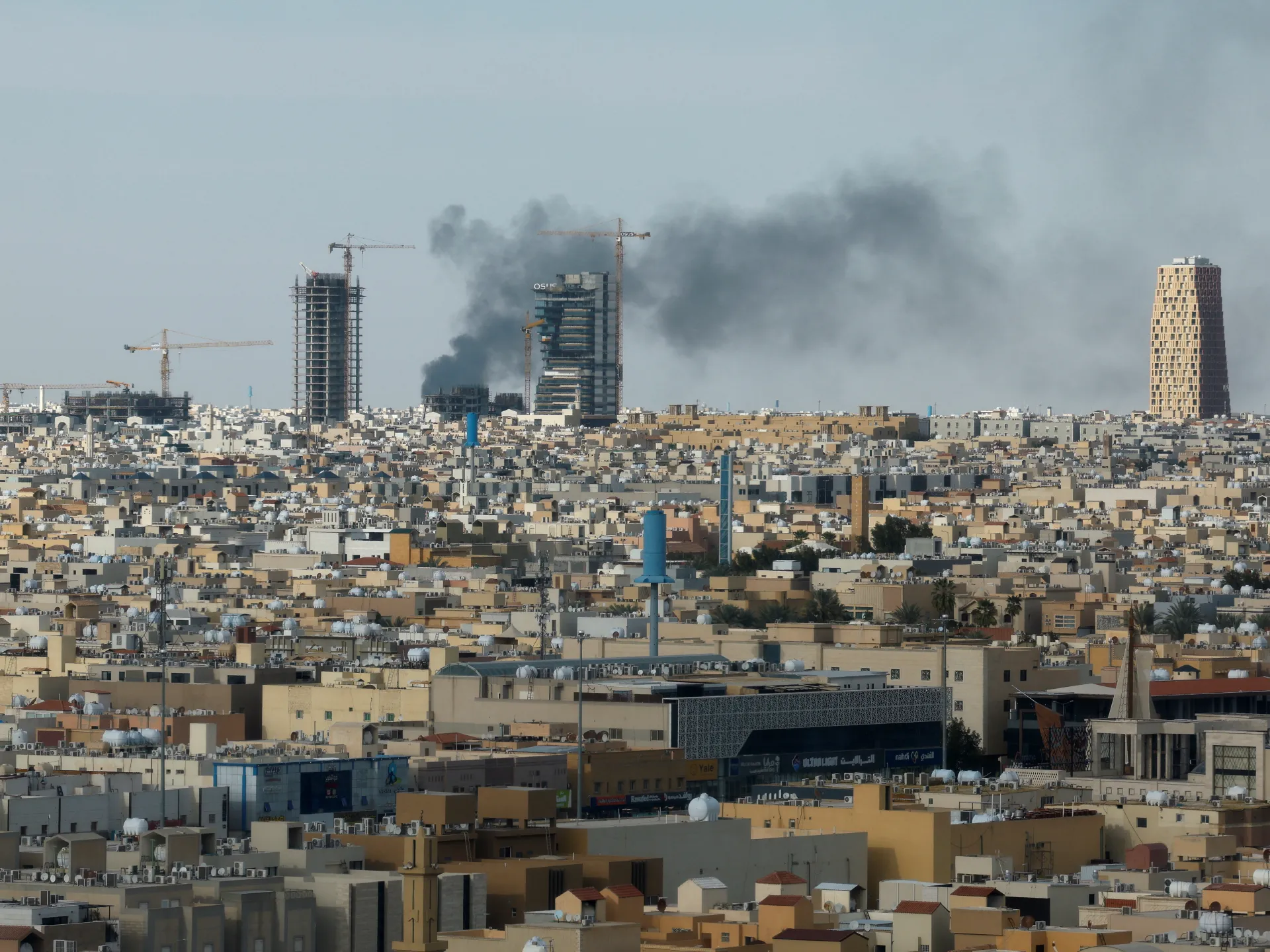
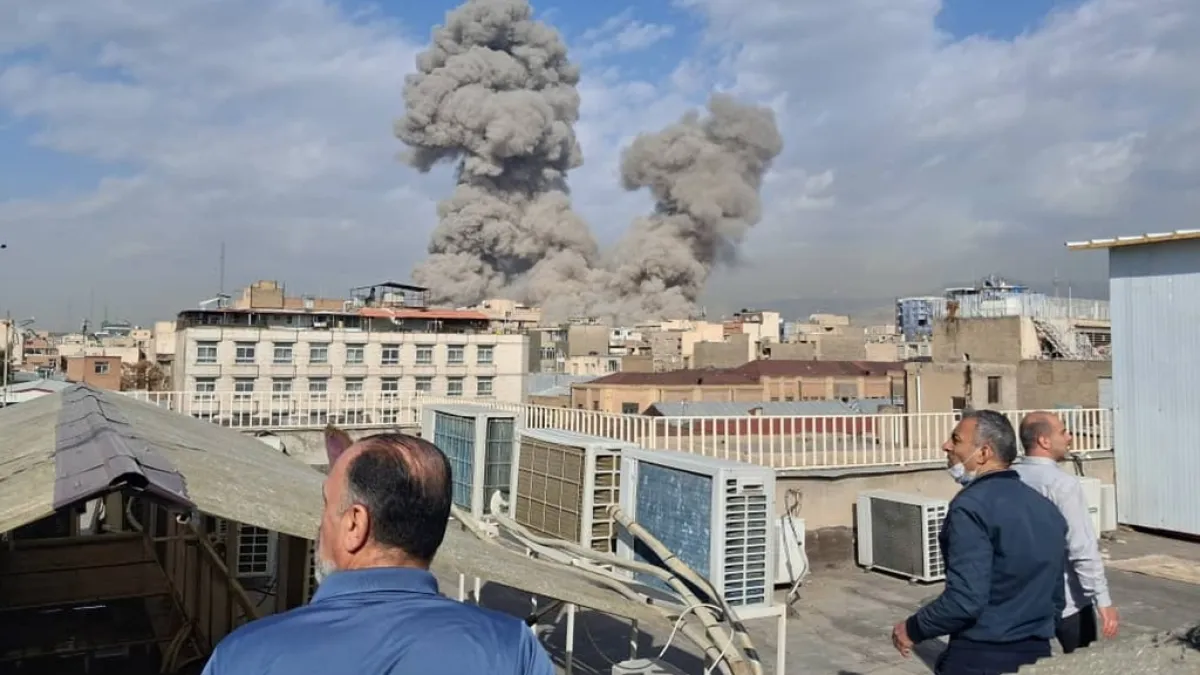
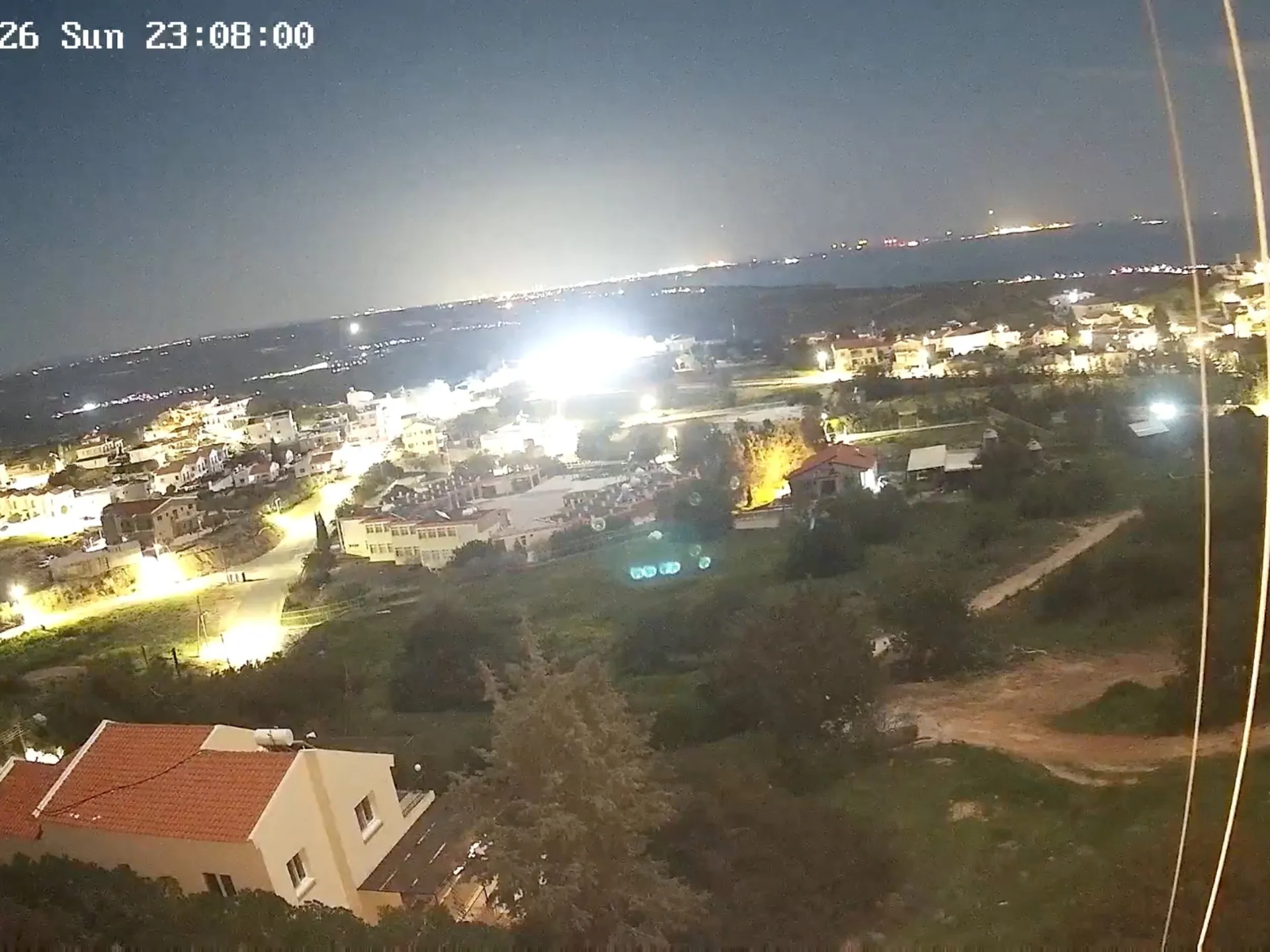
Iran’s legal rationale was always theoretically wrong. What has occurred since February 28, 2026, has made Iran’s actions morally and politically wrong. Iran did not simply target US military assets. The reality of the situation is now documented and undeniable. Ballistic missiles and drones were launched against Gulf states in the opening days of the conflict. This marked the first time one actor had simultaneously attacked all six GCC states. Iran escalated its attacks in deliberate stages. Day 1: Iranian missiles were fired against military bases. Day 2: Iranian missiles were fired against civilian infrastructure and airports. Day 3: Iranian missiles were fired against the energy sector. Days 3 and 4: The US Embassy in Riyadh was attacked by Iran. International airports in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Kuwait were attacked by Iranian missiles, resulting in the suspension of flights throughout the region. Videos from Bahrain documented an Iranian Shahed drone attacking an apartment building. This is not self-defence. This is the collective punishment of sovereign nations that went to extraordinary lengths to avoid the conflict.
The rationale provided by Iran falls flat when one considers the actions Iran itself took. Its doctrine held that only targets involved in the preparation or launch of an attack against Iran were legitimate targets. Civilian airports are not military bases. Hotels in Palm Jumeirah are not military command centres. An apartment complex in Manama is not a weapons storage facility. By Iran’s own stated legal rationale, none of these targets was legitimate, yet they were attacked. This was not a legal doctrine at all; it was a pretext for coercion, and the conduct of war revealed this to be the case.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Al Jazeera’s editorial stance.