Iran-Israel Conflict: Expanding Security Dilemma in Middle East
The Middle East has been one of the most sensitive regions, where one event of insecurity and chaos shakes the entire Middle Eastern dynamics and existing global order. The recent atrocious genocide of Palestinians since October 7, 2023, by Israelis has proved to be a major spark for escalated crises in the region. The recent Iran–Israel conflict ignited a fire from the underlying spark. Strategic attacks between both adversaries took place, which unveiled the volatile and porous security shield of the region concealing deepened internal weaknesses and discords. Israel attacked Iran by relying on its policy of “pre-emptive strike,” a sheer and illegal violation of international law. Iran retaliated while unable to hide the weaknesses and loopholes in its air force and defense system.
The Arab World’s normalization of relations with Israel, the anti-Western ideological perspective of Iran, the sponsorship of terrorism and proxy wars, the expanded nuclear arsenals of both competitors, and the Palestinian genocide by Israel have caused recent escalatory tensions between Iran and Israel. The war between both nuclear powers has escalated regional tensions and generated severe impacts: a vacuum for global powers to exercise influence in the Middle East, strict hatred against the USA and the West by Iran, regional instability and imbalance of power, an arms race, and alliance formation in the region.
The relationship between Iran and Israel can be divided into four phases, spotlighting a roller coaster of instability. The first phase starts from 1947 till 1953, in which bitter relations followed; Iran stood against the British and United Nations (UN) decision of inclusion of Israelis into Palestine (Iran was an anti-Israel state out of 13 states).Then comes the second phase, from 1953 till 1979, in which cordial ties were enjoyed during Iranian President Reza Shah Pahlavi’s regime (he was pro-Western). During the Iranian Revolution of 1979, the pro-Western regime of Reza Shah Pahlavi was ousted by Iran’s first Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, and post-Revolution Iran maintained bitter relations with Israel during its third phase till 1991.
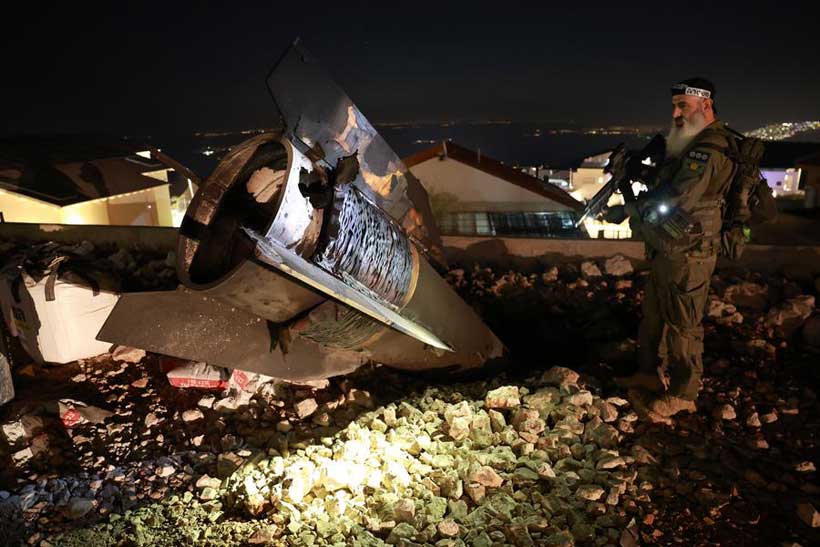
However, further adversarial relations peaked after the disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991 till contemporary times. The series of attacks between both states in the contemporary history of the world marked a possibility of a bigger conventional warfare that can take place between both states via the “Domino Effect.” The unprecedented support for surgical strikes, proxy wars, and attacks on ships, planes, military bases, and nuclear scientists was a common practice. Recent larger-scale tensions expanded when Israelis attacked on April 1, followed by Iranian retaliation on April 13, 2024, then full-scale attacks at the onset of June 2025, while utilizing their nuclear arsenals at a huge pace. Israel’s important port was attacked by Iran, along with the residence of Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, who justified the attack on Gaza concealed under the right of self-defense.
The ground for attack was prepared for a few reasons. Diverse factors escalated war at the conflict ladder, raising serious peace and security concerns and generating severe impacts. One of the major causes of the tensions is the religious factor. Iran being a Shi’ite majority state while Israel’s Zionism’s superiority claimed the conflict’s religious perspective. Iran stood with Palestinians, being a Muslim brother, and warned Israel of an unprecedented war if Israel did not back out, and it proved to be true. The recent Israeli attacks on Palestinians divided the Middle Eastern sections that claim to be united under the umbrella of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
This war took the shape of the Arab World vs. the Non-Arab World. The Arab World normalization of relations with Israel played a major role in heightening the conflict ladder. Israel wants to become a regional hegemon by balancing ties with the Arab States and maintaining superiority on all fronts. The religious factor has caused the formation of blocs and alliances by some states andneutrality by others. The Arab World and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) met failure in proposing a genuine solution for wars in the region. Iran-Israel tensions escalated from small tactics of attacks from both sides. The nuclear warfare conceals religious superiority and intolerance towards other segments of the region.
Ideological differences between parties paved the way for a warfare scenario. Israel being the right hand of the USA in the Middle East is not acceptable to Iran (a staunch anti-Western state) in the region.Post-revolutionary Iran (post-1979) is against western policies and their implementations in the Middle East by any Muslim state. Even Pakistan’s Chief Marshall General Asif Muneer’s visit to the USA on June 14, on the 250th anniversary of the USA military, during regional tensions made Iran uncomfortable. The cover page of the Iranian newspaper “The Tehran Times” raised questions about why Pakistan went to the USA amid tensions in the Muslim world. Iran considers the backing power of Israel, the USA, a major reason for regional instability.
Iran challenges the USA’s interference in the region by confronting Israel. The USA provided military and economic aid to Israel in wars in the Middle East. In the case of Palestine, the Conflictual Theory of Karl Marx implies in this situation that the actions of one state generate the consequences, and the other (weaker) states bear the brunt of those consequences. Iran was against Saudi-led westernization structured on USA models. The USA and Israel mutually adopted a policy to neutralize Iran for being a regional hegemon. A step towards it was initiated by Israel.
Iran has an over-reliance on three elements.
· Drones (struck down by the USA, UK, Israel, and Jordan). Jordan is justifying it by saying that I’ll not allow violation of my airspace.
· Missiles (Ballistic and Hypersonic). Around 80 ballistic missiles were used, not stopped by the USA and others, and reached Israel within 12 minutes. Hypersonic missiles comprise more speed.
· Proxies in region.
The sponsorship of terrorism and proxies by both Iran and Israel in the Middle East is also one of the major reasons for advanced nuclear tensions between both parties, as they cost the peace of the region in the long run. One reason Netanyahu is quoting again and again is that Iran is an existential nuclear threat for Israel, and he is emphasizing diminishing its proxies. Hamas in Palestine, Hezbollah in Lebanon, Mehdi Malaysia in Iraq, the Houthis in Yemen, and Assad’s regime in Syria are all backed by Iran. These groups are alleged to have carried out terrorist activities in the Middle East. Israel claims to stand against them, but the reality check is different.
Israeli atrocities abstained Hamas from bearing tortures and eventually stood on October 7, 2023, by attacking Southern Israel on Yom Kippur Day. The terrorist acts and proxy wars destabilized the region in worst-case scenarios. The militant groups fought for their regional autonomy and basic independence in the states, which were undermined by stakeholders. The militant groups are majorly supported by Iran in their rights for freedom and regional autonomy rather than external influences and perpetual dependency on the global North and West. Houthis in Yemen are at a distance from Iran, and for attacks, Iran has to go through the Red Sea, as their access is strenuous. They stood in solidarity with Palestinians by blocking oil and trade ships of the USA, the UK, and Israel. These states then retaliated and caused much devastation to them by breaking the back of Iran.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) submitted a report in May 2025 that Iran has grossly violated enrichment capacities and expanded its nuclear arsenals. The Israeli nuclear arsenal, backed by the USA and Western alliances, raised the regional imbalance of power and security dilemma but was accepted by the international community.Contrarily, the Iranian Nuclear Program, developed on its own, seems a threat in the region. The nuclear programs, uranium enrichment, expansion of weaponry, development of missiles (cruise and ballistic), and latest conventional warfare techniques have raised serious concerns undermining regional peace. The economic and nuclear sanctions on Iran crippled its societal structure, yet its nuclear standoff is unmatchable. The expansion of nuclear arsenals and weaponry has led to an arms race, with the latest technological advancements having raised serious concerns. Iran has weapons that cannot be detected by the missile defense systems of Israel.
Palestinian genocide by Israel is one of the major reasons behind Iran-Israel tensions. Massive ethnic cleansing of innocent Palestinians has raised serious human rights concerns. Iran has condemned the Arab World for staying silent and not assisting Palestinian liberation via united efforts. They have claimed to retaliate with full force if Israel does not back off from Palestinian genocide. Massive brutal assassinations of Palestinians have taken place. More than 50,000 children have been killed, with millions of deaths of civilians and injuries. In the case of Iran, more than 16 renowned nuclear scientists, with few other state officials, have been killed by Israeli attacks in the past ten days. If this crisis prevails, it will be difficult to mitigate larger regional warfare. Iran sided with Palestine rather than the tame Arab world. They demand immediate genuine solutions;Global Civil Society is already predicting the way towards World War III. Iran launched missile attacks on Israel, sending a clear message that it will not back down if Israel does not stop regional ethnic cleansing in the name of self-defense.
The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) was signed in 2015, from which the USA administration quit under President Trump’s administration in 2017. Trump expanded the process of negotiations on multiple fronts (nuclear enrichment, proxy wars) with Iran after becoming president again in 2024. Oman played a major role in it. The sixth round of talks was ongoing when strikes between both parties took place. Israel was against any kind of negotiations with Iran. Israel has been convincing the Global North and West to attack Iran on the basis of several reasons (speeches), as its fear of unprecedented threats from Iran isn’t hidden. After its October 2023 attacks on Gaza, upon questioning by the journalist about what the common threat of Israel is, in an interview with CNN, Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu said, “Iran, Iran, Iran.” Pivotal stance on attacking Hamas was based on ceasing Iranian support and expansion in the region via Hamas. JCPOA negotiations failed in genuine terms and halted, as they were not acceptable to Israel, and do not seem possible in the future.
Netanyahu is facing opposition on multiple fronts, internally due to a vote of no-confidence against himself in Knesset. In order to foil that move, he successfully created a situation with Iran. Due to genocide and war crimes in Gaza, European allies step back in large numbers. The USA and European populace went to protests for Muslim victims for the first time in contemporary history. A wicked hard image of Netanyahu was projected globally; these steps seemed to make it better to erode it by diverting attention towards Iran.
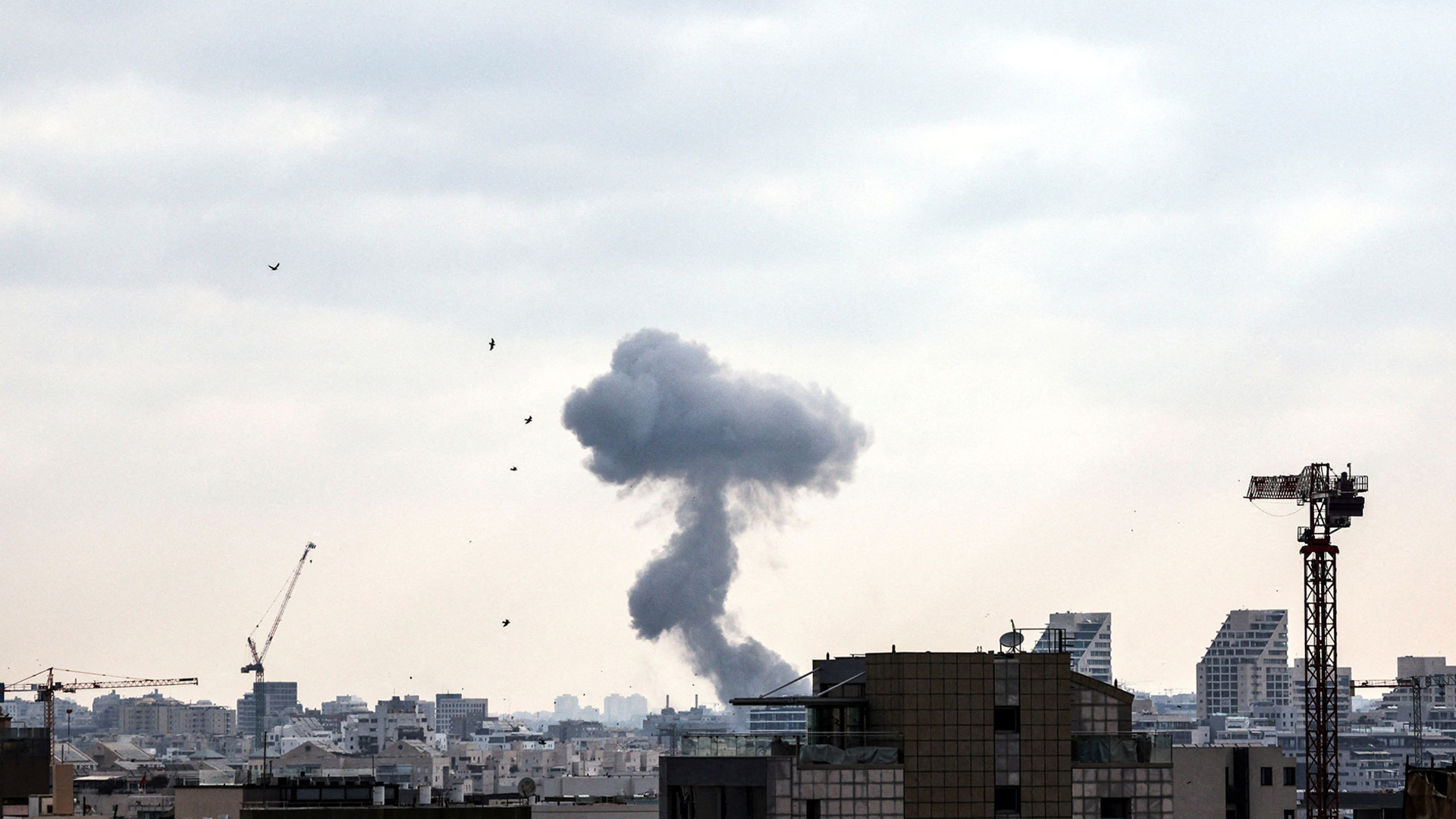
Israel implemented an official policy of “preemptive strikes” against all proxies. This concept matured in the Bush era, mainly in 2003-04. Practically, it was utilized by both adversaries in strikes against each other, yet Israel got its benefits in the recent escalation. The attacks were unprecedented. No official statement was given by Israel, and certain media reports say that missile strikes were carried out and F-35 jet fighters were used. Special forces of Israel have conducted operations in Iran, including attacks in Tehran, at nuclear facilities, and at military bases, targeting journals, scientists, the army chief, military commanders, and around 100 civilians, claiming several precious and innocent lives.
Nuclear facilities of states are mostly underground, and Iran’s are based in Isfahan, Natanz, Fordow, and Arak. The depth of underground facilities is generally 60-80 meters deep underground. Simple missiles are not enough to destroy these, but Bunker Buster bombs are required, which are owned by the USA but lacked by Israel. According to The Security Brief Show (BBC News), nuclear sites in Isfahan were attacked by sea-based USA warships called TAM, or Tomahawk Land Attack Missile, that travels subsonically and can go very deep and is really hard to be detected by radar. The dismantling of the nuclear installations is still doubtful.
However, apart from bases, Iran claimed to have breached Israel’s sophisticated missile defense systems, which are among the most advanced in the world, by hitting a military intelligence center and an operations planning center for the Mossad spy agency. Iranian missiles managed to pierce through the Israeli Air Defense System by exhausting interceptor missiles and cruise and hypersonic missiles, according to an Al-Jazeera report.
Despite all these, the internal weaknesses of the Iranian intelligence system and defense capabilities to strike down attacks by Israel were all unveiled and made Israel more confident. The striking back capabilities of Iran encompassed the Air Force, which was very weak due to protracted sanctions via the international community. It has outdated jets, like the MiG-29. F-14 jet fighters are USA-based. The Israeli intelligence agency Mossad has deep penetration in Iran’s intelligence and military system. The attacks were carried out on the residences of the army chief, the Pasdaran-e-Islam chief, scientists, journals, and many others. The operation by commandos proved to be another bigger penetration of Israel (comprising intelligence and military). Reports by the BBC are claiming that Iran will go to Beijing for advanced fighter jets.
This war has major impacts on China, due to its growing imports and reliance on Middle Eastern hydrocarbons, especially being a major importer of Iran’s hydrocarbons. Absence of safety, hiked prices of energy resources, and escalated insecurity will devastate China in the economic sector via deteriorating trade and investments carried out by China under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and BRICS+. Unlikely, USA entanglement in regional wars has diverted her attention from the Taiwan Strait (emerging Silicon and technological warfare) and the South China Sea, a blessing in disguise for China to reclaim irredentism. The USA has more than 40,000 troops in the Persian Gulf.
The more the attention of the USA is on the Middle East, the less the attention is on China and Russia.
Trump projected himself (self-proclaimed) as a peacemaker—to avoid a confrontation policy with Iran. Iran was not in favor of war either (with the USA and Israel directly) and carried out a policy of utilizing the nuclear enrichment as a bargaining chip with the USA for the removal of sanctions, knowing its defense capacities and loopholes. Trump is projecting its peace-making image via regime change in Syria with more democratic and peaceful political agendas concealing regional influence, genocide in Gaza despite ceasefire truces, launching air and naval strikes on Houthis in Yemen in “Operation Rough Rider” in the name of promoting peace, and giving minute relief to so-called militant groups in the region. According to a recent report on the Red Sea crisis, Israel is urging Trump to resume strikes on Houthis in Yemen.
In the case of Pakistan, the state’s second strike capability is strong, as it remained victorious in recent military strikes with India in post-Pahalgam aggression. India’s ideological isolationist nationalism and political pressure on Prime Minister Modi are shaping the current aggressive behavior of the world’s largest democracy. Its involvement in baking the proxies, extremists, and terrorist activities in neighborhoods and within Pakistan are expected to surge in Afghanistan, ex-FATA,and the Balochistan regions.
A ceasefire brokered by the USA on June 24, 2025, curbed both parties from engaging in further military and nuclear strikes, underlying diplomatic objectives. Iran denounces the claim of the USA. It has not ended fully; episodes still exist on political and diplomatic grounds, as Israel is not accepting negotiations with Iran at any cost. The Israeli Defense Minister said that we will not attack Iran, yet citizens should be prepared for counterattacks. They have to ensure their protection via the Underground Safety System of Israel. In an interview addressing the conflict, the Iranian Parliament Speaker Mohammad Bagher Ghalibaf highlighted that the Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, played a pivotal role in orchestrating decisive strikes of Iran, which urged the USA and Israel to seek a ceasefire after the 12-day war.
Certain causes have generated massive effects, which need immediate and comprehensive solutions in order to de-escalate the deep Iran-Israeli tensions and other wars in the Middle East. Religious differences have to be tolerated and respected until they cross the threshold for massive outrages. Ideological differences have led the region to deepened grievances that need much time for their resolution. Iran is propagating an anti-westernization agenda, while Israel is working on Ideological Expansionist Nationalism (IEN) and Political Separatist Nationalism (PSN). All these have done nothing good in the regional affairs. Global powers take this opportunity to meddle in the regional affairs by being opportunists and want to take full advantage of the absence of an adversary. China filled the vacuum created by the USA in ameliorating the Iran-Saudi rivalry.
To encounter terrorist activities and proxy wars, comprehensive strategic frameworks and effective governance are the ultimate solutions, developed by proper democratic means practiced within the state. Arms control should be ensured by both states by acting with rationality and maturity. The rational actor model best explains the cost and benefit analysis taken before going to war. In today’s world of nuclear warfare, there will be no winners, but devastations will take place at huge levels. The two-state solution will resolve the Palestinian ethnic cleansing. The Muslim world has to unite for brutally suppressed Palestinians and all other factions of the region. The Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) remained slow, as it did not conduct any remarkable session in the past few months. Iran spoke in the OIC session of 2023 for Palestinians. In the case of Iran-Israeli tensions, nothing profound seemed to happen, except the USA called for a ceasefire and mediation.
In the end, the escalated tensions between Iran and Israel generated serious repercussions for regional peace, stability, and security. If this aggression were not controlled (it seemed to be controlled as a ceasefire was brokered by the USA), it would lead towards another great World War III as small bilateral wars advance the ‘domino effect’ in generating large-scale warfare. This issue generated after the Israeli genocide of Palestine, the change of regime in Syria after a long civil war, and Israeli attacks on Lebanon to eliminate Iranian-backed Hezbollah.
The religious, ideological, terrorist, nuclear, and Palestinian factors paved the way for Iran-Israel tensions that are impacting the region at a larger scale. The formation of blocs, the failure of the Muslim world to stand in solidarity with oppressed states in the Middle East, massive terrorist attacks, the nuclear arms race, and the Palestinian blockade all demand immediate solutions. A comprehensive strategic plan for regional stability by the Muslim world is in dire need of time. As the Middle East is the most volatile region with respect to stability and security in the region. Conclusively, instead of sporadic efforts, a concerted plan is required by international stakeholders for the maintenance of the dignity and sanctity of international law, peace, and humanity.