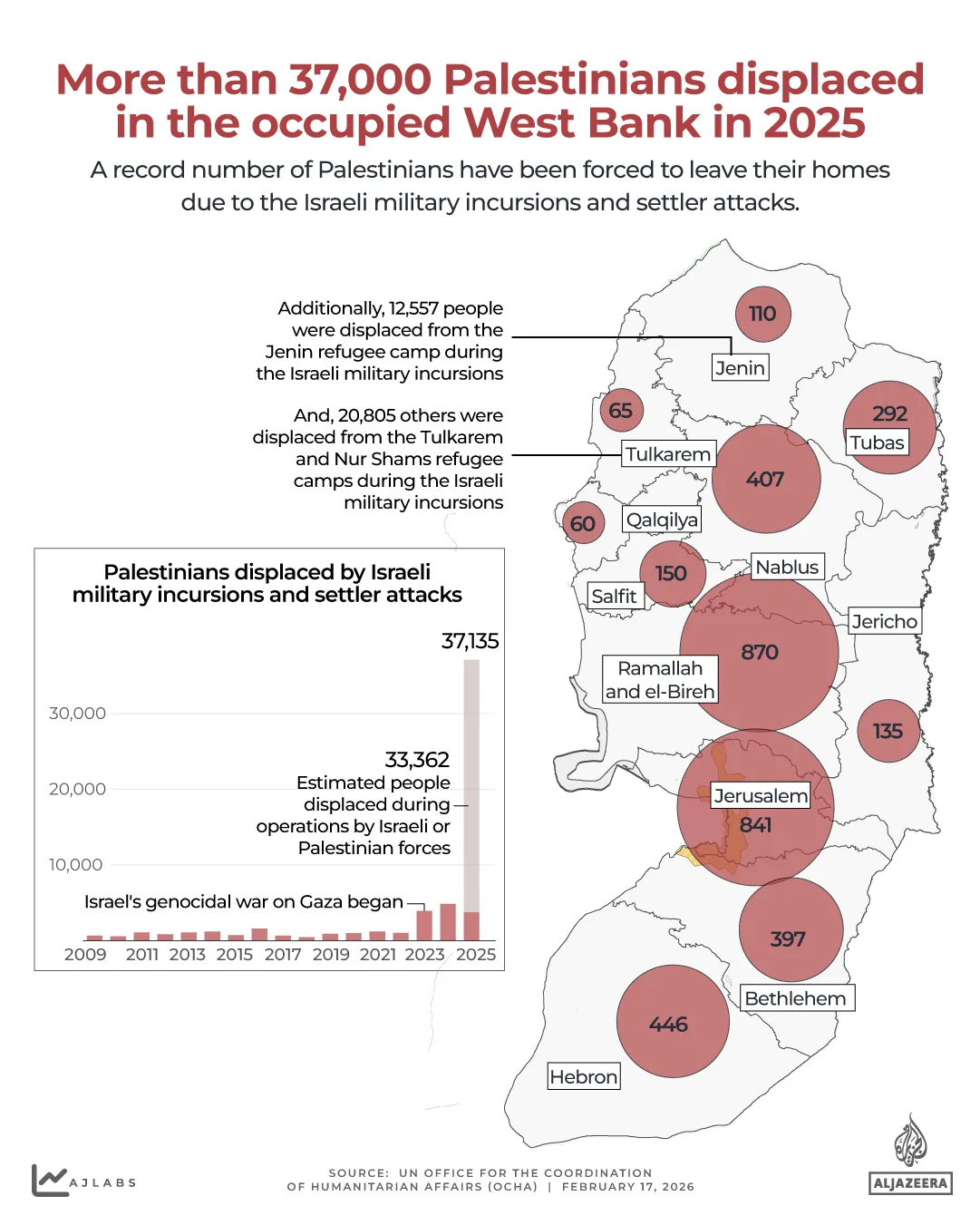
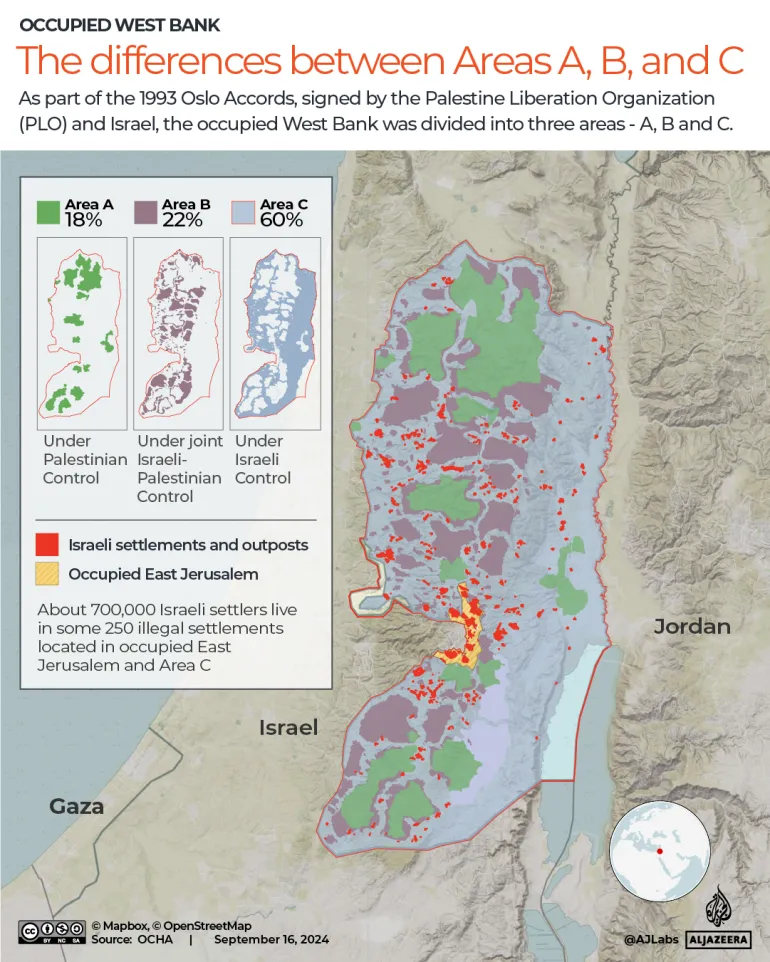
What is Christian Zionism, the pro-Israel ideology invoked by US ambassador | Israel-Palestine conflict News
United States Ambassador to Israel Mike Huckabee has faced condemnation from Arab and Muslim countries after suggesting Israel has a biblical right to much of the Middle East.
In an interview with prominent right-wing American commentator Tucker Carlson, Huckabee suggested that Israel has a God-given right to land stretching from the Euphrates River to the Nile, which would encompass Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and parts of Saudi Arabia.
Recommended Stories
list of 3 itemsend of list
“It would be fine if they took it all,” he said, arguing that the geographical borders of Israel are rooted in the Bible, a belief shared by Christian Zionists.
The US diplomat, a self-professed Christian Zionist and staunch supporter of Israel, later walked back his comments, calling them “somewhat hyperbolic” and adding that Israel is not seeking expansion but has a right to security within its current borders.
But were his comments indeed hyperbolic in the Christian Zionist worldview? Or is that precisely what he and his fellow proponents of the ideology believe?
How did Christian Zionism begin, and what are its tenets?
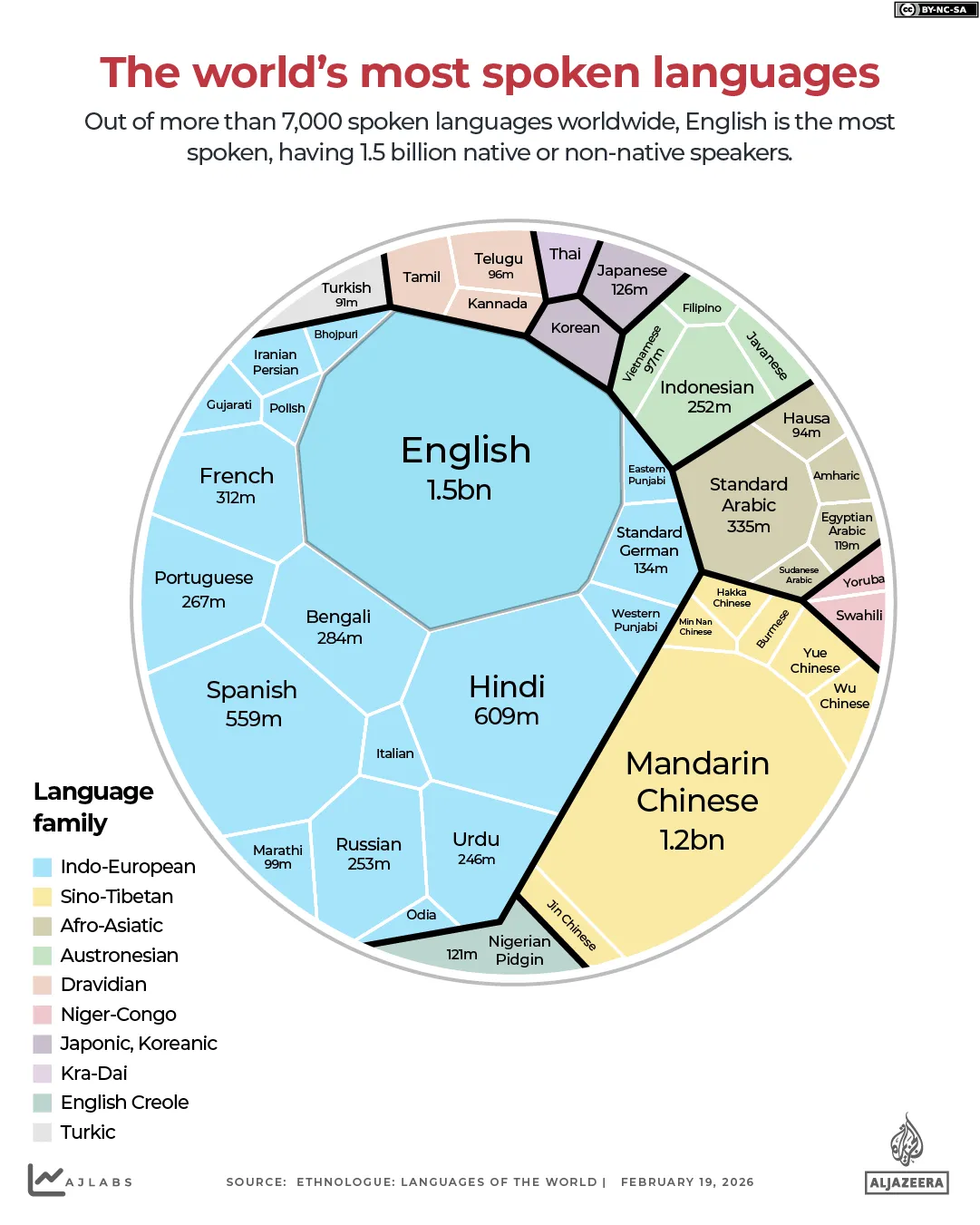
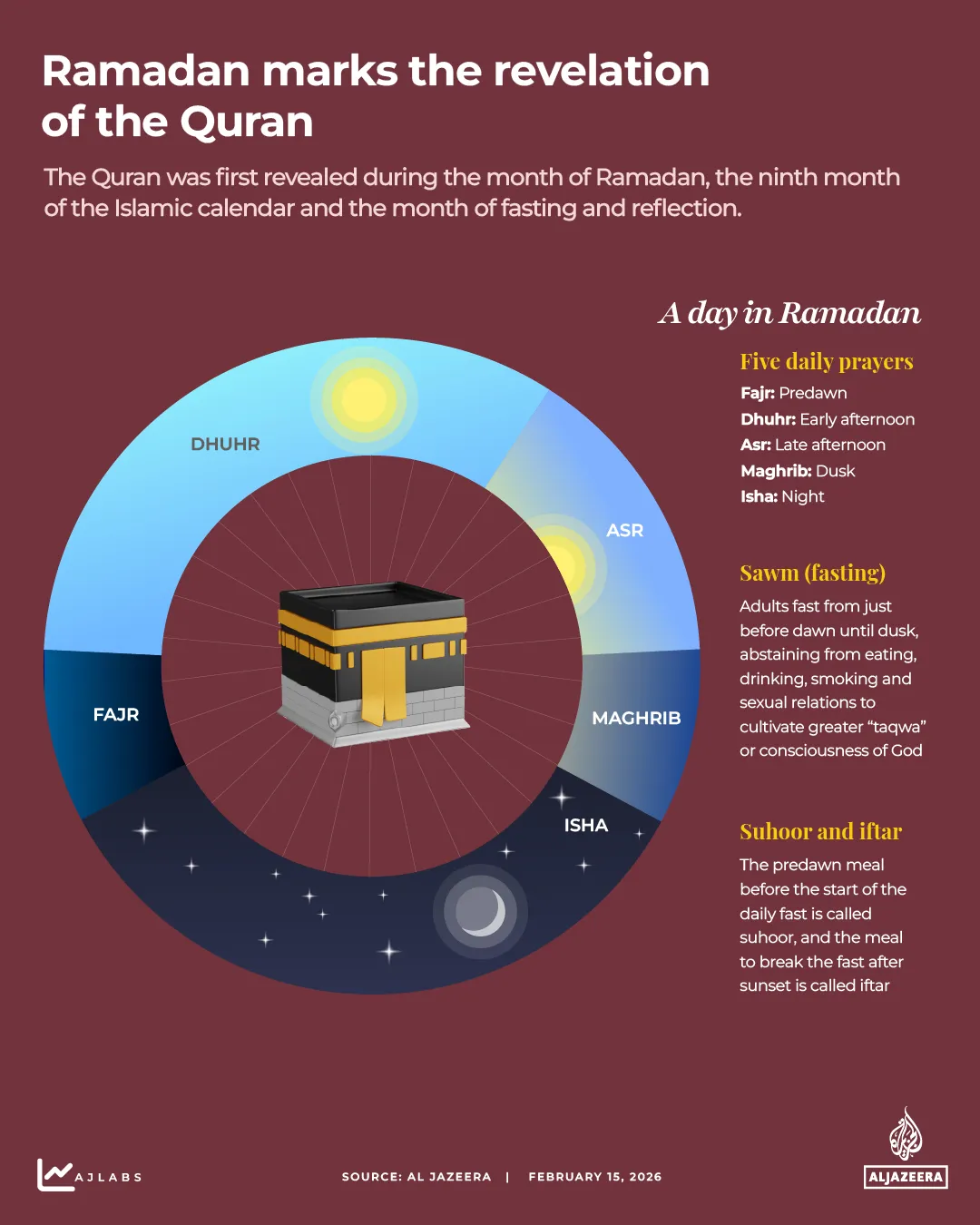
In 1878, William Blackstone, a student of the prominent American evangelist Dwight Moody and a believer in the biblical restoration of Israel, published a book titled Jesus Is Coming. The best-selling work popularised among Americans a belief held by some Christian leaders: that God had given the land of Israel to the Jewish people.
This conviction, often taken from a Protestant evangelical perspective, draws on the ancient biblical idea that, nearly four millennia ago, God promised the land to the Jews, who would rule it until the return of Jesus to Jerusalem for the rapture. According to this theology, Christians will be saved upon Christ’s return while non-Christians who do not convert will face damnation.
The most commonly quoted Bible verse relating to this covenant is Genesis 12:3, in which God tells Abraham: “I will bless those who bless you and I will curse those who curse you and in you all the families of the earth will be blessed,” according to the Religion Media Centre.
According to ChristianZionism.org, a website run by professors, pastors and leaders of church-related organisations, four themes can be found in Christian Zionist thought: One, the founding of today’s nation-state of Israel in 1948 marked the final human era and signals an end of times. Two, the ongoing conflict in the Middle East is a part of God’s plan with a great and final war preceding the second coming of Christ. Three, God’s covenant with Israel is eternal and unconditional. And four, failing to support Israel’s political dominance today will incur divine judgement.
Writer and historian David Swift said that although many Christians – evangelical or otherwise – supported the creation of Israel before 1948, they cannot be called Christian Zionists in the modern parlance.
“This is because Christian Zionism essentially fuses religious belief with a military, strategic and even economic programme,” Swift told Al Jazeera.
“Specifically, Christian Zionism is not just the belief that the biblical land of Israel is the ordained country of the Jewish people but that it is in America’s strategic, military and economic interest to support the expansion of Israel.”
Fathi Nimer, a policy fellow at Al-Shabaka: The Palestinian Policy Network, described the movement as one that “translates into absolute unquestioning support for the Israeli regime”.
He described hearing a podcast about a Christian Zionist woman visiting Bethlehem who, after seeing the separation wall, Israeli soldiers and the harsh conditions in Palestinian refugee camps, remarked: “I feel bad for them, but scripture is scripture.”
“‘Scripture is scripture’ – that overrides everything,” Nimer told Al Jazeera.
“That’s why it’s such a powerful tool for brainwashing.”
How many American Christian Zionists are there?
According to author and academic Tristan Sturm, the largest population of Christian Zionists is in the US, and it numbers more than 30 million. Most are affiliated with evangelical churches in the southeast and south-central regions, often referred to as the “Bible Belt”.
The biggest organisation is Christians United for Israel, which itself boasts 10 million members, Nimer said.
“They are overwhelmingly conservative Republicans, found mostly in the Bible Belt, but also other places in the United States, and they form one of the most formidable voting blocs in the Republican Party,” he said.
Swift stated that only a few million from this group, however, are “fully signed up to the political, military and religious aspects of Christian Zionism”.
What impact do Christian Zionists have on US policy?
Nimer argued that Christian Zionists are “deeply intertwined” with American politics. “A lot of the major donors to the Republican Party and also the Democratic Party are Christian Zionists,” Nimer said.
According to the analyst, Christian Zionists are a cornerstone of Israeli lobbying groups, ranging from the American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC) to the Anti-Defamation League, “that work to spread the Israeli narrative” in American society.
Meanwhile, a lot of members of the US Congress are “openly” Christian Zionist, Nimer said.
“[Politicians like] Mike Huckabee, … they reached the highest echelons of the state. And they bring these beliefs into their politics, into their policies,” the analyst said.
US foreign policy on Israel is, therefore, heavily influenced and shaped around the underlying biblical premise that the Jewish people are divinely destined to be restored to Palestine, he argued.
“When it comes to Palestine and the region in general, as you see right now with the [potential] war in Iran, they’re saying that the ballistic missile programme is now on the table,” Nimer said.
“It has nothing to do with the nuclear deal, … but the idea is that Israel must be able to maintain its superiority over every country in the region, and that’s a decree by God because if Israel prospers, then that’s another step towards the end of the world.”
Christian Zionist groups have also backed Israel’s illegal settlement project in the occupied West Bank and other measures that they see as reinforcing Israeli Jewish sovereignty.
Furthermore, for two decades, organisations such as HaYovel have been bringing in hundreds of American Christian volunteers to work in Israeli settlement agricultural projects, especially during the genocidal war on Gaza, when Jewish Israelis were called for military duty. Many also strongly endorsed US President Donald Trump’s moving of the US embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem in 2017.
Swift, however, said Christian Zionists have played only a minor role in shaping US support for Israel and their influence is waning.
He argued that while Christian Zionism is integrated with a “broader neoconservative foreign policy agenda” also tied to the “US defence industry and broader military-industrial complex”, the group does not have much influence in American politics, and, in fact, it is declining.
Traditionally, US government support for Israel was driven by Cold War considerations and by pressure from the Jewish community within the US and lobbying groups like AIPAC. What played less of a role was support for Israel from evangelical Christians and the smaller community of Christian Zionists, Swift said.
“The US president is finally de facto abandoning the previous theoretical support for a two-state solution – although not for Christian Zionist reasons. When Trump talks of ethnically cleansing Gaza and turning it into a beach resort, he uses the language of real estate, not the Old Testament,” the historian said.
According to the analysts, very representative.
“It is pretty representative: Christian Zionists derive their understanding of the proper borders of Israel from the same place as people like [Israeli National Security Minister] Itamar Ben-Gvir and [Israeli Finance Minister] Bezalel Smotrich: the Old Testament. Therefore, they think Israel should expand to include all of the territory of ‘biblical Israel’,” Swift said, referring to the far-right Israeli cabinet members who have worked to expand and protect Israeli settlements and outposts in the occupied West Bank, which are illegal under international law.
Nimer said Huckabee’s statement is also not something that can be criticised within the Christian Zionist community.
“You’re not allowed to criticise that because it’s like you’re criticising prophecy and you’re criticising God and the return of Jesus,” he said.
Huckabee’s comments, therefore, come as no surprise despite infringing upon the sovereignty of US allies in the Middle East, Nimer said.
On Monday, Smotrich said Israel would eventually occupy the Gaza Strip and establish a Jewish settlement there despite a “ceasefire” that went into effect in October.
“We are giving US President Donald Trump the opportunity to do it in his own way. If he does not succeed in eliminating Hamas, the Israeli army will get international legitimacy and American support to do it,” he said in statements to Israeli radio.
How do Jewish Israelis view Christian Zionists?
Mimi Kirk, the director of the Institute for the Study of Christian Zionism and the associate director of Georgetown University’s Center for Contemporary Arab Studies, writes that “despite the matter of their supposed end-of-times demise according to this view, Jewish Israeli leaders have embraced the money and influence on US foreign policy that Christian Zionists offer,” especially as its adherents include top officials from the first Trump administration, including former Vice President Mike Pence and Secretary of State Mike Pompeo.
Nimer said it’s a rather “cynical relationship”, given that the Christian Zionist worldview, which sees all non-Christians going to hell, is “anti-Semitic to the bone”.
“But they support Israel, so it’s fine,” the policy analyst said.
“They care about what they can get out of them right now as the biggest support base in the West currently.”
Israel is further banking on this support because it is quickly losing its “progressive facade” of a “liberal democracy” with “all these progressive rights”, Nimer added.
“This has completely faded over the last few decades, and especially since the genocide in Gaza, this has become completely unacceptable.”
How do Christians in Palestine view Christian Zionists?
Palestinian Christians have long voiced concern that the Christian Zionist position threatens their existence, further entrenching Israel’s occupation while marginalising their community and undermining the historic churches of the Holy Land.
Just last month, the Patriarchs and Heads of the Churches in Jerusalem said activities by local individuals advancing “damaging ideologies, such as Christian Zionism” “mislead the public, sow confusion, and harm the unity of our flock”.
The Christian leaders warned that these efforts could undermine the Christian presence not only in the Holy Land but across the wider Middle East.
The statement came amid growing concern among Palestinian Christians that Israel’s policies – including land confiscation, settlement expansion and pressure on church property – are accelerating the erosion of one of the world’s oldest Christian communities.
Are there critiques of Christian Zionism among other Christians?
Criticism of Christian Zionists from within Christianity is abundant.
In the US, the Institute for the Study of Christian Zionism was created to critique and combat the movement through liberation theology, seeking justice for Palestinians and a resolution to the ongoing conflict.
Swift pointed out that many of the world’s most Catholic countries, from Ireland to those in South America and Southern Europe, “tend to be quite pro-Palestinian”.
Meanwhile, Palestinian Christian scholars “have written very detailed theological critiques of Christian Zionism”, Nimer said, as have pastors from other parts of the Global South.
A prize awarded by the Nelson Mandela Foundation last year was explicitly aimed at initiatives working against Christian Zionism, and a conference next month in Turkiye is being organised to combat the ideology, Nimer said.
“The world is waking up to how insidious this ideology is and how it creeps into societies and makes it impossible to have any kind of solidarity with Palestinians as long as they believe it,” he said.