Travel experts have named the places you could find yourself at risk – including in Spain, France, Italy, Turkey and Thailand
Holiday season is almost in full swing with just weeks until we hit the peak summer travel window, and millions of people will head from the UK to familiar locations in the sun. Each year we make more than 55million holiday trips abroad, with places like Spain, France, Italy, Greece and Portugal topping the list of destinations.
People from the UK usually travel to familiar locations, believing they will be safe from crime and disease, while shunning places they think may be more ‘trouble’. But travel experts have warned some of the most familiar spots are actually the most dangerous – where you are most likely to experience things like becoming a victim of crime.
Those destinations include familiar favourites such as Spain, France, Italy and Turkey.
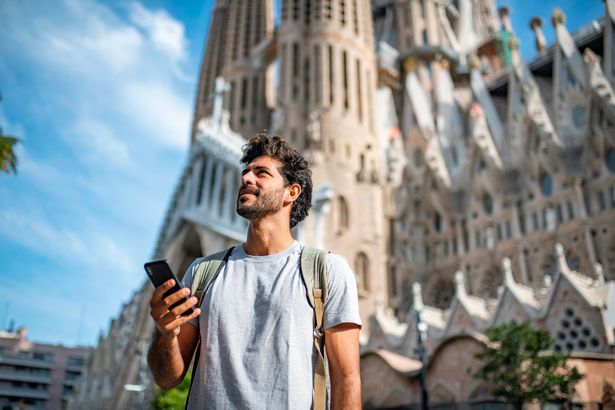
Diana Peng from Just Wanderlust said: “Places that are regarded as safe but aren’t include popular places such as Paris and Barcelona. I’ve heard so many horror stories from travelers to those cities and I’ve also been the target of crime in those cities – it is rampant and yet, it’s barely discussed.
“Groups of pickpockets and scammers frequently work the tourist crowds in these popular cities. They are also easy targets: preoccupied, lost, or trying to get photos more so than paying attention to their surroundings.”
Patrick Farrell of Viceroy Bali added: “Regions like Cancun and Acapulco in Mexico make me think they are safe, when in fact, they are not. I have received clients who booked luxury wellness retreats there, only for them to experience unforeseen safety concerns outside the resort areas.
“Furthermore, cities like Paris and Barcelona are pretty in their own right, but they do pose some level of safety concern. The two cities have a high risk of pickpocketing and scamming tourists. My advice always is to look at government-issued travel advisories, and talking to someone who knows the city is very useful.”
Ross Thompson at Covac Global said: “Places like Naples, Italy and Tokyo, Japan sit on massive seismic and geologic risks. Naples sits near Mt Vesuvius which is an active volcano that last erupted in 1944. While it’s closely monitored it sits near a highly dense population and is closely monitored for a reason.
“Tokyo sits on a major seismic zone where an earthquake or tsunami can strike not only Tokyo but many other highly visited Japanese cities without warning causing massive destruction.”
He added: “Hidden risks can manifest politically, even if they say it is welcoming to Western tourists, they may have less noted political or civil strife either internally or externally. Think about the attempted coup in Turkey in 2016 where the opposition actually seized airports, bridges and media entities and both tanks and fighter jets filled the cities and skies.”
Ross also warned about ‘kidnapping in Mexico’s most popular cities’ and the risk of illness in Western Africa, Thailand and Brazil.
He highlighted Bali in Indonesia as a particular risk – surrounded by active volcanoes, at threat of political upheaval and home to ‘a host of exotic diseases including Dengue Fever, Malaria and Typhoid’
He said: “And when disaster does strike – you’re on an island and you and everyone else wants out.”
Christian Petzold, travel expert at BCN Travel, said: “Mexico is the proverbial example. Cities like Cancun, Playa del Carmen, and Tulum are tourist havens: splendour and creation in concert. Yet, in the past few years, intermittent conflicts of criminal gangs have touched even these sanctuaries of tourism, some directly in the proximity of tourist zones.”
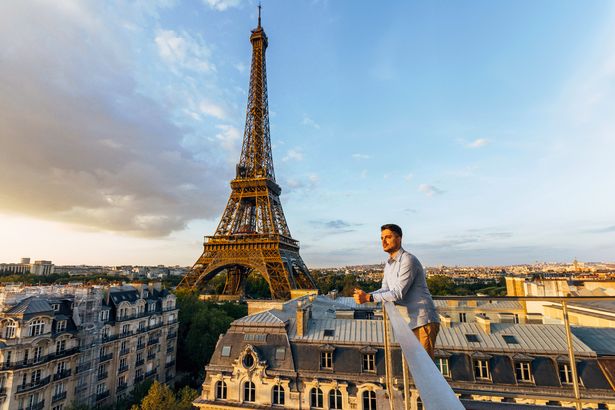
He added: “Paris, on the other hand, although arguably one of the most visited cities, is known for petty crimes around Gare du Nord, Montmartre, and near the Eiffel Tower. Pickpocketing is almost a fine art there, whereas protests and strikes disrupt transport and city services with unpredictability. I always recommend guests carry crossbody bags, beware of strangers who get too friendly too fast, and keep eyes and ears open for local news updates.
“Rome has a similar ambience. Whereas it is rich in history and culture, Termini Station and some venues near the Vatican attract scams and thefts: from fake helpful locals to those touting friendship bracelets or petitions, the usual distraction-and-robbery routine.
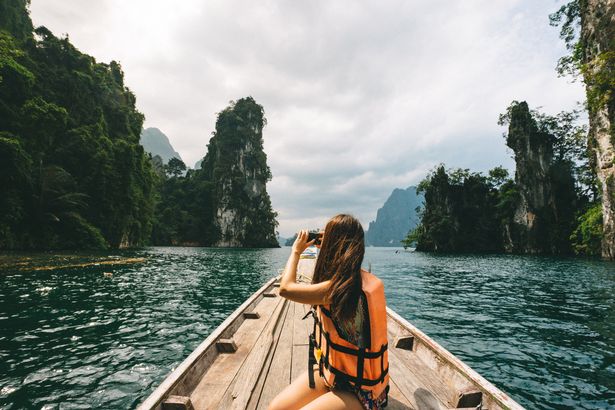
“Thailand poses a curious case. Generally safe and world-renowned for hospitality, guests should be wary of certain transportation modes, especially tuk-tuks and motorbike taxis, which are often unregulated. Some islands like Koh Tao have been in the spotlight due to a string of deaths of tourists that went unsolved amidst rumblings of local corruption. When it comes to political differences in Bangkok, protests tend to escalate relatively quickly, thereby promptly throwing an alienated tourist into the midst of demonstrations.”
How to stay safe on a foreign holiday
Staying safe on a foreign holiday involves a mix of preparation, awareness, and common sense. Here’s the best advice broken down into key areas:
Before You Go
- Research the Destination Check travel advice from the UK Foreign Office: gov.uk/foreign-travel-advice. Understand local laws, customs, and any safety concerns (crime, weather, political instability, etc.).
- Get Travel Insurance Make sure it covers health emergencies, cancellations, theft, and adventure activities if applicable.
- Copies of Important Documents Keep digital and printed copies of your passport, travel insurance, visa, and emergency contacts.
While You’re There
- Stay Aware of Your Surroundings Avoid walking alone at night in unfamiliar or poorly lit areas. Be cautious of pickpockets, especially in crowded places (tourist hotspots, public transport).
- Protect Your Valuables Use a money belt or hidden pouch. Leave expensive jewellery and unnecessary tech at home or in a safe.
- Use Reliable Transport Use official taxis, ride apps (e.g., Uber), or public transport where safe. Don’t hitchhike.
- Be Cautious with Alcohol Drink in moderation and never leave drinks unattended. Avoid accepting drinks from strangers.
- Local Laws and Etiquette Respect dress codes, especially in religious or conservative areas. Know what’s illegal – e.g., vaping in Thailand, chewing gum in Singapore.
Health & Emergency
- Know Emergency Numbers Not all countries use 112 or 999. Look up the local emergency number.
- Medications Bring enough prescribed medication with a copy of your prescription. Check if your medication is legal in your destination country.
- Vaccinations & Health Risks Visit a travel clinic for any necessary jabs or malaria tablets.
- Avoid Unsafe Food/Water In higher-risk areas, stick to bottled water and avoid street food that isn’t freshly cooked.
Tech & Communication
- Stay Connected Get a local SIM or roaming plan. Share your itinerary and daily check-ins with someone back home.
- Download Essential Apps Maps, translation, local transport, embassy locator, travel insurance app.