Control, choke points: The battle lines in southern Sudan | Sudan war News
Recent battlefield gains by the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) may turn the tide in Kordofan, analysts have told Al Jazeera.
Sudan’s devastating war between the SAF and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) has raged for two and a half years, resulting in massive displacement and the world’s worst humanitarian crisis, according to the United Nations.
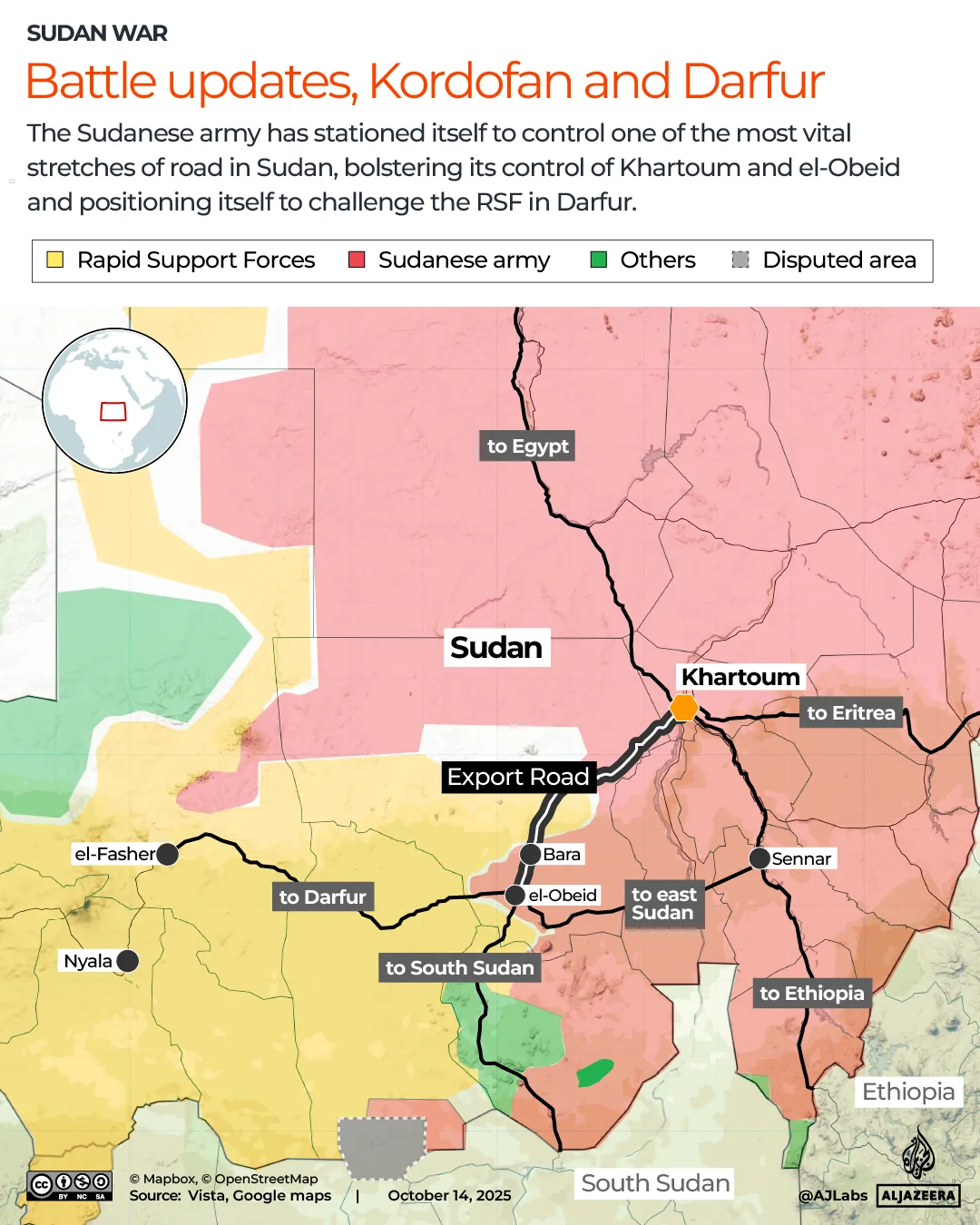
Yet SAF’s capture in September of the strategic city of Bara, which the RSF was using for logistics, supplies, and as a muster point for reinforcements, is seen as a sign that SAF may have swung the pendulum in its favour.
Why is Bara important?
Bara lies about 350km (217 miles) southwest of the capital Khartoum along the “Export Road” used to truck goods from Khartoum to el-Obeid, capital of North Kordofan State.
It also exports its own agricultural products and livestock to the rest of Sudan.
The Khartoum-el-Obeid connection is vital because from el-Obeid, roads lead outwards to South Sudan and Sudan’s east and Darfur in the west.
From Khartoum, roads lead northeast to Port Sudan on the Red Sea, where the wartime government was until recently. Roads also lead north to Egypt and east to Eritrea and Ethiopia.
SAF took el-Obeid in February, after a two-year RSF siege, and took Khartoum in March, so taking Bara gave it solid control over the Export Road to use as a supply route, independent Sudanese military and political analyst Akram Ali told Al Jazeera.

Bara and el-Obeid lie near the westernmost reaches of SAF control, well to the east of el-Fasher, the capital of North Darfur and the last city SAF holds in the vast western region. Between the two is a stretch of RSF control – and siege on el-Fasher – that SAF has to breach.
For the RSF, keeping Bara and a foothold in Kordofan was important because it allowed it to put pressure on SAF, which holds territory to the north, and to link the areas it controls in Kordofan and Darfur to South Sudan, links it uses to move weapons and fighters.
How did SAF take Bara?
The army launched an offensive on Bara from the south on September 11, while RSF defences were concentrated on the eastern side, analyst Abdul Majeed Abdul Hamid said.
SAF sent continuous drone strikes against RSF targets, then launched the Darfur Track Armed Struggle Movement, an assault force known for mobility and speed, from el-Obeid.
The force successfully engaged and defeated the RSF unit defending Bara, then entered the city with heavy firepower, according to a military officer who spoke on condition of anonymity.
The officer said the operation relied on speed and keeping the RSF occupied on several fronts to prevent it from sending reinforcements.
Most of Bara’s civilians supported SAF, according to Abdul Hamid, and the RSF quickly retreated.
The operation cut off RSF supply and military support lines, he added, isolating their remaining positions in areas such as al-Khuwei to the west and al-Nahud to the east.
For the RSF, keeping Bara and a foothold in Kordofan was important because it allowed it to put pressure on SAF, which holds territory to the north, and to link the areas it controls in Kordofan and Darfur to South Sudan, links it uses to move weapons and fighters.
Losing Bara also meant that the RSF could no longer keep the city of el-Obeid under siege.
Will the RSF lose the Kordofans?
The RSF announced in February this year that it had entered an alliance with the Southern People’s Liberation Movement-North (SPLM-N). South Kordofan includes the Abyei region, disputed between Sudan and South Sudan. The SPLM-N controls the vast, isolated Nuba Mountains region in South Kordofan, right up against the border with South Sudan.
However, despite that new stronghold, analysts told Al Jazeera that losing control over the Export Road spells a serious deterioration in the RSF’s power in the Kordofans.
“The army’s entry into el-Obeid marked the beginning of their actual collapse,” said Ali.
![Widespread disease outbreak overwhelms hospitals in war-torn Sudan [Screengrab/Al Jazeera]](https://www.aljazeera.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Screenshot-2025-09-23-at-11.47.58-AM-1758617507.png?w=770&resize=770%2C509&quality=80)
An army unit called “Al-Sayyad” – named after a commander killed in the early days of the war – had moved from Rabak, capital of White Nile State, in a campaign that eventually reached el-Obeid.
Political analyst Ahmed Shamukh said liberating Bara opens the door to reactivating the SAF air base in el-Obeid, the largest in Kordofan, after two years of inactivity, “significantly [enhancing] the logistical and combat capabilities of the Sudanese army” and helping SAF’s campaign to expel RSF from the Kordofans.
Taking back all of Kordofan would allow SAF to work towards liberating Darfur, Abdul Hamid said.
“The army has combat experience and personnel capable of liberating Kordofan with the same capabilities it used to retake the cities of central Sudan and the capital,” Abdul Hamid continued.
The war has killed tens of thousands of people and displaced more than 10 million in what has become the world’s largest humanitarian crisis.
According to the UN, a total of 24.6 million people face acute food insecurity, while 19 million people lack access to safe water and sanitation.