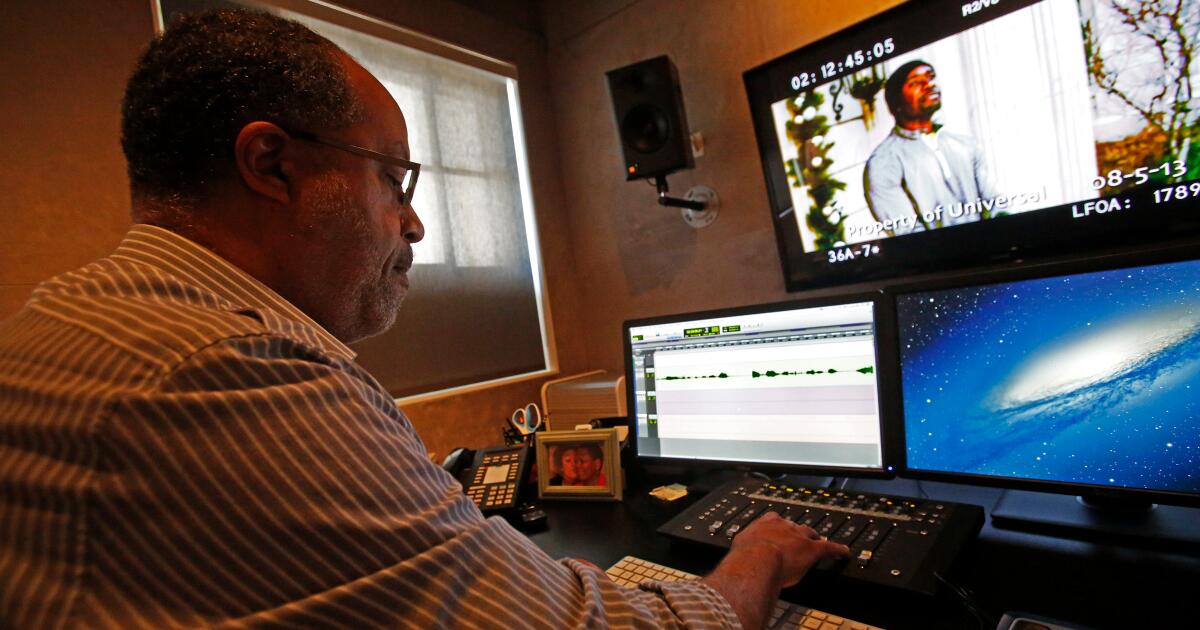
Workers restore the Philadelphia President’s House slavery exhibit

The names of nine former slaves owned by George Washington appear at the President’s House in Philadelphia, where workers continued restoring a slavery exhibit on Thursday. Photo by Joseph E.B. Elliott/National Park Service
Feb. 19 (UPI) — Workers are restoring a slavery exhibit at the site of the nation’s first presidential mansion in Philadelphia ahead of a Friday deadline to do so.
U.S. District Court of Eastern Pennsylvania Judge Cynthia Rufe on Monday ordered the Interior Department to restore the exhibit, which was removed in January amid the Trump administration’s anti-DEI policy.
The exhibit features nine panel illustrations of nine slaves, whom President George Washington brought with him to the mansion while serving as president.
Rufe likened the slavery exhibit’s removal to author George Orwell‘s novel “1984” and said the exhibit supports “historic truths,” The Hill reported.
The Trump administration on Wednesday filed a motion to stay Rufe’s order to reinstate the exhibit, but workers began reinstalling it on Tuesday.
Philadelphia Mayor Cherelle Parker welcomed the change and vowed to oppose efforts to remove the exhibit.
“Today, we celebrate the return of our history at this important site,” Parker said in a post on X. “We are thankful for all the supporters across the city to get us to this point.”
Parker said the legal challenges have not ended and said they will be handled with “rigor and gravity” as they arise.
The exhibit features panels depicting slavery in the United States from the time of the Revolutionary War through the Civil War and the eventual outlawing of slavery upon the ratification of the 13th Amendment.
The President’s House formerly was the official residence for Presidents George Washington and John Adams when Philadelphia was the nation’s capital and is located at the corner of 6th and Market streets.
Adams did not own slaves, which is why the panels focus on Washington’s ownership and use of slaves while living at the presidential home.
The house was demolished 32 years after the nation’s capital moved to Washington in 1800, but its foundation and footprint remain.
The site been converted into an outdoor exhibit that features the dichotomy of slavery in a nation that was founded on the principles of freedom and equality and is managed by the National Park Service.