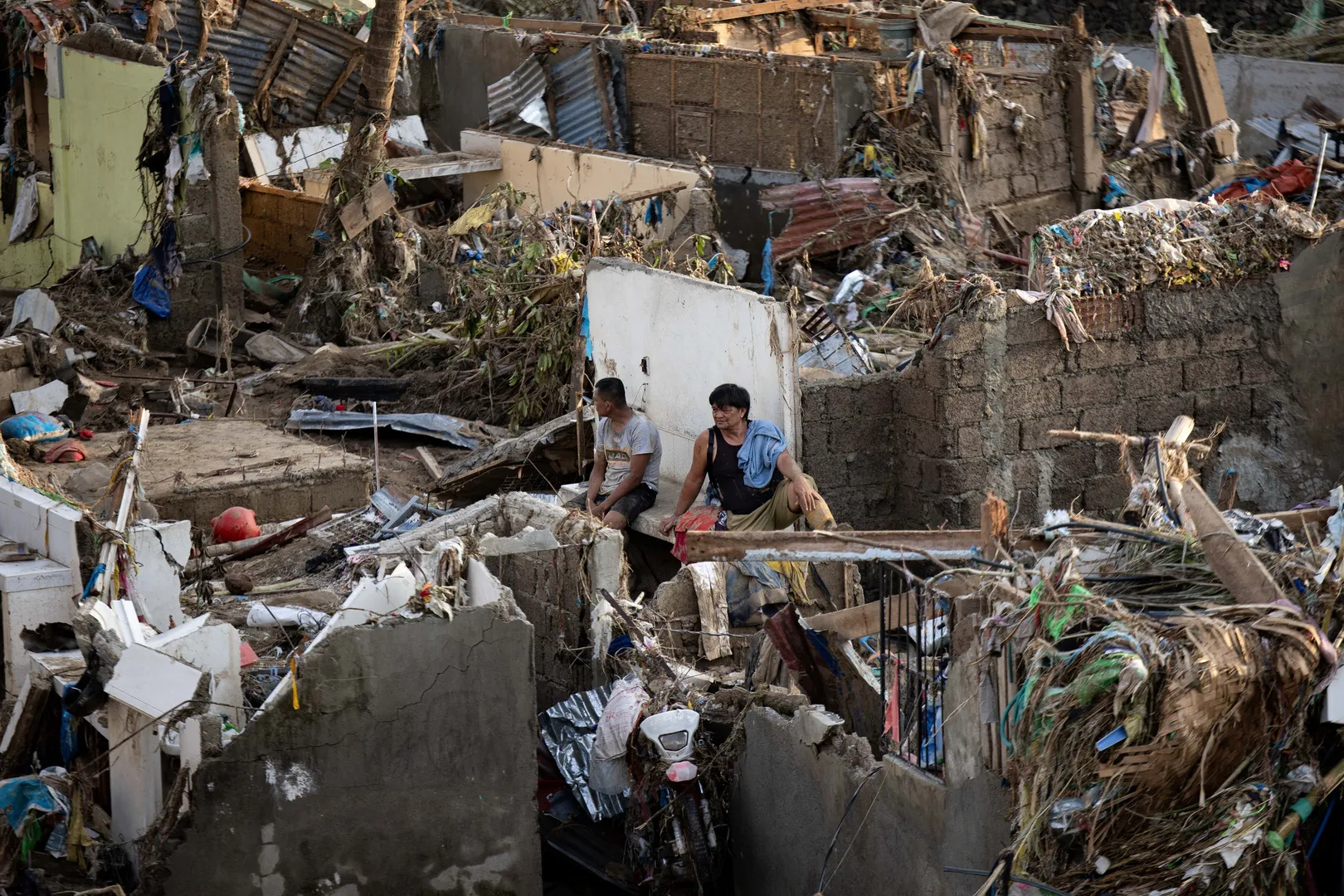Philippines reeling from deadly floods triggered by Typhoon Kalmaegi | Infrastructure
Heavy flooding in Talisay City, Cebu has destroyed homes after Typhoon Kalmaegi dumped a month’s worth of rain. One person died in a low-income area that evacuated early, while dozens may be trapped in a nearby subdivision where residents did not leave. Al Jazeera’s Barnaby Lo is there.
Published On 6 Nov 2025