Seoul stocks rally over 2 pct to land at fresh record high above 5,900 on tech rally

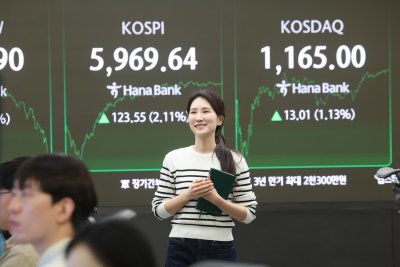
The Korea Composite Stock Price Index (KOSPI), shown on a screen in the trading room at Hana Bank in Seoul, topped a record-high 5,000 on Tuesday. Photo by Yonhap
Seoul shares surged more than 2 percent Tuesday to close at a fresh record high above the 5,900-point mark, driven by strong gains in technology shares. The Korean won fell against the U.S. dollar.
The benchmark Korea Composite Stock Price Index (KOSPI) advanced 123.55 points, or 2.11 percent, to finish at an all-time high of 5,969.64.
The index has extended its upward momentum in recent weeks, surpassing the 5,000-point mark for the first time on Jan. 27 and crossing 5,500 on Feb. 12. It moved above 5,800 on Friday.
Trading volume was heavy at 1.58 billion shares worth 30.73 trillion won (US$21.3 billion), with decliners outnumbering gainers 465 to 407.
Institutions bought a net 2.37 trillion won worth of stocks, offsetting net sales of 199.16 billion won by foreign investors and 2.28 trillion won by retail investors.
The rally came despite overnight losses on Wall Street.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 1.66 percent, and the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite declined 1.13 percent.
In Seoul, investors scooped up major chip stocks ahead of an earnings report from U.S. chipmaker Nvidia later this week, while remaining cautious over U.S. President Donald Trump‘s push to impose new tariffs after the Supreme Court struck down his original sweeping duties, analysts said.
Trump signed an executive order Friday (U.S. time) authorizing new 10 percent global tariffs that took effect Tuesday. He has also threatened to raise the rate to 15 percent, though no formal order has been issued.
“Even if the global tariffs are raised to 15 percent, there will be no major impact on the local stock market because current U.S. tariffs on Korean imports already stand at 15 percent,” an analyst at IBK Securities Co. said.
Technology and automobile stocks led the gains.
Market bellwether Samsung Electronics jumped 3.63 percent to 200,000 won, while chip giant SK hynix surged 5.68 percent to a record high of 1,005,000 won.
Top automaker Hyundai Motor rose 0.19 percent to 524,000 won, and leading battery maker LG Energy Solution gained 4.17 percent to 412,500 won.
Among decliners, shipbuilder Hanwha Ocean fell 2.79 percent to 143,100 won, and Lotte Shopping declined 1.67 percent to 111,700 won.
The Korean won was quoted at 1,442.50 won against the U.S. dollar at 3:30 p.m., down 2.5 won from the previous session.
Bond prices, which move inversely to yields, closed lower. The yield on three-year Treasurys rose 0.4 basis point to 3.158 percent, and the return on the benchmark five-year government bonds also climbed 0.5 basis point to 3.410 percent.
Copyright (c) Yonhap News Agency prohibits its content from being redistributed or reprinted without consent, and forbids the content from being learned and used by artificial intelligence systems.