From blackouts to food shortages: How US blockade is crippling life in Cuba | Explainer News
A US oil blockade is causing a severe energy crisis in Cuba, as the government has been forced to ration fuel and cut electricity for many hours a day, paralysing life in the communist-ruled island nation of 11 million.
Bus stops are empty, and families are turning to wood and coal for cooking, living through near-constant power outages amid an economic crisis worsened by the Trump administration’s steps in recent weeks.
President Miguel Diaz-Canel has imposed harsh emergency restrictions – from reduced office hours to fuel sales – in the backdrop of looming threats of regime change from the White House.
The Caribbean region has been on edge since the US forces abducted Venezuela’s President Nicolas Maduro last month and upped the pressure to isolate Havana and strangle its economy. Venezuela, Cuba’s closest ally in the region, provided the country with the much-needed fuel.
So, how dire is the situation in Cuba? What does United States President Donald Trump want from Havana? And how long can Cuba sustain?

What are Cuba’s emergency measures?
Blaming the US for the crisis, Cuba’s Deputy Prime Minister Oscar Perez‑Oliva Fraga appeared on state television on Friday to inform the millions of the emergency steps “to preserve the country’s essential functions and basic services while managing limited fuel resources”.
Now, the Cuban state companies will shift to a four‑day workweek, with transport between provinces dialled down, main tourism facilities closed, shorter schooldays and reduced in‑person attendance requirements at universities.
“Fuel will be used to protect essential services for the population and indispensable economic activities,” said Perez-Oliva. “This is an opportunity and a challenge that we have no doubt we will overcome. We are not going to collapse.”
The government says it will prioritise available fuel for essential services – public health, food production and defence – and push the installation of solar-based renewable energy sector and incentives therein. It will prioritise shifting energy to selected food production regions and accelerate the use of renewable energy sources, while cutting down on culture and sport activities and diverting resources towards the country’s early warning systems.

Why has the US blocked oil to Cuba?
Decades of strict US economic sanctions against Cuba, the largest island nation in the Caribbean, have destroyed its economy and isolated it from international trade. Cuba relied on foreign allies for oil shipments, such as Mexico, Russia, and Venezuela.
However, after the US forces abducted Venezuelan President Maduro, Washington blocked any Venezuelan oil from going to Cuba. Trump now says the Cuban government is ready to fall.
Under Trump, Washington has pivoted to the Western Hemisphere, which it wants to dominate. The military actions in Venezuela, the pledge to take over Greenland and changing the government in Cuba are part of the new policy.
Last month, Trump signed an executive order – labelling Cuba a threat to national security – imposing tariffs on any country that sells or provides oil to the island nation. Further pressure on the Mexican government reportedly led to oil stocks reaching a record low in Cuba.
“It looks like it’s something that’s just not going to be able to survive,” Trump told reporters last month, when questioned about the Cuban economy. “It is a failed nation.”
Havana has rejected accusations that it poses a threat to US security. Last week, the Cuban Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement calling for dialogue.
“The Cuban people and the American people benefit from constructive engagement, lawful cooperation, and peaceful coexistence. Cuba reaffirms its willingness to maintain a respectful and reciprocal dialogue, oriented toward tangible results, with the United States government, based on mutual interest and international law,” a statement from the ministry said on February 2.
Trump’s goals in Cuba remain unclear; however, US officials have noted on multiple occasions that they would like to see the government change.
Responding to a question during a US Senate hearing on Venezuela, Secretary of State Marco Rubio said, “We would like to see the regime there change. That doesn’t mean that we’re going to make a change, but we would love to see a change.”
Rubio, who is of Cuban descent, is one of the most powerful figures in Trump’s administration.
“The Cuban-American lobby, which Rubio represents, is one of the most powerful foreign policy lobbies in the United States today,” Ed Augustin, an independent journalist in Havana, told Al Jazeera’s The Take.
“In the new Trump administration, [with] an unprecedented number of Cuban Americans, the lobbyists have become the policymakers,” he said, adding that Rubio has built firm control over the lobby.
On January 31, Trump told reporters, “It doesn’t have to be a humanitarian crisis. I think they probably would come to us and want to make a deal. So Cuba would be free again.”
He said Washington would make a deal with Cuba, but offered no clarity on what that means.

History of US-Cuba relations
Since Fidel Castro overthrew the pro-US regime in the Cuban revolution in 1959, the country has been under US embargo. Decades of sanctions have denied Cuba access to global markets, making even supply medicines difficult.
Castro nationalised US-owned properties, mainly the oil sector, and Washington responded with trade restrictions that soon became a full economic embargo that continues to this day, undermining Cuba’s economy.
The US also cut diplomatic ties with Havana, and three years later, a missile crisis almost brought Washington and the erstwhile USSR, an ally of Cuba, to the brink of nuclear war.
In 2014, Washington and Havana restored ties after 50 years. Two years later, US President Barack Obama travelled to Havana to meet Raul Castro.
However, during his first term as president, Trump reversed the historic move in 2017. Since then, the US has reimposed a raft of sanctions against Cuba, especially economic restrictions, leading to one of the worst economic crises in the island nation’s history. Within hours of his inauguration in January 2025, Trump reversed the previous administration’s policy of engagement with Havana.

How long can Cuba sustain?
Until last month, Mexico reportedly remained Cuba’s major oil supplier, sending nearly 44 percent of total oil imports, followed by Venezuela at 33 percent, while nearly 10 percent was sourced from Russia and a smaller amount from Algeria.
According to Kpler, a data company, by January 30, Cuba was left with oil enough to last only 15 to 20 days at current levels of demand.
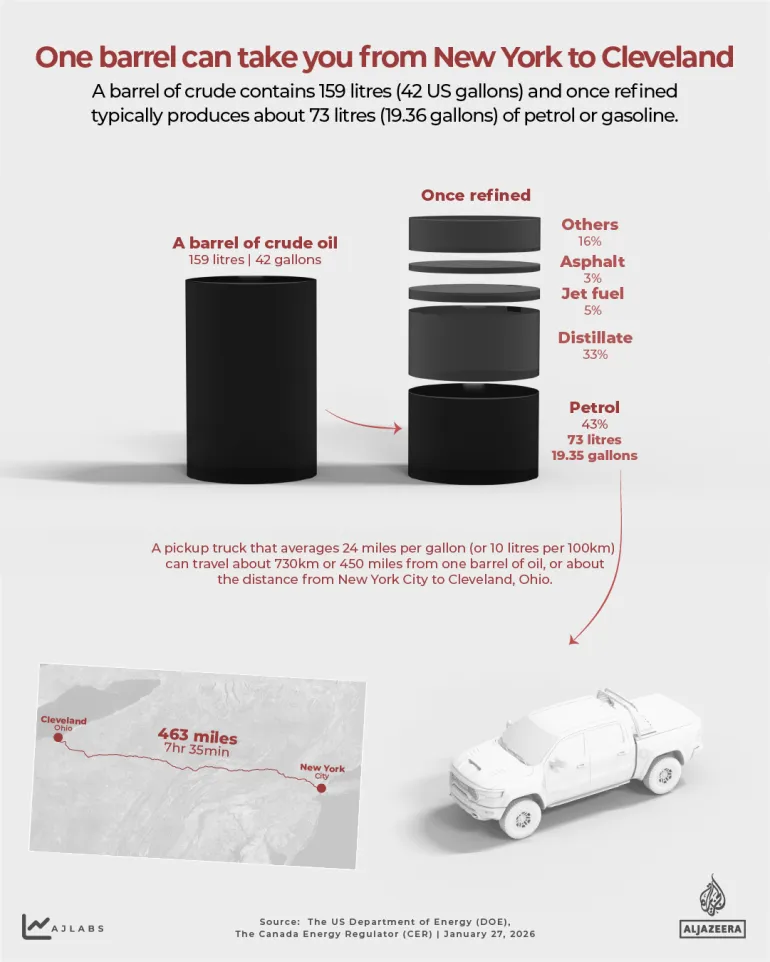
Cuba currently needs an estimated 100,000 barrels of crude oil per day.

What has the UN said about the Cuban crisis?
United Nations spokesperson Stephane Dujarric told reporters on Wednesday that “the secretary-general is extremely concerned about the humanitarian situation in Cuba, which will worsen, and if not collapse, if its oil needs go unmet”.
Dujarric said, for more than three decades, the UN General Assembly has consistently called for an end to the embargo imposed by the US on Cuba, adding that the UN urges “all parties to pursue dialogue and respect for international law”.
Francisco Pichon, the senior-most UN official in Cuba, described “a combination of emotions” in the country – “a mix of resilience, but also grief, sorrow and indignation, and some concern about the regional developments”.
The UN team in Havana says the vast majority of Cubans are hit by rolling blackouts, with the number of people in vulnerable situations increasing significantly.
“The last two years have been quite tough,” Pichon said, adding that urgent changes are needed to sustain Cuba “in the midst of the severe economic, financial and trade sanctions”.