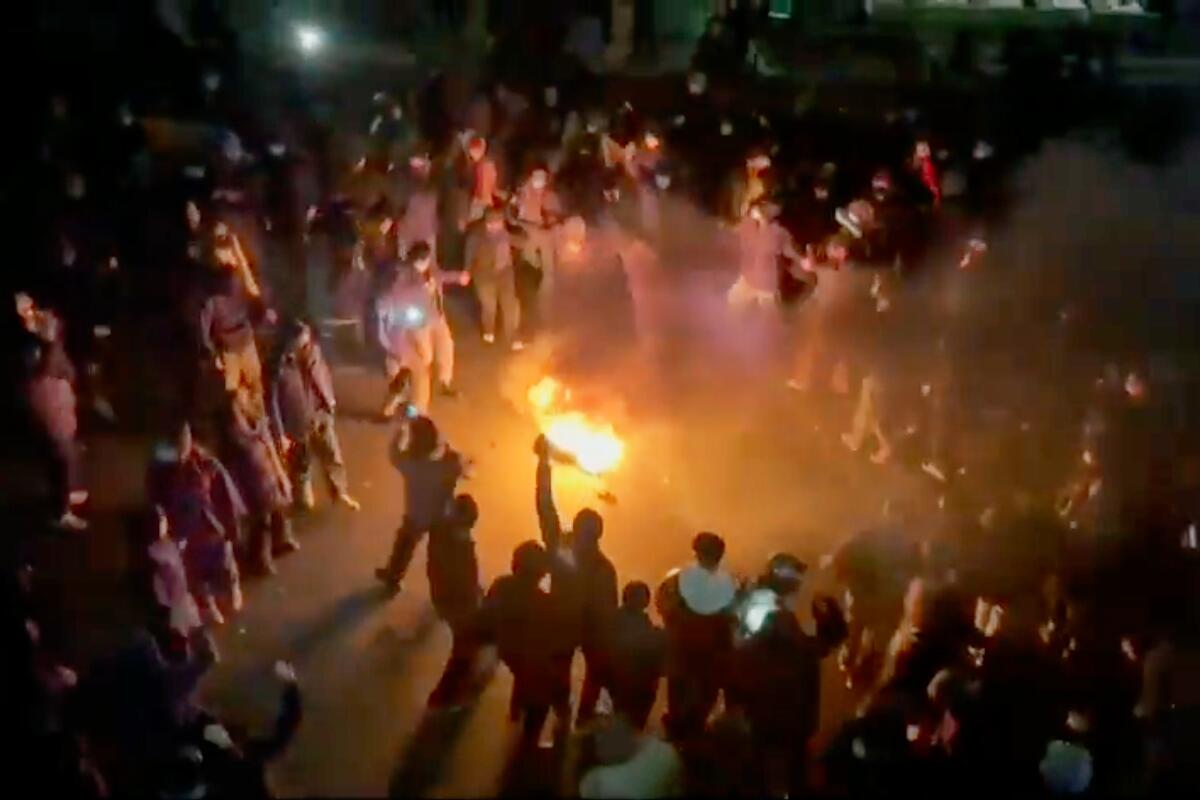Why Iran resists giving up its nuclear program, even as Trump threatens strikes
Embassy staffers and dependents evacuating, airlines suspending service, eyes in Iran warily turning skyward for signs of an attack.
The prospects of a showdown between the U.S. and Iran loom ever higher, as massive American naval and air power lies in wait off Iran’s shores and land borders.
Yet little of that urgency is felt in Iran’s government. Rather than quickly acquiescing to President Trump’s demands, Iranian diplomats persist in the kind of torturously slow diplomatic dance that marked previous discussions with the U.S., a pace that prompted Trump to declare on Friday that the Iranians were not negotiating in “good faith.”
But For Iran’s leadership, Iranian experts say, concessions of the sort Trump are asking for about nuclear power and the country’s role in the Middle East undermine the very ethos of the Islamic Republic and the decades-old project it has created.
“As an Islamic theocracy, Iran serves as a role model for the Islamic world. And as a role model, we cannot capitulate,” said Hamid Reza Taraghi, who heads international affairs for Iran’s Islamic Coalition Party, or Hezb-e Motalefeh Eslami.
Besides, he added, “militarily we are strong enough to fight back and make any enemy regret attacking us.”
Even as another round of negotiations ended with no resolution this week, the U.S. has completed a buildup involving more than 150 aircraft into the region, along with roughly a third of all active U.S. ships.
Observers say those forces remain insufficient for anything beyond a short campaign of a few weeks or a high-intensity kinetic strike.
Iran would be sure to retaliate, perhaps against an aircraft carrier or the many U.S. military bases arrayed in the region. Though such an attack is unlikely to destroy its target, it could damage or at least disrupt operations, demonstrating that “American power is not untouchable,” said Hooshang Talé, a former Iranian parliamentarian.
Tehran could also mobilize paramilitary groups it cultivated in the region, including Iraqi militias and Yemen’s Houthis, Talé added. Other U.S. rivals, such as Russia and China, may seize the opportunity to launch their own campaigns elsewhere in the world while the U.S. remains preoccupied in the Middle East, he said.
“From this perspective, Iran would not be acting entirely alone,” Tale said. “Indirect alignment among U.S. adversaries — even without a formal alliance — would create a cascading effect.”
We’re not exactly happy with the way they’re negotiating and, again, they cannot have nuclear weapons
— President Trump
The U.S. demands Iran give up all nuclear enrichment and relinquish existing stockpiles of enriched uranium so as to stop any path to developing a bomb. Iran has repeatedly stated it does not want to build a nuclear weapon and that nuclear enrichment would be for exclusively peaceful purposes.
The Trump administration has also talked about curtailing Iran’s ballistic missile program and its support to proxy groups, such as Hezbollah, in the region, though those have not been consistent demands. Tehran insists the talks should be limited to the nuclear issue.
After indirect negotiations on Thursday, Oman’s Foreign Minister Badr al-Busaidi — the mediator for the talks in Geneva — lauded what he said was “significant progress.” Iranian Foreign Ministry spokesman Esmail Baghaei said there had been “constructive proposals.”
Trump, however, struck a frustrated tone when speaking to reporters on Friday.
“We’re not exactly happy with the way they’re negotiating and, again, they cannot have nuclear weapons,” he said.
Trump also downplayed concerns that an attack could escalate into a longer conflict.

This frame grab from footage circulating on social media shows protesters dancing and cheering around a bonfire during an anti-government protest in Tehran, Iran, on Jan. 9.
(Uncredited / Associated Press)
“I guess you could say there’s always a risk. You know, when there’s war, there’s a risk in anything, both good and bad,” Trump said.
Three days earlier, in his State of the Union address Tuesday, said, “My preference is to solve this problem through diplomacy. But one thing is certain, I will never allow the world’s number one sponsor of terror, which they are by far, to have a nuclear weapon — can’t let that happen.”
There are other signs an attack could be imminent.
On Friday, the U.S. Embassy in Israel allowed staff to leave the country if they wished. That followed an earlier move this week to evacuate dependents in the embassy in Lebanon. Other countries have followed suit, including the U.K, which pulled its embassy staff in Tehran. Meanwhile, several airlines have suspended service to Israel and Iran.
A U.S. military campaign would come at a sensitive time for Iran’s leadership.
The country’s armed forces are still recovering from the June war with Israel and the U.S, which left more than 1,200 people dead and more than 6,000 injured in Iran. In Israel, 28 people were killed and dozens injured.
Unrest in January — when security forces killed anywhere from 3,000 to 30,000 protesters (estimates range wildly) — means the government has no shortage of domestic enemies. Meanwhile, long-term sanctions have hobbled Iran’s economy and left most Iranians desperately poor.
Despite those vulnerabilities, observers say the U.S. buildup is likely to make Iran dig in its heels, especially because it would not want to set the precedent of giving up positions at the barrel of a U.S. gun.
Other U.S. demands would constitute red lines. Its missile arsenal, for example, counts as its main counter to the U.S. and Israel, said Rose Kelanic, Director of the Middle East Program at the Defense Priorities think tank.
“Iran’s deterrence policy is defense by attrition. They act like a porcupine so the bear will drop them… The missiles are the quills,” she said, adding that the strategy means Iran cannot fully defend against the U.S., but could inflict pain.
At the same time, although mechanisms to monitor nuclear enrichment exist, reining in Tehran’s support for proxy groups would be a much harder matter to verify.
But the larger issue is that Iran doesn’t trust Trump to follow through on whatever the negotiations reach.
After all, it was Trump who withdrew from an Obama-era deal designed to curb Iran’s nuclear ambitions, despite widespread consensus Iran was in compliance.
Trump and numerous other critics complained Iran was not constrained in its other “malign activities,” such as support for militant groups in the Middle East and development of ballistic missiles. The Trump administration embarked on a policy of “maximum pressure” hoping to bring Iran to its knees, but it was met with what Iran watchers called maximum resistance.
In June, he joined Israel in attacking Iran’s nuclear facilities, a move that didn’t result in the Islamic Republic returning to negotiations and accepting Trump’s terms. And he has waxed wistfully about regime change.
“Trump has worked very hard to make U.S. threats credible by amassing this huge military force offshore, and they’re extremely credible at this point,” Kelanic said.
“But he also has to make his assurances credible that if Iran agrees to U.S. demands, that the U.S. won’t attack Iran anyway.”
Talé, the former parliamentarian, put it differently.
“If Iranian diplomats demonstrate flexibility, Trump will be more emboldened,” he said. “That’s why Iran, as a sovereign nation, must not capitulate to any foreign power, including America.”