HumAngle Foundation Holds Roundtable with Plateau Peacebuilding Actors
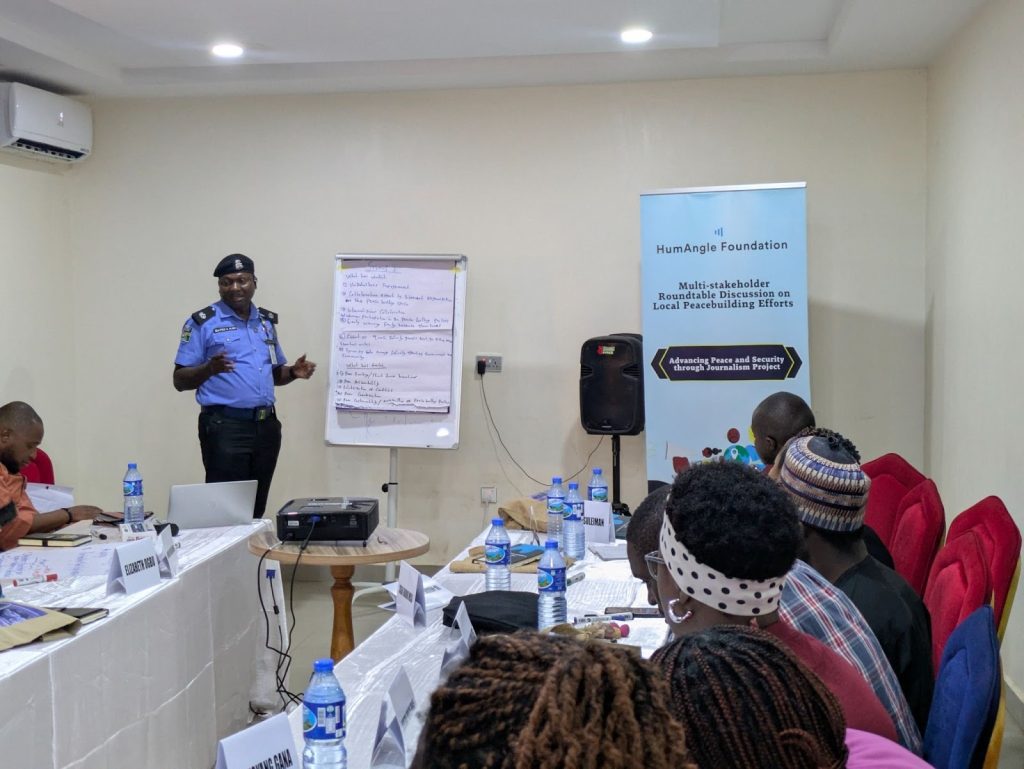
HumAngle Foundation, a sister organisation of HumAngle Media, has convened 17 peacebuilding actors, including civil society organisations, government institutions, and security agencies, for a two-day multi-stakeholder roundtable on local peacebuilding efforts in Plateau State, North Central Nigeria.
The roundtable, supported by the National Endowment for Democracy (NED), was held from February 5 to 6 in Jos, the Plateau State capital. It forms part of the Advancing Peace and Security through Journalism (APSJ) Project, launched by the Foundation in 2024 to strengthen the technological capacity of journalists and community-based organisations to promote peacebuilding, accountability, and good governance in conflict-affected areas.
Plateau State has, for decades, experienced recurrent communal violence driven by a complex mix of farmer–herder tensions, identity-based disputes, land ownership conflicts, and political grievances. The state has also suffered terror attacks by armed groups, further compounding insecurity, displacement, and trauma among affected communities. These overlapping forms of violence have resulted in significant loss of lives, widespread displacement, and deep-seated mistrust, underscoring the need for inclusive, locally driven peacebuilding approaches.
Speaking at the event, Angela Umoru-David, the Foundation’s Programme Director, said the roundtable was designed to bridge gaps between stakeholders who often work in isolation.
“Our objective is to deepen collective understanding of local peacebuilding efforts in Plateau state and promote knowledge exchange on innovative approaches to curbing violent conflict,” she said. “As the project progresses, we intend to also create linkages to journalists so that civil society organisations (CSOs) and community-based organisations (CBOs) can engage with media practitioners in a meaningful way and contribute to journalism for peace.”
Participants discussed emerging trends, persistent gaps, and new opportunities within Plateau State’s peacebuilding ecosystem. Describing the engagement as timely, Nanmak Bali, President of the Plateau Peace Practitioners Network, an umbrella body for peacebuilding organisations in the state, noted that the discussions would improve coordination among actors. “The roundtable is apt, and it is coming at the right time,” he said. “These conversations will strengthen our approach to information sharing and guide how we design and implement our interventions.”
Bwemana Hailey Adanchin, an officer at the Mediation and Dialogue Unit of the Plateau Peace Building Agency, also highlighted the value of collaboration fostered by the meeting. “Participating in this roundtable has been very impactful, especially the lessons on collaboration,” she told HumAngle. “It reinforces the fact that no single institution can build peace alone.”
The roundtable featured plenary sessions and breakout discussions, during which participants examined the progress and limitations of existing peacebuilding interventions in the state.
Alfred Alabo, spokesperson of the Plateau State Police Command, said security agencies were increasingly recognising the limits of force-based responses to conflict. “There is a growing understanding that peace cannot be achieved through kinetic approaches alone,” he said. “When we engage more deeply, we realise that dialogue and community engagement are essential. In many cases, civil society organisations are already on the ground before we arrive, and we work together to resolve issues.”

Other participants echoed similar sentiments, emphasising the importance of early engagement, coordinated responses, and the responsible use of information in conflict-sensitive environments, and collaboration.
Fatima Suleiman, Executive Director of the Islamic Counselling Initiative of Northern Nigeria, described the roundtable as a moment of self-reflection. “This engagement has made me think more critically about stakeholder mapping and inclusion,” she said. “It highlighted gaps in how we identify and engage relevant actors in peacebuilding.”
Similarly, Kangyang Gana, Executive Director of Claire Aid Foundation, said the sessions helped her reassess her organisation’s interventions. “The discussions helped me identify gaps in our current interventions,” she said. “It has given me clarity on what needs to be adjusted to make our peacebuilding efforts more effective.”
Aliyu Dahiru, HumAngle’s Head of the Extremism and Radicalisation Desk, led a dedicated session on extremists’ use of media for propaganda, radicalisation, and recruitment. He stressed the role of journalists and peace actors in countering harmful narratives.

“Violent groups understand the power of information,” he said. “Our responsibility is to ensure that media and community voices are not exploited to inflame tensions but are instead used to promote understanding, resilience, and peace.”
In another session, Abdussamad Ahmad, HumAngle’s Human Security and Policy Analyst, introduced participants to in-house tools, including the HumAngle FOI Hub and Maps.HumAngle, designed to help civil society organisations and local communities strengthen advocacy and accountability efforts.
“Our hope is that over time, stronger multistakeholder networks that understand their local contexts will be built and sustained,” Angela added.
Since its launch, the APSJ Project has hosted similar roundtable discussions in northwestern Nigeria. The initiative has also trained journalists and awarded grants to those reporting on grassroots peacebuilding efforts across the country, particularly in Adamawa, Borno, Cross River, Lagos, and Taraba states.
HumAngle Foundation organized a two-day multi-stakeholder roundtable in Plateau State, Nigeria, gathering civil society organizations, government institutions, and security agencies to address local peacebuilding efforts in the region.
Supported by the National Endowment for Democracy, this event forms part of the Advancing Peace and Security through Journalism (APSJ) Project aimed at enhancing peacebuilding, accountability, and governance in conflict-affected areas by strengthening technological capacities.
The roundtable addressed recurring communal violence in Plateau State, emphasizing the need for inclusive, locally-driven peacebuilding approaches. Discussions focused on emerging trends, persistent gaps, and new opportunities, emphasizing information sharing, and collaboration. The dialogue recognized the limits of force-based responses to conflict and highlighted the value of early engagement and coordinated efforts for effective peacebuilding.
Participants like Nanmak Bali and Fatima Suleiman, emphasized the importance of collaboration and self-reflection on stakeholder inclusion. Sessions led by Aliyu Dahiru and Abdussamad Ahmad highlighted the media’s role in countering harmful narratives, while introducing advocacy tools for community organizations.
Overall, the roundtable aimed to foster sustainable networks for peace and has previously hosted similar discussions in other Nigerian states to advance grassroots peacebuilding efforts.