How the Warner Bros. deal has divided Hollywood
The pitched battle for Warner Bros. took yet another turn Monday night as Paramount Skydance enhanced its bid for the storied studio.
The decision by Warner Bros. Discovery to leave the door slightly ajar for Paramount came after weeks of pressure from its leader, tech scion David Ellison, and his billionaire father, Oracle co-founder Larry Ellison.
The media company has been vying to acquire Warner since late last year, and that fight only increased after the “Casablanca” and “Harry Potter” studio chose Netflix as the winning bidder back in December.
The bidding war has divided Hollywood’s creative community, with filmmakers, producers and unions all staking positions on the deal.
The latest to weigh in was “Avatar” and “Titanic” director James Cameron, who reportedly described Warner’s sale to Netflix as “disastrous for the theatrical motion picture business” in a Feb. 10 letter to Sen. Mike Lee (R-Utah), chair of the Senate subcommittee on antitrust, competition policy and consumer rights.
“I am very familiar not only with ships that sail, but also those that sink,” he wrote. “And the theatrical experience of movies could become a sinking ship.”
Actor Mark Ruffalo shot back at Cameron: “Are you also against the monopolization that a Paramount acquisition would create? Or is it just that of Netflix?” he posted on Threads over the weekend, adding that he was “speaking on behalf of hundreds of thousands of filmmakers worldwide.”
Regardless of which bidder prevails, consolidation in the industry is a major fear, particularly after waves of job cuts due to the pandemic and pullbacks in production spending amid streaming losses. And for the theatrical exhibition business, any merger revives concerns about an even greater decrease in films headed to theaters — particularly if the winning bidder is Netflix.
The health and future of cinemas is an especially sensitive topic in Hollywood. Box office revenue still has not returned to pre-pandemic levels, and some fear it never will, leaving theaters scrambling for alternative ways to fill their auditoriums.
Paramount has positioned itself as a champion for theatrical films, and David Ellison has said a combined Paramount and Warner Bros. would release 30 films a year.
But theater owner trade group Cinema United and the Writers Guild of America have warned that further consolidation would further concentrate the entertainment business, bringing more layoffs and theater closures.
Netflix co-Chief Executive Ted Sarandos has since tried to temper these concerns.
In a recent Senate subcommittee hearing, he pledged to maintain a 45-day theatrical window for Warner Bros. films, while also saying the deal would increase production investments going forward. In a recent letter to Lee responding to Cameron’s missive, Sarandos said he had previously spoken with the director in December about Netflix’s plans for Warner Bros., and that he had been “very supportive.”
Then there’s the politics of it all.
My colleague Meg James has written about Paramount’s efforts to use its political influence with the Trump administration to push its deal — and undermine Netflix’s. Paramount has declined to comment on the matter.
To put it mildly, Trump is a deeply unpopular figure in liberal-leaning Hollywood.
Creatives have feared a chilling effect on speech, particularly after Federal Communications Commission Chair Brendan Carr has aggressively tried to enforce long-dormant rules that require broadcast TV stations to give equal time to opposing candidates. The free-speech matter came to a head last year, when Carr warned that ABC could lose its TV station licenses after late-night host Jimmy Kimmel made a remark about slain conservative activist Charlie Kirk.
More recently, the equal-time rules resurfaced when CBS late-night host Stephen Colbert blasted his own network over its handling of his interview with Democratic Senate candidate James Talarico. Colbert said that CBS told him he could not air the interview because it would require giving equal time to Talarico’s opponents in the Senate primary and that he was instructed not to talk about the issue on the air, which he refused. CBS has disputed Colbert’s comments, saying he was not prohibited from airing the interview.
News industry insiders also raised concerns after the installation of Bari Weiss as editor in chief of CBS News. Two months into her tenure, she made the decision to pull a “60 Minutes” episode that investigated the alleged abuse of detainees sent from the U.S. to an El Salvador prison, a highly unusual step that critics interpreted as a decision to placate the Trump administration.
CBS News, which aired the episode in January, denied the claim, saying the piece had only been held for additional reporting.
On the film side, Paramount continues to make deals with creatives, including the irreverent South Park creators, who have churned out parodies of the Trump administration, “Wicked” director Jon M. Chu and writer, producer and actor Issa Rae, who in a statement earlier this year vowed to “tell stories for and by the diverse communities that have supported my work over the years.”
As the Warner Bros. deal drama unfolds, we’ll see how the lines continue to form in Hollywood’s creative class.
Stuff We Wrote
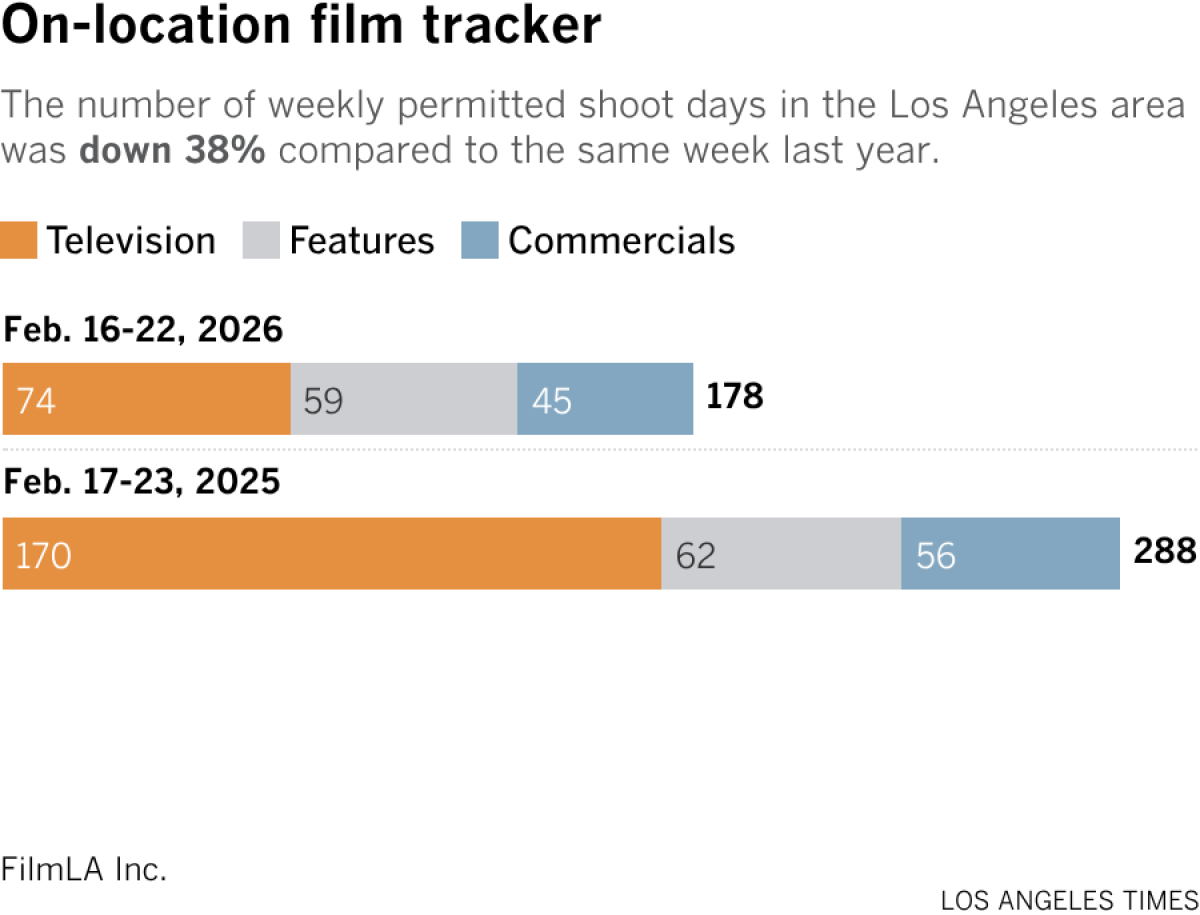
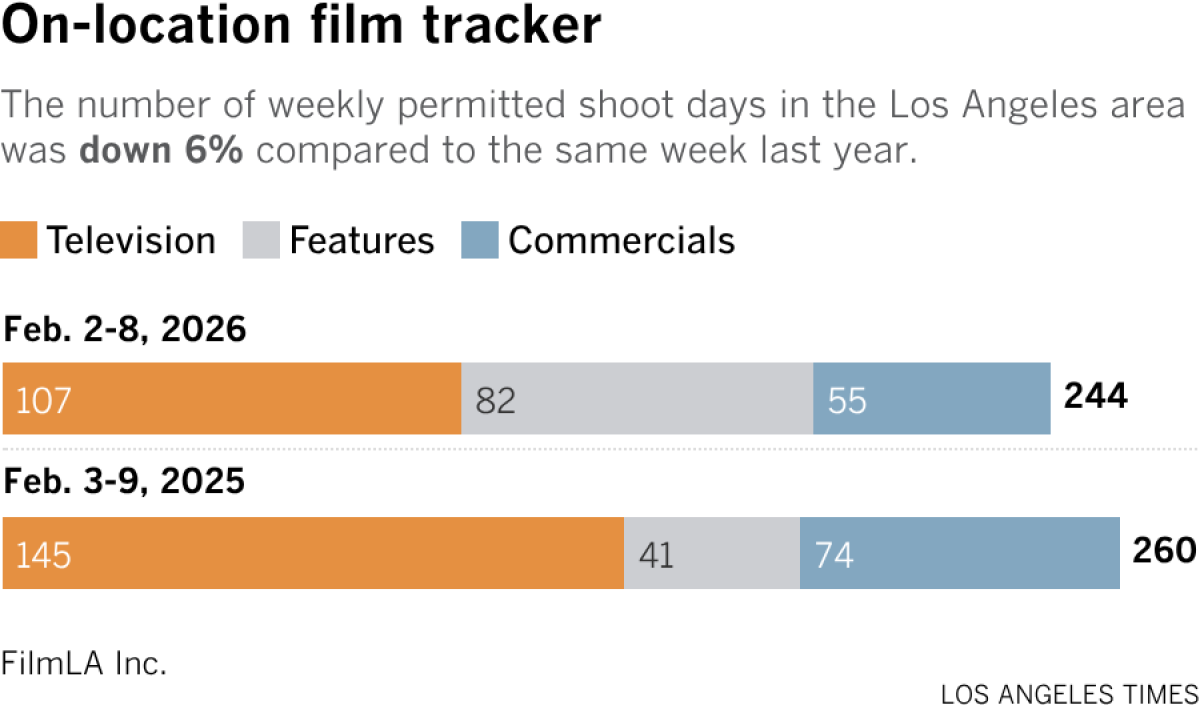
Film shoots
Number of the week

Sony Pictures Animation’s “Goat” led the domestic box office this weekend with an estimated three-day total of $17 million, beating out the Margot Robbie and Jacob Elordi-led “Wuthering Heights.”
The film, which was also produced by Warriors star Stephen Curry’s production company, has bucked the trend for original animated movies, which have largely faltered at theaters in recent years.
What I’m watching
Last week, I watched more Olympic figure skating (who didn’t watch Alysa Liu’s joyful, gold medal-winning performance?), but I’m also now re-watching 2000s teen detective drama “Veronica Mars.” I’m not Gen Z, but my newfound zeal for comfort TV is not unlike the story my colleague Stephen Battaglio wrote last year about young people’s interest in nostalgic shows.