China’s Largest Modern Naval Gun To Date Just Appeared On A Test Ship
What looks to be a new 155mm naval gun has been installed on a Chinese weapons trials ship. This is larger than any gun currently found on People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) warships. The weapon could offer a boost in naval gunfire support capability to aid in future amphibious operations, as well as additional firepower for use against enemy ships and aerial threats, including possibly incoming missiles.
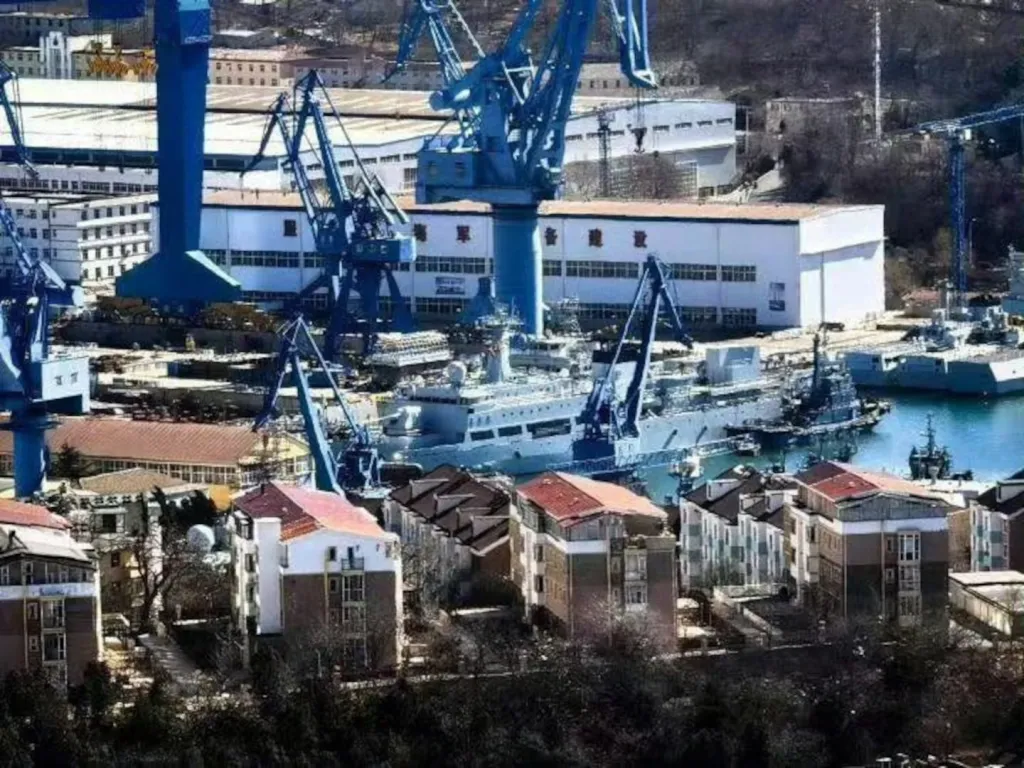
A picture showing what appears to be a Type 910 test vessel with a very large caliber gun mounted in a turret on the bow began circulating online yesterday, but it is unknown when exactly it was taken. The location is readily identifiable as Liaoning Shipyard, also known as Dalian Liaoning South Shipyard. This yard, which is situated adjacent to the PLAN’s Lushun Naval Base, has been involved in other advanced naval developments in the past, including the testing of a stealthy Chinese corvette or light frigate.


Though it is a relatively low-quality image, what is visible of the weapon and its turret aligns with what has emerged in the past year or so about a new 155mm naval gun under development in China.


Specific details about the 155mm gun remain limited, but a picture of a data plate that previously appeared online indicates that it weighs 21,800 kilograms (roughly 48,060 pounds) and is capable of firing guided projectiles. There have also been reports that the Inner Mongolia Northern Heavy Industries Group division of the state-run China North Industries Group Corporation (NORINCO) has been responsible for the design. NORINCO is a heavy industrial conglomerate involved in a wide variety of military and commercial enterprises, including the development and production of ground-based 155mm howitzers and other large caliber guns.
The largest caliber gun in active PLAN service today is a single-barrel 130mm (roughly 5-inch) type known variously as the H/PJ-38 and the H/PJ-45. The design was reverse-engineered from the Soviet-era AK-130, a twin-barrel weapon. The H/PJ-38 / H/PJ-45 first appeared on the Type 052D destroyer in the early 2000s and is also now found on newer Type 055 destroyers.

Though the maximum range of the H/PJ-38 / H/PJ-45 is unclear, the AK-130 is said to have a maximum range of around 14 miles (23 kilometers). One would expect, then, that the new 155mm naval gun would have greater reach.
The larger 155mm caliber could also open the door to more novel ammunition types in line with other developments globally. The U.S. Army, for instance, has been actively pursuing ramjet-powered 155mm rounds for ground-based howitzers in recent years. The Army, as well as the U.S. Navy, have also been supporting work on a 155mm gun-launched glide munition from General Atomics called the Long Range Maneuvering Projectile (LRMP). Hypervelocity projectiles that could be fired from howitzers on the ground and naval guns on ships, and be used to engage land, sea, and aerial targets, have been another area of active development in the United States.


Long-Range Maneuvering Projectile
Other known 155mm naval gun developments elsewhere in the world have historically focused primarily on meeting requirements for naval gunfire support for amphibious operations. China has uniquely relevant needs to be able to bombard targets ashore, especially in the context of any future intervention against Taiwan, as well as operations in the hotly contested South China Sea and other littorals it may seek to control.
The PLAN has been making other major investments in recent years to expand its amphibious warfare capabilities, overall. This has included the construction of the new supersized Type 076 amphibious assault ship Sichuan, as well as the continued expansion of its fleet of smaller Type 075s. China has also been acquiring a fleet of barges with jack-up legs that could be used to establish temporary piers after beachheads are secured.

Chinese PLA Navy’s First Type 076 Amphibious Assault Ship “Sichuan” Conducts First Sea Trial
A long-range naval gun capable of firing hypervelocity projectiles, as well as other ammunition types, could offer new cost and flexibility advantages over missiles in certain scenarios against other types of targets, as well. The U.S. military has previously demonstrated the ability of a 155mm howitzer to down incoming subsonic cruise missiles when firing hypervelocity rounds that could cost $100,000 or less when produced at scale.

At the same time, the reach of any gun is still likely to be relatively short in the context of modern naval warfare, which is dominated today by missiles, another area where the PLAN has been making major investments. As such, there are still questions about the utility of a new longer-ranged gun in any naval context, given what it might take to get a ship armed with one within range of relevant targets. TWZ explored exactly these issues in detail when U.S. President Donald Trump made his first comments about plans for a new class of “battleships” for the U.S. Navy last year.
This is all reflective of a larger debate over the value, or lack thereof, of naval gunfire support globally. This played a notably central role in the development of the Zumwalt class stealth destroyers for the U.S. Navy. A pair of 155mm guns that would sit fully concealed with their turrets when not in use, and that would fire long-range guided rounds, was central to the original Zumwalt design. The Navy subsequently balked at the cost of the Long-Range Land Attack Projectiles (LRLAP), the unit price of which was pegged at approximately $800,000. That, in turn, threw the future of the guns into limbo. The U.S. Navy is now refitting its Zumwalt class ships with new vertical launch system cells for hypersonic missiles in place of the guns.

BAE Systems – 155mm Advanced Gun System (AGS) Long Range Land Attack Projectile (LRLAP) [480p]
The Trump class “battleship” design that has now emerged does feature an electromagnetic railgun, as well as multiple 5-inch guns, but also various types of missiles and laser directed energy weapons. The U.S. Navy had shelved previous work on railguns in the early 2020s, despite having seen promising progress, due to significant technological impediments.
China has also been developing railguns for naval use. A prototype design mounted in a large turret emerged on a PLAN ship in 2018, but the current status of that program is unclear. It is possible that Chinese work now on a traditional 155mm naval gun could be, at least in part, a hedge against issues with the railgun effort.

Other countries are also pursuing railguns for naval use, with Japan notably having now conducted multiple at-sea tests of a prototype design, as you can read more about here.

How the development of the new Chinese 155mm naval gun proceeds is still to be seen, but the project does look to be advancing now toward at least initial at-sea testing.
Contact the author: joe@twz.com