Japan’s minority gov’t faces election setback over inflation, immigration | Elections News
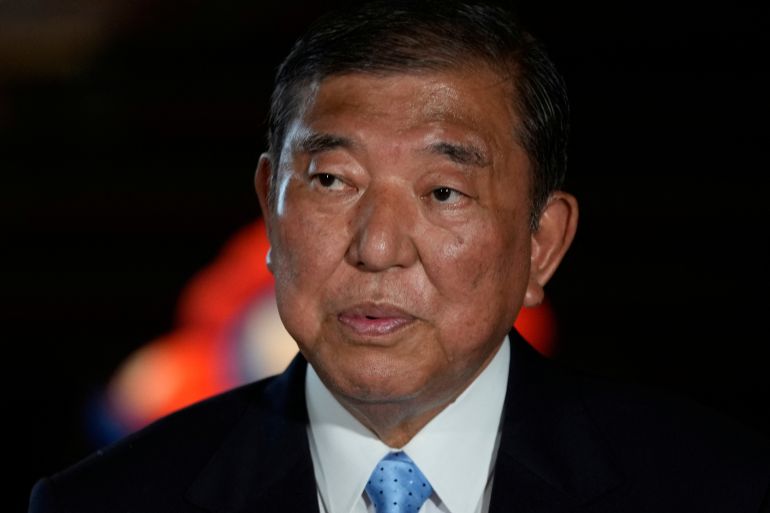
Japan’s shaky minority government looks poised for another setback in a crucial upper house vote this weekend, in the first national election since Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba took office last year.
Half of the 248 seats in Japan’s Upper House of Parliament will be contested on Sunday. Ishiba’s Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), along with its longtime junior coalition partner Komeito, need to win 50 of its 66 seats up for re-election to hold on to its majority.
But polling suggests the coalition will fail to do so, in a potential repeat of October’s disastrous election, when the LDP-Komeito coalition lost its parliamentary majority in Japan’s more powerful lower house – the worst result since briefly losing power in 2009.
The LDP has ruled Japan for almost all of the country’s post-war history.
Inflation has been a killer issue for Ishiba, with the price of rice – which has doubled since last year due to poor harvests and government policies – becoming a lightning rod for voter discontent.
In response, opposition parties have promised tax cuts and welfare spending to soften the blow of Japan’s long-running economic stagnation.

While locals face a rising cost of living, the country’s weak Yen has attracted significant numbers of foreign tourists. Concerns about over-tourism and a lack of respect for local customs have fed local discontent, which has been capitalised on by upstart populist party Sanseito.
Initially launched on YouTube by streamer Kazuya Kyoumoto, politician Sohei Kamiya, and political analyst Yuuya Watase in 2019, the party rose to prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic as it peddled conspiracy theories and far-right talking points.
In the years since, Sanseito has successfully appealed to a small but growing section of Japan’s electorate with its “Japanese First” campaign and anti-immigration stance, rallying against what it describes as a “silent invasion” of immigrants.
While foreigners still only make up a small fraction of Japan’s population, at about 3 percent, the country has taken in about a million immigrant workers over the past three years to fill jobs left vacant by its ageing population.
Kamiya, the party’s 47-year-old leader, said Sanseito is forcing the government to address growing concerns about foreigners in Japan, as it drags rhetoric once confined to the political fringe into the mainstream.
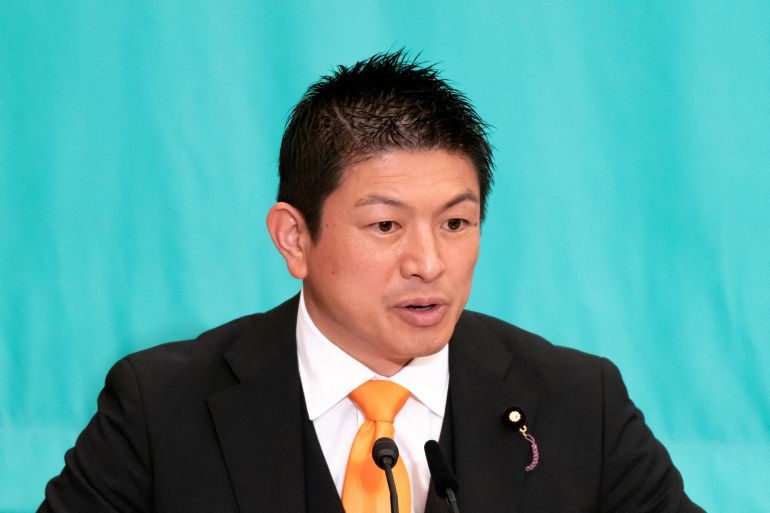

“In the past, anyone who brought up immigration would be attacked by the left. We are getting bashed too, but are also gaining support,” Kamiya told the Reuters news agency this week.
“The LDP and Komeito can’t stay silent if they want to keep their support,” Kamiya added.
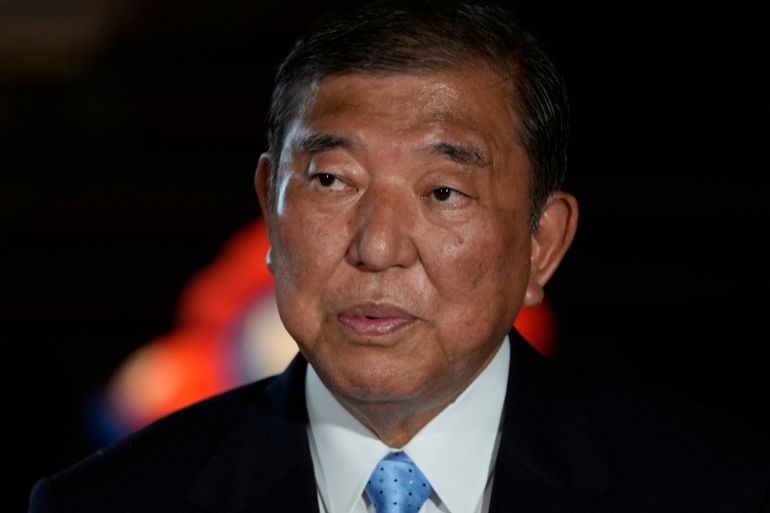
While polls show Sanseito may only secure 10 to 15 of the 125 seats up for grabs in this vote, each loss is crucial for Prime Minister Ishiba’s shaky minority government – increasingly beholden to opposition parties to cling to power.
Should the LDP’s seat share be eroded, as expected, Ishiba will almost certainly seek to broaden his coalition or strike informal deals with opposition parties.
But doing so with Sanseito could prove problematic for the LDP, which owes much of its longevity to its broad appeal and centrist image.
“If the party [LDP] goes too far right, it loses the centrists,” Tsuneo Watanabe, a senior fellow at the Sasakawa Peace Foundation think tank in Tokyo, told Reuters.
In a worst-case election outcome for the LDP, David Boling, director for Japan and Asian trade at political risk consultancy Eurasia Group, says he believes Ishiba may be forced out of office.
“If he had an overwhelming loss, I think he would have to resign,” Boling said.
But a move such as that would unleash political turmoil, at a time when Japan is frantically seeking to secure a reprieve from Donald Trump’s proposed 25 percent tariffs before an August 1 deadline touted by the US president.
Illustrating the urgency of the issue, on Friday Ishiba took a break from campaigning to urge Washington’s chief tariff negotiator and Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent to continue talks with Japan’s top tariff negotiator Ryosei Akazawa.
Following his meeting with Ishiba, Bessent said “a good deal is more important than a rushed deal.
“A mutually beneficial trade agreement between the United States and Japan remains within the realm of possibility,” he added.