Public opinion is split as US marks 80th anniversary of Hiroshima bombing | Nuclear Weapons News
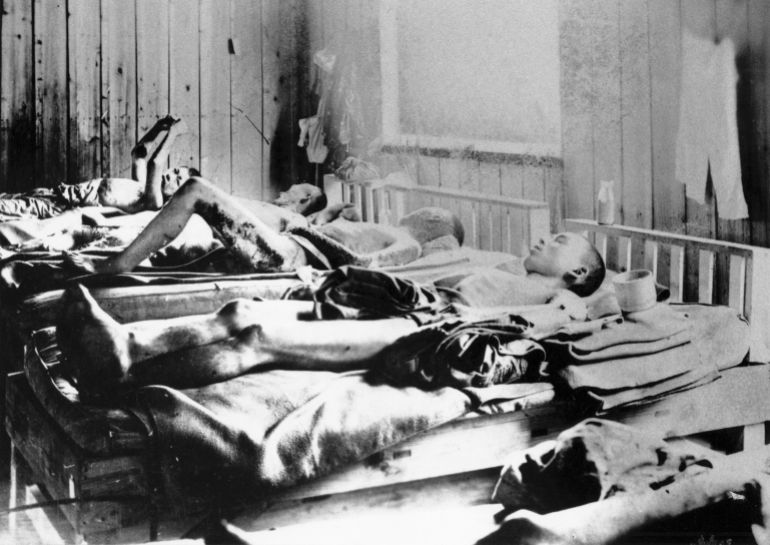
On August 6, 1945, the United States became the first and only country in history to carry out a nuclear attack when it dropped an atomic bomb on the Japanese city of Hiroshima.
While the death toll of the bombing remains a subject of debate, at least 70,000 people were killed, though other figures are nearly twice as high.
Three days later, the US dropped another atomic bomb on the city of Nagasaki, killing at least 40,000 people.
The stunning toll on Japanese civilians at first seemed to have little impact on public opinion in the US, where pollsters found approval for the bombing reached 85 percent in the days afterwards.
To this day, US politicians continue to credit the bombing with saving American lives and ending World War II.
But as the US marks the 80th anniversary of the bombing of Hiroshima, perceptions have become increasingly mixed. A Pew Research Center poll last month indicated that Americans are split almost evenly into three categories.
Nearly a third of respondents believe the use of the bomb was justified. Another third feels it was not. And the rest are uncertain about deciding either way.
“The trendline is that there is a steady decline in the share of Americans who believe these bombings were justified at the time,” Eileen Yam, the director of science and society research at Pew Research Center, told Al Jazeera in a recent phone call.
“This is something Americans have gotten less and less supportive of as time has gone by.”
Tumbling approval rates
Doubts about the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the advent of nuclear weapons in general, did not take long to set in.
“From the beginning, it was understood that this was something different, a weapon that could destroy entire cities,” said Kai Bird, a US author who has written about Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
His Pulitzer Prize-winning book, American Prometheus, served as the basis for director Christopher Nolan’s 2023 film, Oppenheimer.
Bird pointed out that, even in the immediate aftermath of the bombing, some key politicians and public figures denounced it as a war crime.
Early critics included physicist Albert Einstein and former President Herbert Hoover, who was quick to speak out against the civilian bloodshed.
“The use of the atomic bomb, with its indiscriminate killing of women and children, revolts my soul,” Hoover wrote within days of the bombing.

Over time, historians have increasingly cast doubt on the most common justification for the atomic attacks: that they played a decisive role in ending World War II.
Some academics point out that other factors likely played a larger role in the Japanese decision to surrender, including the Soviet Union’s declaration of war against the island nation on August 8.
Others have speculated whether the bombings were meant mostly as a demonstration of strength as the US prepared for its confrontation with the Soviet Union in what would become the Cold War.
Accounts from Japanese survivors and media reports also played a role in changing public perceptions.
John Hersey’s 1946 profile of six victims, for instance, took up an entire edition of The New Yorker magazine. It chronicled, in harrowing detail, everything from the crushing power of the blast to the fever, nausea and death brought on by radiation sickness.
By 1990, a Pew poll found that a shrinking majority in the US approved of the atomic bomb’s use on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Only 53 percent felt it was merited.
Rationalising US use of force
But even at the close of the 20th century, the legacy of the attacks remained contentious in the US.
For the 50th anniversary of the bombing in 1995, the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC, had planned a special exhibit.
But it was cancelled amid public furore over sections of the display that explored the experiences of Japanese civilians and the debate about the use of the atomic bomb. US veterans groups argued that the exhibit undermined their sacrifices, even after it underwent extensive revision.
“The exhibit still says in essence that we were the aggressors and the Japanese were the victims,” William Detweiler, a leader at the American Legion, a veterans group, told The Associated Press at the time.
Incensed members of Congress opened an investigation, and the museum’s director resigned.
The exhibit, meanwhile, never opened to the public. All that remained was a display of the Enola Gay, the aeroplane that dropped the first atomic bomb.
Erik Baker, a lecturer on the history of science at Harvard University, says that the debate over the atomic bomb often serves as a stand-in for larger questions about the way the US wields power in the world.

“What’s at stake is the role of World War II in legitimising the subsequent history of the American empire, right up to the current day,” he told Al Jazeera.
Baker explained that the US narrative about its role in the defeat of Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan — the main “Axis Powers” in World War II — has been frequently referenced to assert the righteousness of US interventions around the world.
“If it was justifiable for the US to not just go to war but to do ‘whatever was necessary’ to defeat the Axis powers, by a similar token, there can’t be any objection to the US doing what is necessary to defeat the ‘bad guys’ today,” he added.
A resurgence of nuclear anxiety
But as the generations that lived through World War II grow older and pass away, cultural shifts are emerging in how different age groups approach US intervention — and use of force — abroad.
The scepticism is especially pronounced among young people, large numbers of whom have expressed dissatisfaction with policies such as US support for Israel’s war in Gaza.
In an April 2024 poll, the Pew Research Center found a dramatic generational divide among Americans over the question of global engagement.
Approximately 74 percent of older respondents, aged 65 and up, expressed a strong belief that the US should play an active role on the world stage. But only 33 percent of younger respondents, aged 18 to 35, felt the same way.
Last month’s Pew poll on the atomic bomb also found stark differences in age. People over the age of 65 were more than twice as likely to believe that the bombings were justified than people between the ages of 18 and 29.
Yam, the Pew researcher, said that age was the “most pronounced factor” in the results, beating out other characteristics, such as party affiliation and veteran status.
The 80th anniversary of the Hiroshima bombing also coincides with a period of renewed anxiety about nuclear weapons.
US President Donald Trump, for instance, repeatedly warned during his re-election campaign in 2024 that the globe was on the precipice of “World War III”.
“The threat is nuclear weapons,” Trump told a rally in Chesapeake, Virginia. “That can happen tomorrow.”
“We’re at a place where, for the first time in more than three decades, nuclear weapons are back at the forefront of international politics,” said Ankit Panda, a senior fellow in the nuclear policy programme at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, a US-based think tank.
Panda says that such concerns are linked to geopolitical tensions between different states, pointing to the recent fighting between India and Pakistan in May as one example.
The war in Ukraine, meanwhile, has prompted Russia and the US, the world’s two biggest nuclear powers, to exchange nuclear-tinged threats.
And in June, the US and Israel carried out attacks on Iranian nuclear facilities with the stated aim of setting back the country’s ability to develop nuclear weapons.
But as the US marks the 80th anniversary of the Hiroshima bombings, advocates hope the shift in public opinion will encourage world leaders to turn away from nuclear sabre-rattling and work towards the elimination of nuclear weapons.
Seth Shelden, the United Nations liaison for the International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons, explained that countries with nuclear weapons argue that their arsenals discourage acts of aggression. But he said those arguments diminish the “civilisation-ending” dangers of nuclear warfare.
“As long as the nuclear-armed states prioritise nuclear weapons for their own security, they’re going to incentivise others to pursue them as well,” he said.
“The question shouldn’t be whether nuclear deterrence can work or whether it ever has worked,” he added. “It should be whether it will work in perpetuity.”