‘Will I make it back alive?’: Gaza journalists fear targeting by Israel | Israel-Palestine conflict News
After Israel’s attack on a tent housing journalists in Gaza City, Palestinians say press vests now feel like a target.
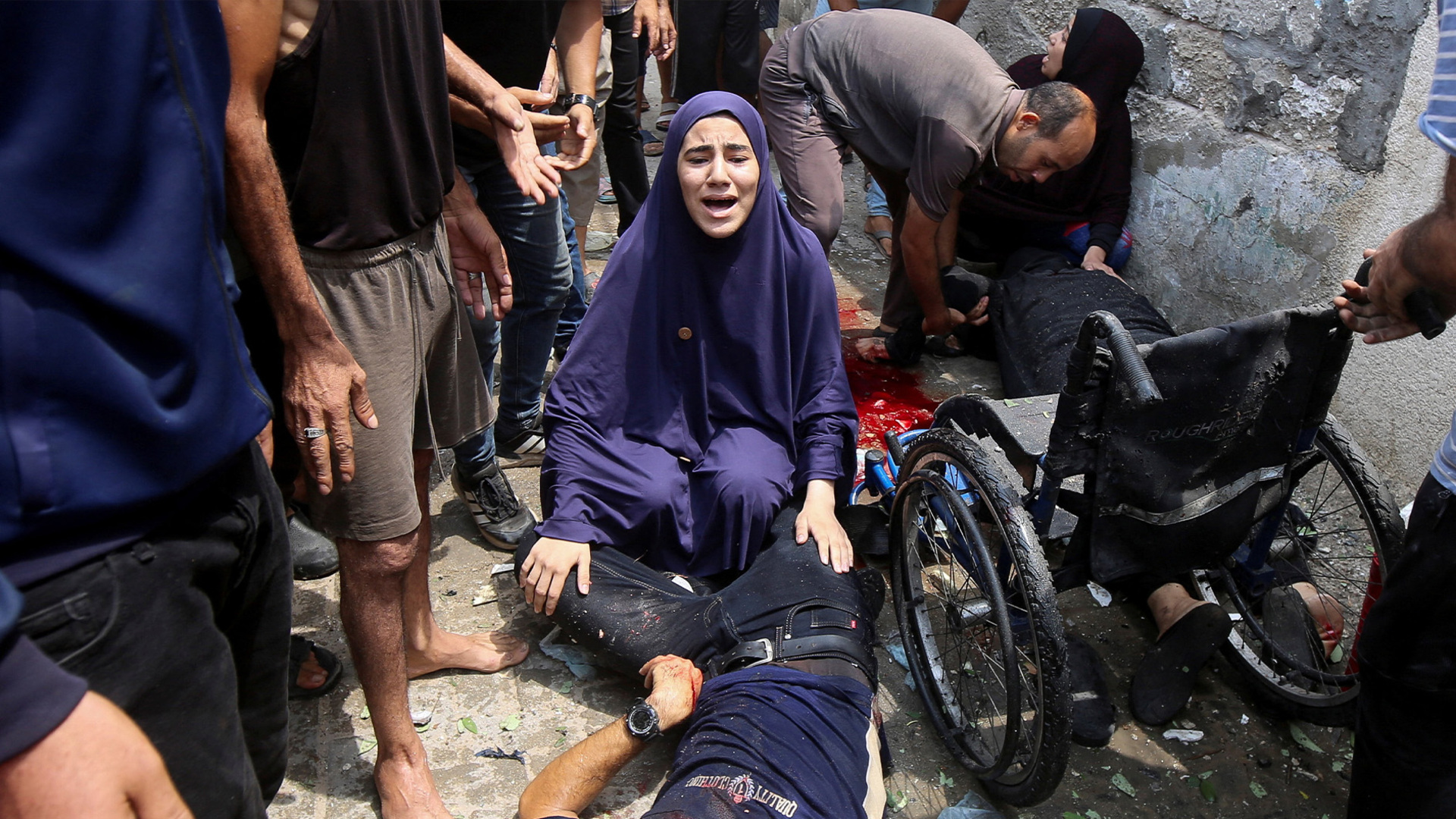
Palestinian journalists have long known Gaza to be the most dangerous place on earth for media workers, but Israel’s latest attack on a tent housing journalists in Gaza City has left many reeling from shock and fear.
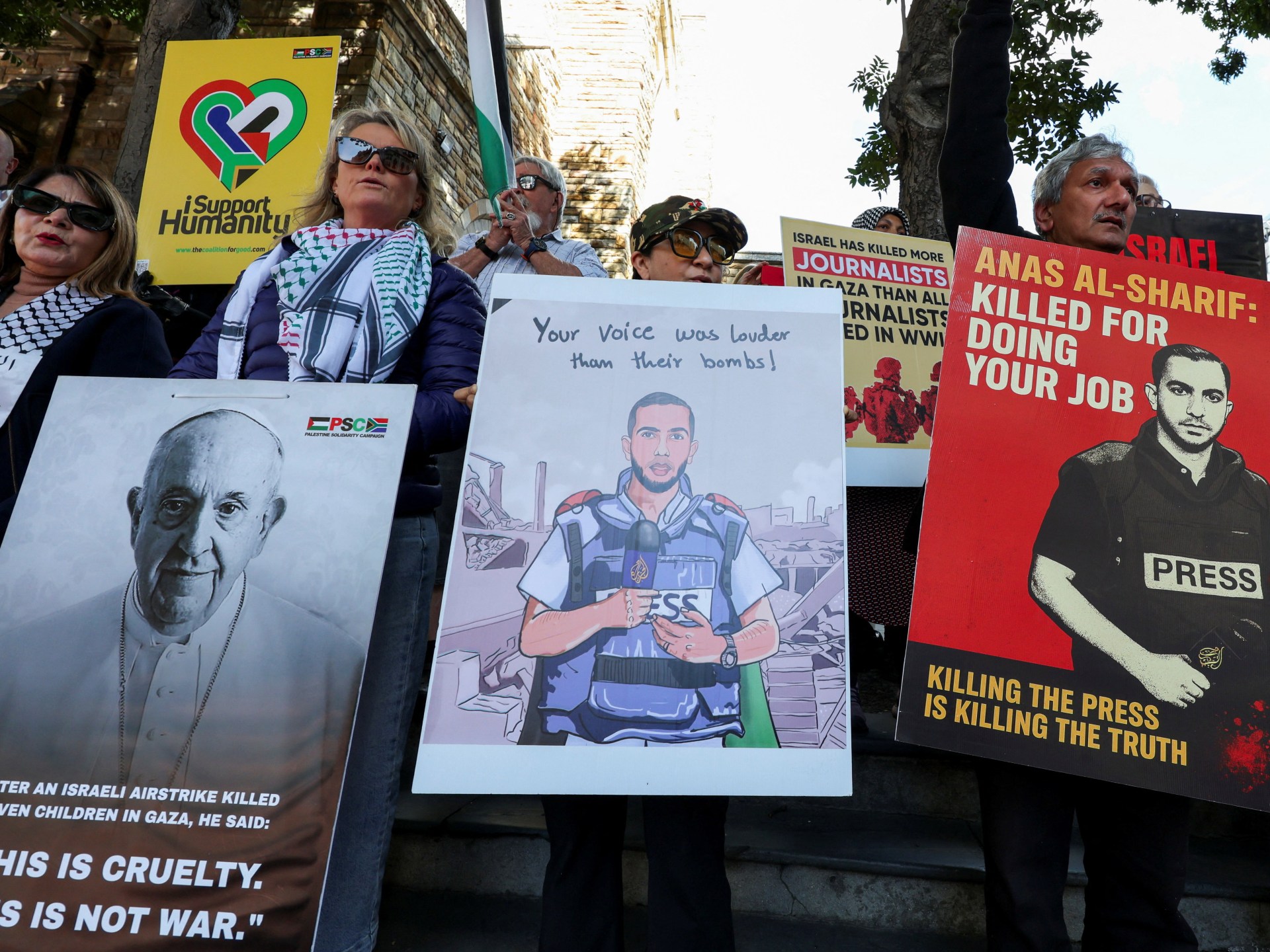
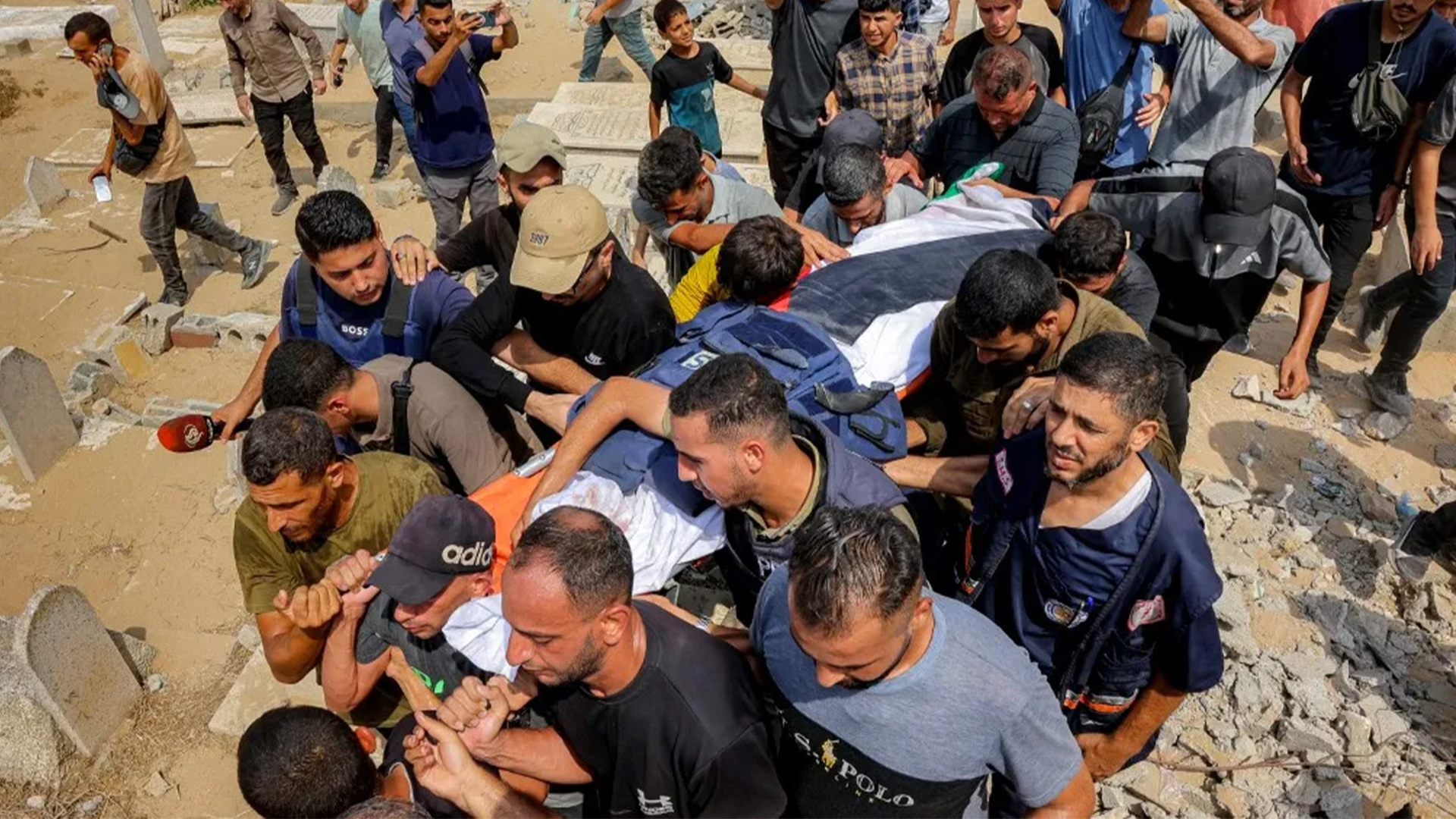
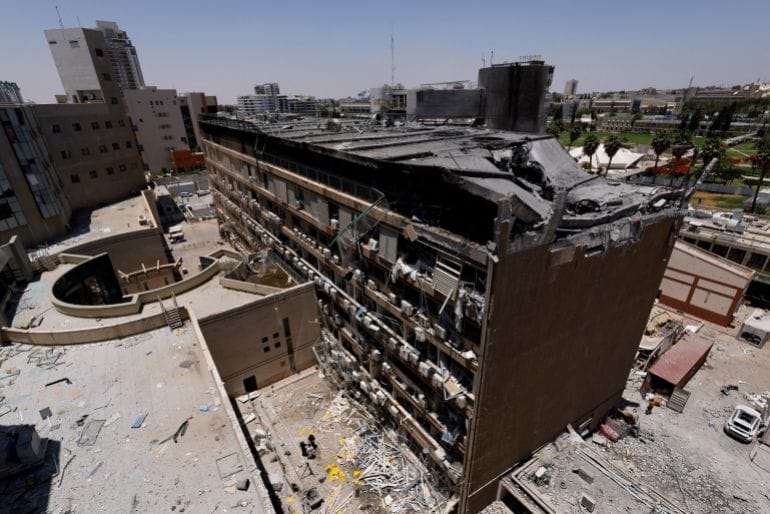
Four Al Jazeera staff were among seven people killed in an Israeli drone strike outside al-Shifa Hospital on August 10. The Israeli military has admitted to deliberately targeting the tent after making unsubstantiated accusations that one of those killed, Al Jazeera journalist Anas al-Sharif, was a member of Hamas.
Israeli attacks in Gaza have killed at least 238 media workers since October 2023, according to Gaza’s Government Media Office. This toll is higher than that of World Wars I and II, the Vietnam War, the war in Afghanistan and the Yugoslavia wars combined.
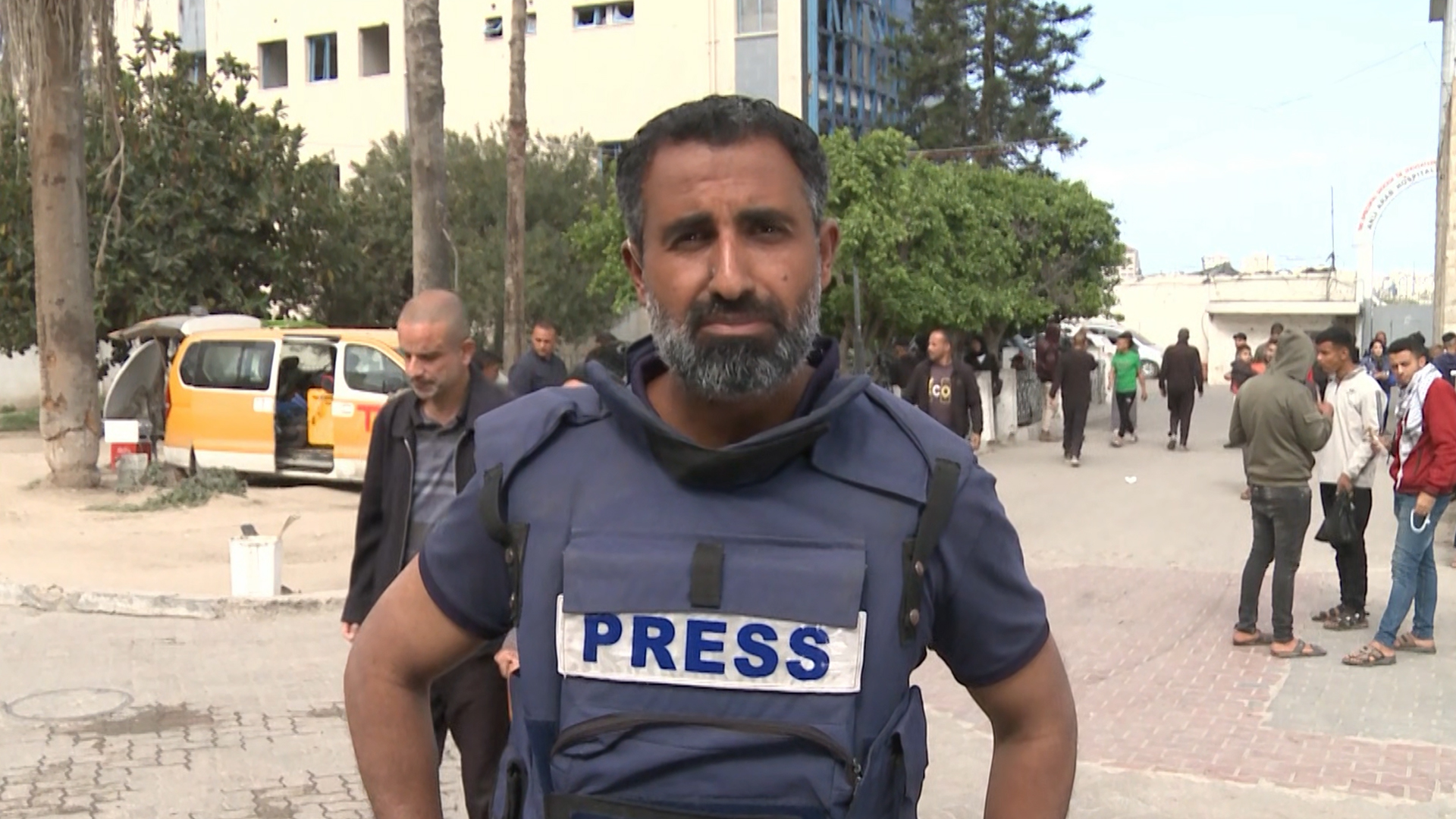
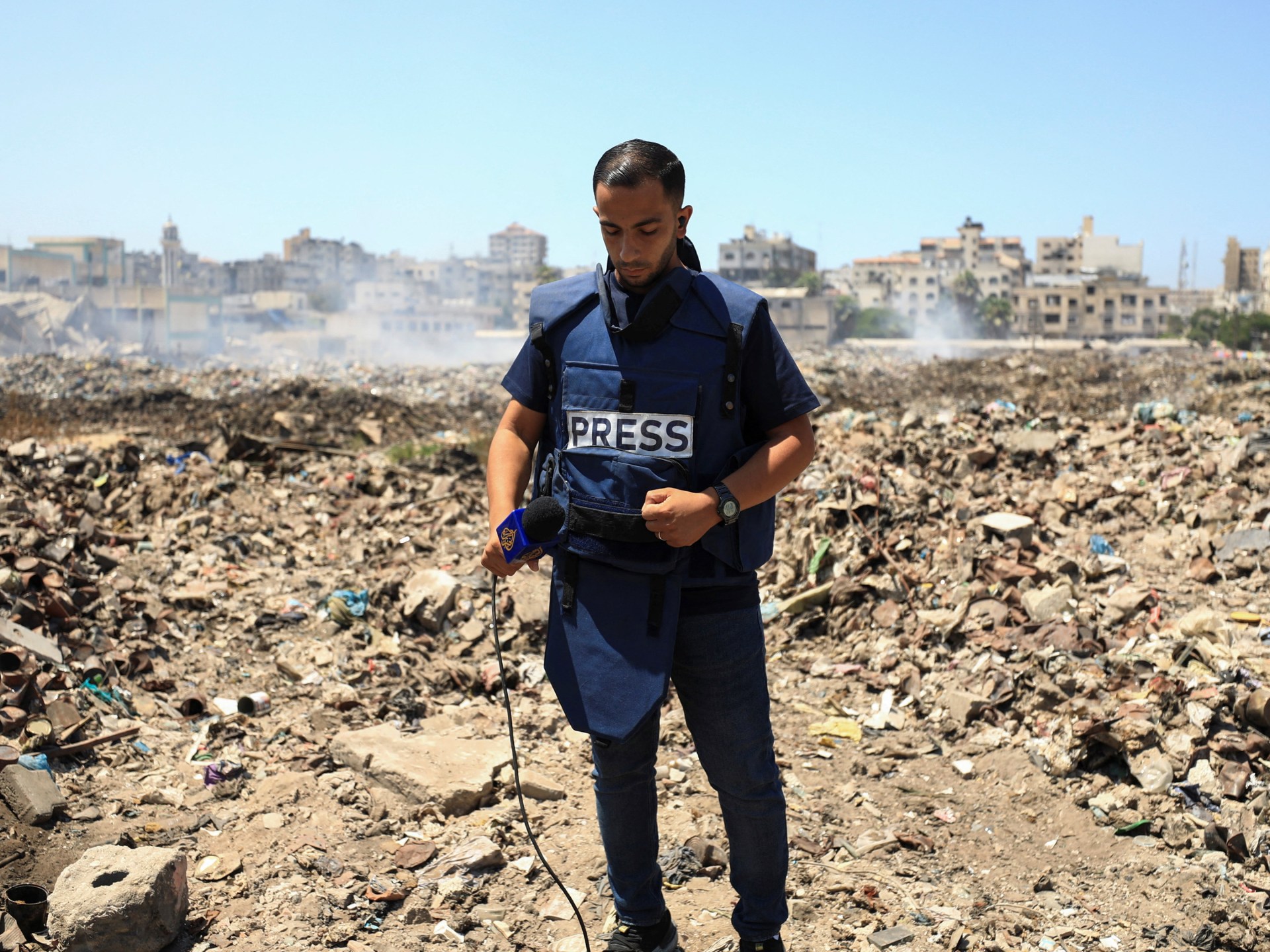
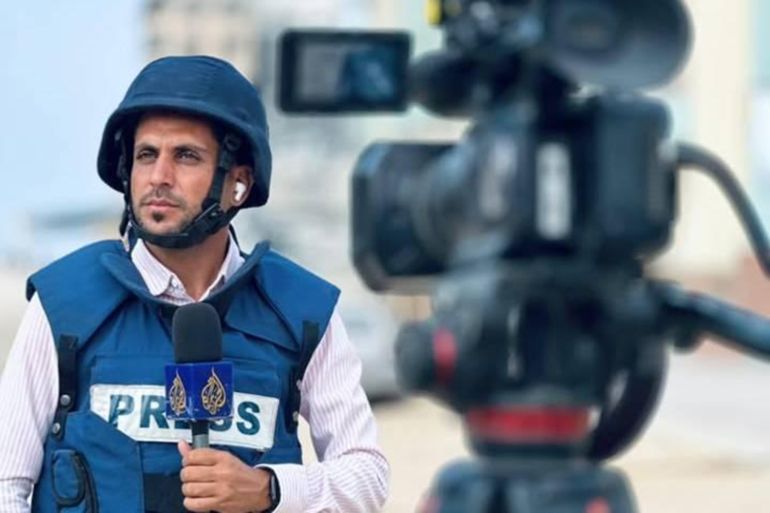
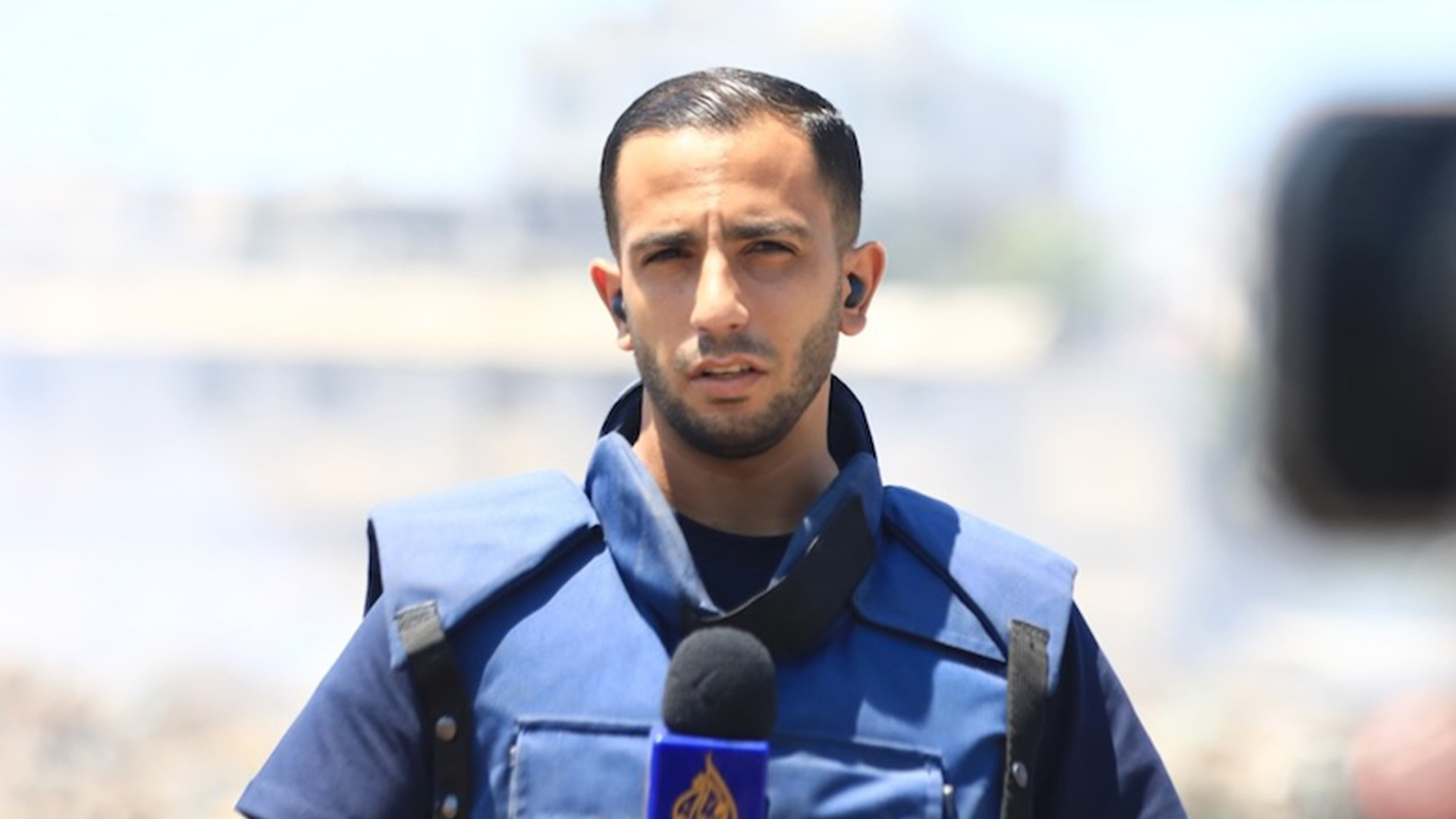
Al Jazeera correspondent Hani Mahmoud said, “Press vests and helmets, once considered a shield, now feel like a target.”
“The fear is constant — and justified,” Mahmoud said. “Every assignment is accompanied by the same unspoken question: Will [I] make it back alive?”
The US-based Committee to Protect Journalists has been among several organisations denouncing Israel’s longstanding pattern of accusing journalists of being “terrorists” without credible proof.
“It is no coincidence that the smears against al-Sharif — who has reported night and day for Al Jazeera since the start of the war — surfaced every time he reported on a major development in the war, most recently the starvation brought about by Israel’s refusal to allow sufficient aid into the territory,” CPJ Regional Director Sara Qudah said in the aftermath of Israel’s attack.
In light of Israel’s systematic targeting of journalists, media workers in Gaza are forced to make difficult choices.
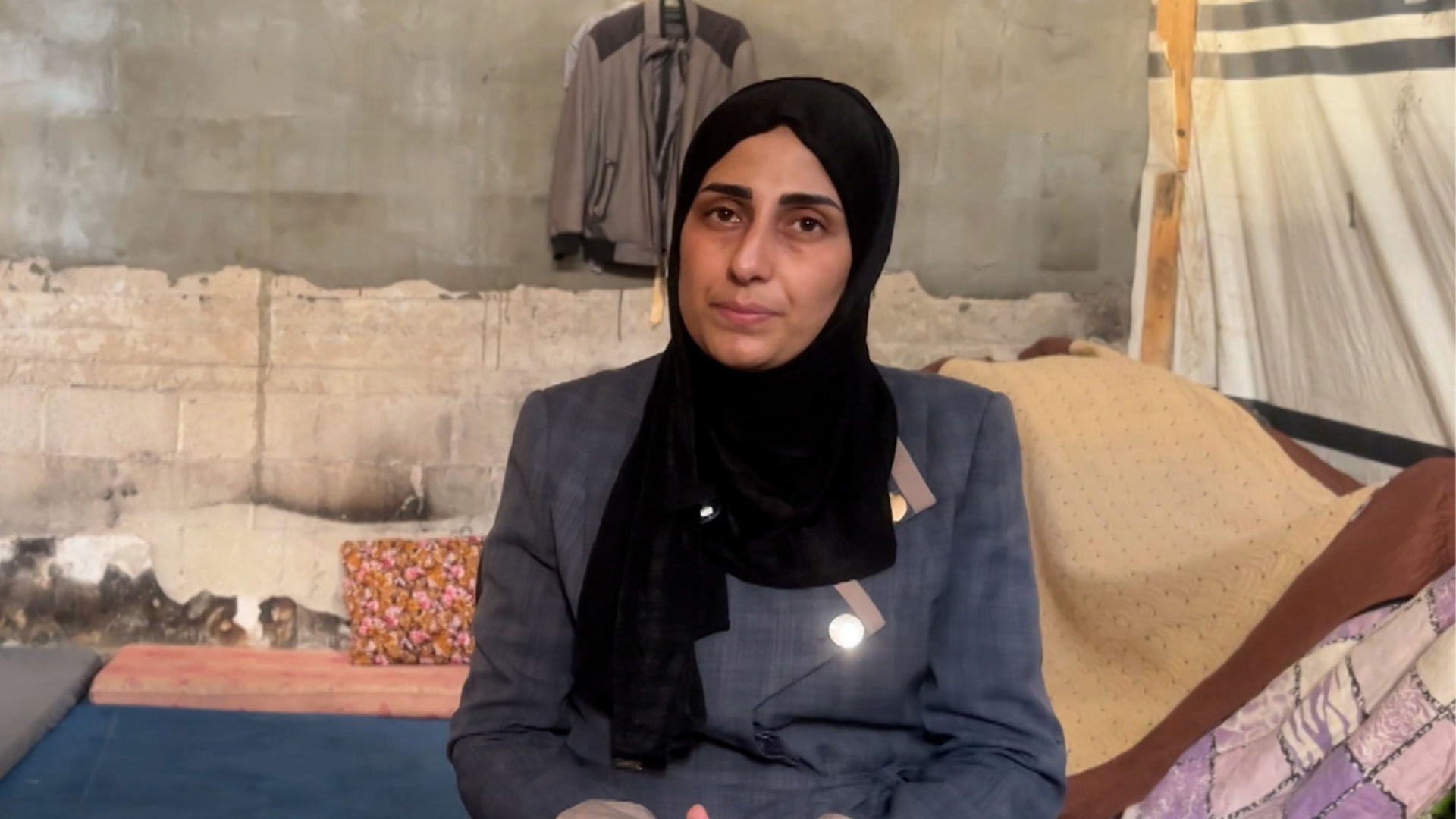
“As a mother and a journalist, I go through this mental dissonance almost daily, whether to go to work or stay with my daughters and being afraid of the random shelling of the Israeli occupation army,” Palestinian journalist Sally Thabet told Al Jazeera.
Across the street from the ruins of the School of Media Studies at al-Quds Open University in Gaza City, where he used to teach, Hussein Saad has been recovering from an injury he sustained while running to safety.
“The deliberate targeting of Palestinian journalists has a strong effect on the disappearance of the Palestinian story and the disappearance of the media narrative,” he said. Saad argued the Strip was witnessing “the disappearance of the truth”.
While journalists report on mass killings, human suffering and starvation, they also cope with their own losses and deprivation. Photographer and correspondent Amer al-Sultan said hunger was a major challenge.
“I used to go to work, and when I didn’t find anything to eat, I would just drink water,” he said. “I did this for two days. I had to live for two or three days on water. This is one of the most difficult challenges we face amid this war against our people: starvation.”
Journalist and film director Hassan Abu Dan said reporters “live in conditions that are more difficult than the mind can imagine.”
“You live in a tent. You drink water that is not good for drinking. You eat unhealthy food … We are all, as journalists, confused. There is a part of our lives that has been ruined and gone far away,” he said.
Al Jazeera’s Mahmoud said that despite the psychological trauma and the personal risks, Palestinian journalists continue to do their jobs, “driven by a belief that documenting the truth is not just a profession, but a duty to their people and history”.