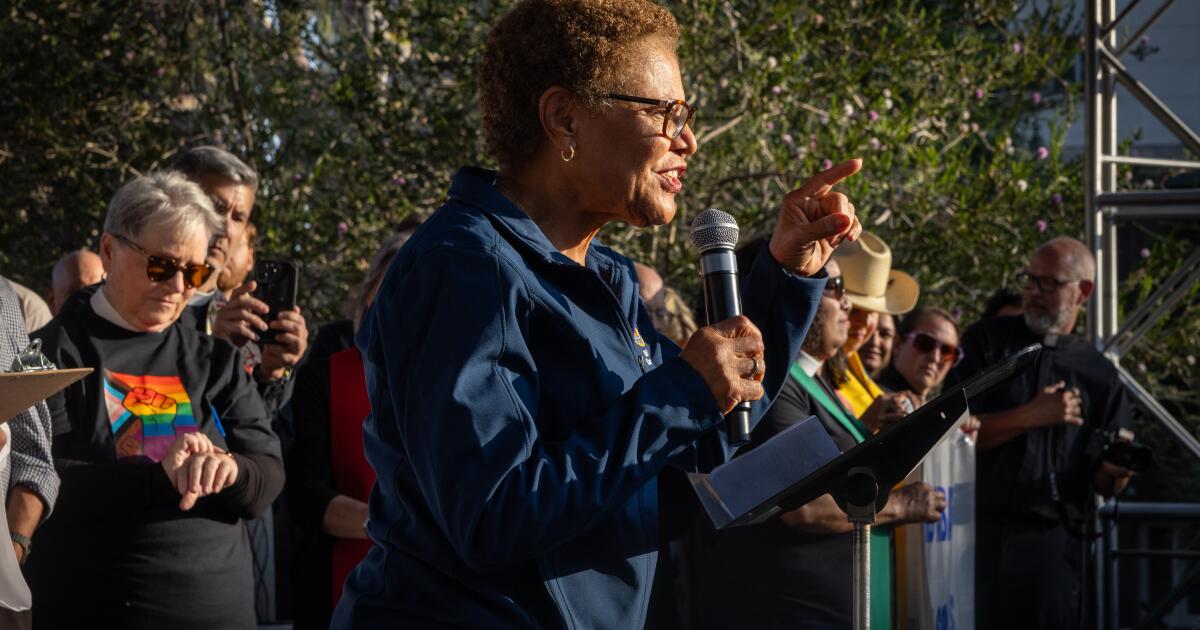
Trump Administration sues Mayor Karen Bass, City Council over sanctuary policy
The U.S. Department of Justice sued the city of Los Angeles, Mayor Karen Bass and City Council members Monday, calling L.A.’s sanctuary city law “illegal” and asking that it be blocked from being enforced.
The lawsuit, filed in California’s Central District federal court by the Trump Administration, said the country is “facing a crisis of illegal immigration” and that its efforts to address it “are hindered by Sanctuary Cities such as the City of Los Angeles, which refuse to cooperate or share information, even when requested, with federal immigration authorities.”
Over the last month, immigration agents have descended on Southern California, arresting more than 1,600 immigrants and prompting furious protests in downtown Los Angeles, Paramount and other communities. According to the lawsuit, L.A.’s refusal to cooperate with federal immigration authorities since June 6 has resulted in “lawlessness, rioting, looting, and vandalism.”
“The situation became so dire that the Federal Government deployed the California National Guard and United States Marines to quell the chaos,” the lawsuit states. “A direct confrontation with federal immigration authorities was the inevitable outcome of the Sanctuary City law.”
Atty. Gen. Pam Bondi called the city’s sanctuary policies “the driving cause of the violence, chaos, and attacks on law enforcement that Americans recently witnessed in Los Angeles.”
“Jurisdictions like Los Angeles that flout federal law by prioritizing illegal aliens over American citizens are undermining law enforcement at every level — it ends under President Trump,” Bondi said in a statement Monday.
Bass did not immediately respond to a request for comment. In recent weeks, she has pushed back against the Trump Administration’s portrayal of L.A. as a city enveloped in violence, saying that immigration agents are the ones sowing chaos, terrorizing families and harming the city’s economy.
“To characterize what is going on in our city as a city of mayhem is just an outright lie,” Bass said earlier this month. “I’m not going to call it an untruth. I’m not going to sugarcoat it. I’m going to call it for what it is, which is a lie.”
L.A.’s sanctuary city law was proposed in early 2023, long before Trump’s election, but finalized in the wake of his victory in November.
Under the ordinance, city employees and city property may not be used to “investigate, cite, arrest, hold, transfer or detain any person” for the purpose of immigration enforcement. An exception is made for law enforcement investigating serious offenses.
The ordinance bars city employees from seeking out information about an individual’s citizenship or immigration status unless it is needed to provide a city service. They also must treat data or information that can be used to trace a person’s citizenship or immigration status as confidential.
In the lawsuit, federal prosecutors allege that the city’s ordinance and other policies intentionally discriminate against the federal government by “treating federal immigration authorities differently than other law enforcement agents,” by restricting access to property and to individual detainees, by prohibiting contractors and sub-contractors from providing information, and by “disfavoring federal criminal laws that the City of Los Angeles has decided not to comply with.”
“The Supremacy Clause prohibits the City of Los Angeles and its officials from singling out the Federal Government for adverse treatment—as the challenged law and policies do—thereby discriminating against the Federal Government,” the lawsuit says. “Accordingly, the law and policies challenged here are invalid and should be enjoined.”
Trump’s Department of Justice contends that L.A.’s Sanctuary City ordinance goes much further than similar laws in other jurisdictions, by “seeking to undermine the Federal Government’s immigration enforcement efforts.”
The lawsuit also cites a June 10 meeting in which council members grilled Police Chief Jim McDonnell about his department’s handling of the immigration raids. During that session, Councilmember Imelda Padilla, who represents a heavily Latino district in the San Fernando Valley, asked McDonnell if the LAPD would consider warning warn council members about impending raids.
“Chief McDonnell correctly identified that request for what it was: ‘obstruction of justice,’” the lawsuit states.
The federal filing comes as the city’s elected officials are weighing their own lawsuit against the Trump administration, one aimed at barring immigration agents from violating the constitutional rights of their constituents.
The City Council is scheduled to meet Tuesday to ask City Atty. Hydee Feldstein Soto to prioritize “immediate legal action” to protect L.A. residents from being racially profiled or unlawfully searched or detained.
Bass has been outspoken about the harm she says the immigration raids have been inflicting on her city, saying they have torn families apart and created a climate of fear at parks, churches, shopping areas and other locations. The city was peaceful, she said, until federal agents began showing up at Home Depots, parking lots and other locations.
“I want to tell him to stop the raids,” she said earlier this month. “I want to tell him that this is a city of immigrants. I want to tell him that if you want to devastate the economy of the city of Los Angeles, then attack the immigrant population.”
Times staff writer Dakota Smith contributed to this report.