Who is Leqaa Kordia, the Columbia protester still in ICE detention? | Explainer News
Leqaa Kordia, a 33-year-old Palestinian woman detained in the United States by the Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agency since March, has been rushed to a hospital after a medical episode, according to media reports.
Kordia is being held in Texas after being detained as part of US President Donald Trump’s crackdown on pro-Palestine protests on college campuses across the country.
Her legal team said she was targeted for her protest against Israel’s genocidal war in Gaza near Columbia University in New York in 2024, but the federal government said she was arrested for allegedly overstaying her student visa.
Since her hospitalisation on Friday, Kordia’s legal team and family said they have not been able to speak with her and do not know her whereabouts.
Here is everything we know about Kordia and why she continues to remain in detention:
Who is Kordia?
Kordia grew up in the occupied West Bank city of Ramallah before coming to the US in 2016. She arrived on a visitor’s visa, staying with her mother, a US citizen, in Paterson, New Jersey, home to one of the largest Arab communities in the country.
She later transitioned from a tourist visa to a student visa, according to her habeas corpus petition.
After her mother applied for Kordia to remain in the US as the relative of a citizen, her green card application was approved in 2021. However, she received incorrect advice from a teacher that led to her student visa expiring in 2022, according to her lawyers.
Before her arrest, Kordia worked as a server at a Middle Eastern restaurant on Palestine Way in New Jersey and helped to care for her autistic half-brother.
Kordia was moved to protest against Israel’s war due to personal loss. Since the start of the war in October 2023, Kordia said, more than 200 of her relatives have been killed.
Israel has killed more than 71,000 Palestinians in Gaza and wounded more than 170,000 in a war that human rights groups, a United Nations commission and a growing number of scholars said amounts to genocide. Since a “ceasefire” began in October, Israel has killed more than 500 Palestinians and continues to impose curbs on the entry of aid into Gaza.
If deported, Kordia would be handed over to the Israeli government.

Why was Kordia arrested?
She was first arrested in April 2024 during a protest outside the gates of Columbia University, but the case was soon dropped.
On March 13, 2025, Kordia showed up at the ICE headquarters in Newark, New Jersey, for what she believed to be routine immigration questions. She was detained there, “thrown into an unmarked van and sent 1,500 miles [more than 2,400km] away”, Kordia wrote in the USA Today newspaper last month.
Kordia was neither a student at Columbia University nor a part of political circles.
“Though I was not a student, I felt compelled to participate. After all, Israel, with the backing of the United States, has laid waste to Gaza, forcibly displacing my family, killing nearly 200 of my relatives,” she wrote in USA Today.
Today, Kordia is the only person who remains in detention from the Columbia campus demonstrations. She has been held at Prairieland Detention Center in Alvarado, Texas.
A leader of the protests, Mahmoud Khalil, a Palestinian student with Algerian citizenship and a US green card, and others have been released. Khalil, however, is still in a legal battle to remain in the US with his American wife and child. Last month, an appeals court panel dismissed a lawsuit Khalil filed challenging his detention and deportation order. The judges concluded that the federal court that ordered Khalil’s release last year lacked jurisdiction over the matter.

What are the charges against Kordia?
The US government has called Kordia’s money transfers to relatives in the Middle East evidence of possible ties to “terrorists”.
Kordia’s lawyers have continuously argued for her release, saying she was targeted by federal officials for her participation in pro-Palestinian protests.
The federal government has maintained that the case against Kordia is of overstaying a student visa.
“Her arrest had nothing to do with her radical activities,” the Department of Homeland Security said in April. “Kordia was arrested for immigration violations due to having overstayed her F-1 student visa, which had been terminated on January 26, 2022, for lack of attendance.”
Writing in USA Today last month, Kordia said she does not consider herself either a leader or an activist.
“I am a devout Muslim who is deeply committed to my faith and community. I’m a Palestinian woman who enjoys playing the oud, making pottery and hiking,” Kordia wrote. “Speaking out against what rights groups and experts have called a genocide is my moral duty and – I thought – a constitutionally protected right for all in this country. Except, it seems, when that speech defends Palestinian life.”
An immigration judge has called for Kordia’s release twice. However, it has been repeatedly blocked through a series of procedural and administrative moves.
“[The] Trump administration has exploited rarely used procedural loopholes to keep me confined, a practice now being challenged in federal district courts across the country, with many finding the practice unconstitutional,” Kordia wrote.

How has Kordia lived in ICE detention?
Since Kordia was moved to the ICE detention facility in Alvarado in March, she has been facing a range of issues, from sleeping on a bare mattress on the floor to being denied religious accommodations, including halal meals.
“Inside the ICE facility where I’m being held, conditions are filthy, overcrowded and inhumane,” Kordia wrote in her piece for USA Today. “For months, I slept in a plastic shell, known as a ‘boat,’ surrounded by cockroaches and only a thin blanket. Privacy does not exist here.”
Last year, when Kordia’s cousin Hamzah Abushaban visited her a week after her arrest, he told The Associated Press news agency in an interview that he was taken aback by the dark circles under her eyes and her state of confusion.
“One of the first things she asked me was why she was there,” Abushaban said. “She cried a lot. She looked like death.”
Rights groups and some Democratic Party leaders have called her a “political prisoner”, condemning the way her case has proceeded.
State Representative Salman Bhojani said the conditions at the detention facility were “suffocating”.
Kordia’s dorm, he said, had 60 mattresses crammed into a space designed for 20 women.
“She does not even have clothing that fully covers her body. Community organizations have tried to provide more appropriate clothing and have been turned away,” Bhojani said. “Male staff enter the dorm at any time, leaving her body exposed in violation of her religious obligations.”
Calling for her release, Amnesty International noted that ICE has “repeatedly violated” Kordia’s religious rights. “She has been served almost no halal meals, forcing her to eat food that doesn’t meet her dietary requirements and causing significant weight loss,” the human rights group said in a statement.
“During Ramadan, staff refused to let her save food for when she could break her fast, forcing her either to go hungry or to break her fast early,” Amnesty said. “She has not been provided with clothing suitable for prayer or a clean prayer space.”

Why was Kordia hospitalised?
On Friday, Abushaban said he heard about Kordia’s hospitalisation in the morning from a person formerly detained with his cousin.
Kordia had fallen, hit her head and suffered a seizure in a bathroom at the Prairieland Detention Center, he told The Dallas Morning News newspaper.
In a statement on Saturday, Kordia’s attorneys and family members demanded answers from the Department of Homeland Security and Prairieland Detention Center regarding her health and whereabouts.
“[Kordia] was reportedly hospitalised yesterday morning after fainting and having a seizure at the Prairieland Detention Center,” the statement said, adding: “Neither her legal team nor family have been provided answers about where she has been hospitalised, the specifics of her health status, and whether and how ICE will ensure her health upon discharge from the undisclosed, off-site hospital.”
“We have since learned that she is expected to spend another night there, but we still have not been able to speak with her directly or have any confirmation of what brought her to the hospital in the first place,” the statement said.
The family members told US media that they called all hospitals in the vicinity but could not locate Kordia.

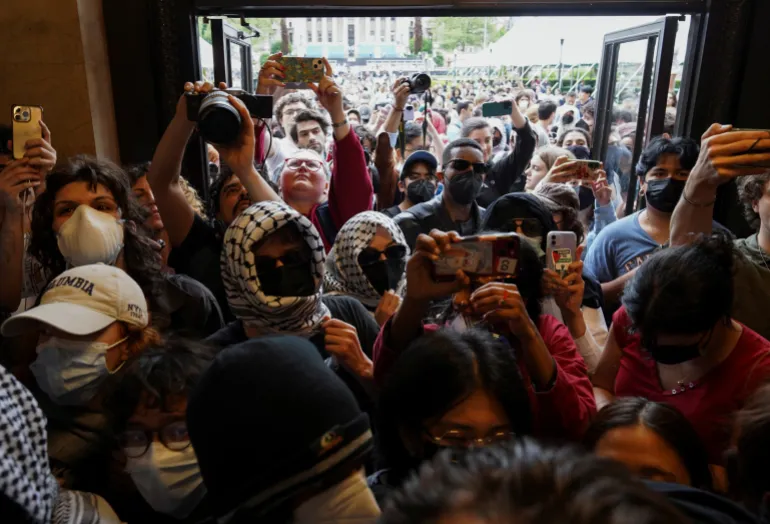
What were the Columbia protests about?
In 2024, pro-Palestinian student encampments at Columbia University helped ignite a global movement against Israel’s genocidal war on Gaza.
The protest sites, however, were broken up after Columbia University allowed hundreds of New York City police officers on campus, leading to dozens of arrests.
The student protesters demanded an end to Israel’s war in Gaza and the university’s divestment from companies linked to the Israeli military.
Columbia University imposed severe punishments, including expulsion and revocation of academic degrees, on dozens of students who participated in the protests. University President Nemat “Minouche” Shafik, who was criticised for the handling of the student protests, stepped down.
The protests also put Columbia at odds with the Trump administration, whose officials alleged anti-Semitism on campus. Campaigners said the campus crackdown violated US free speech rights.
Trump also cancelled millions of dollars in federal funding for the university, accusing it of failing to protect Jewish students. Later, Columbia settled and agreed to pay $200m to the government over three years. In exchange, the Trump administration agreed to return parts of the $400m in grants it froze or terminated.