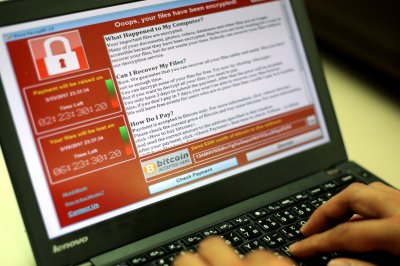
Cyberattack closes dozens of Mississippi medical clinics

Feb. 20 (UPI) — The University of Mississippi Medical Center closed its 35 clinics throughout Mississippi on Friday after being targeted in a ransomware attack.
Medical center officials also canceled all elective medical procedures that were scheduled for the day and rescheduled all but dialysis appointments at the medical center’s location in the Jackson Medical Mall in the state’s capital.
That medical center remained open and provided medical services on Friday. Hospital officials said they and federal law enforcement were in contact with those who carried out the ransomware attack.
“We continue to work with federal authorities and national experts in cyberattack response as we evaluate the extent of the attack and our next steps,” medical center officials said in a Facebook post Thursday.
“We expect this to be a multi-day event and will communicate helpful information when available.”
The university medical center’s hospitals and emergency departments also were open. Officials said they plan to announce any closures that might affect those healthcare service providers if it becomes necessary.
University officials also canceled all online classes Friday, but in-person classes were held.
University Vice Chancellor for Health Affairs LouAnn Woodward confirmed a ransomware attack affected the medical center’s key network systems, including Epic and its medical records.
Woodward said officials at the medical center shut down its IT systems out of precaution and do not know when the matter might be resolved.
In the meantime, doctors and medical center staff were using pen and paper while continuing to provide medical services for patients until the IT system is restored.
The university health clinics provide many services, including treating cancer and chronic pain.