Ukraine pulls plug on Russian Starlink, beefs up drone defence | Russia-Ukraine war News
Ukraine braced for more attacks on its energy infrastructure this week as winter temperatures continued to fall to -20 degrees Celsius (-4 degrees Fahrenheit), and sought to adapt its defences against Russian drones.
On Thursday, Ukraine’s energy minister, Denys Shmyal, warned Ukrainians to prepare for more power blackouts in the coming days as Russian air attacks continued.
Prime Minister Yulia Svyrydenko said Russia had struck energy infrastructure 217 times this year. Shmyal said 200 emergency crews were working to restore power to 1,100 buildings in Kyiv alone.
Russia has been targeting Ukrainian power stations, gas pipelines and power cables since mid-January, leaving hundreds of thousands of people without heat or electricity at various points.
On January 29, US President Donald Trump told a cabinet meeting that Russian President Vladimir Putin had agreed to halt strikes on Ukraine’s energy infrastructure for a week, something the Kremlin confirmed.
“I personally asked President Putin not to fire into Kyiv and various towns for a week, and he agreed to do that,” Trump said.
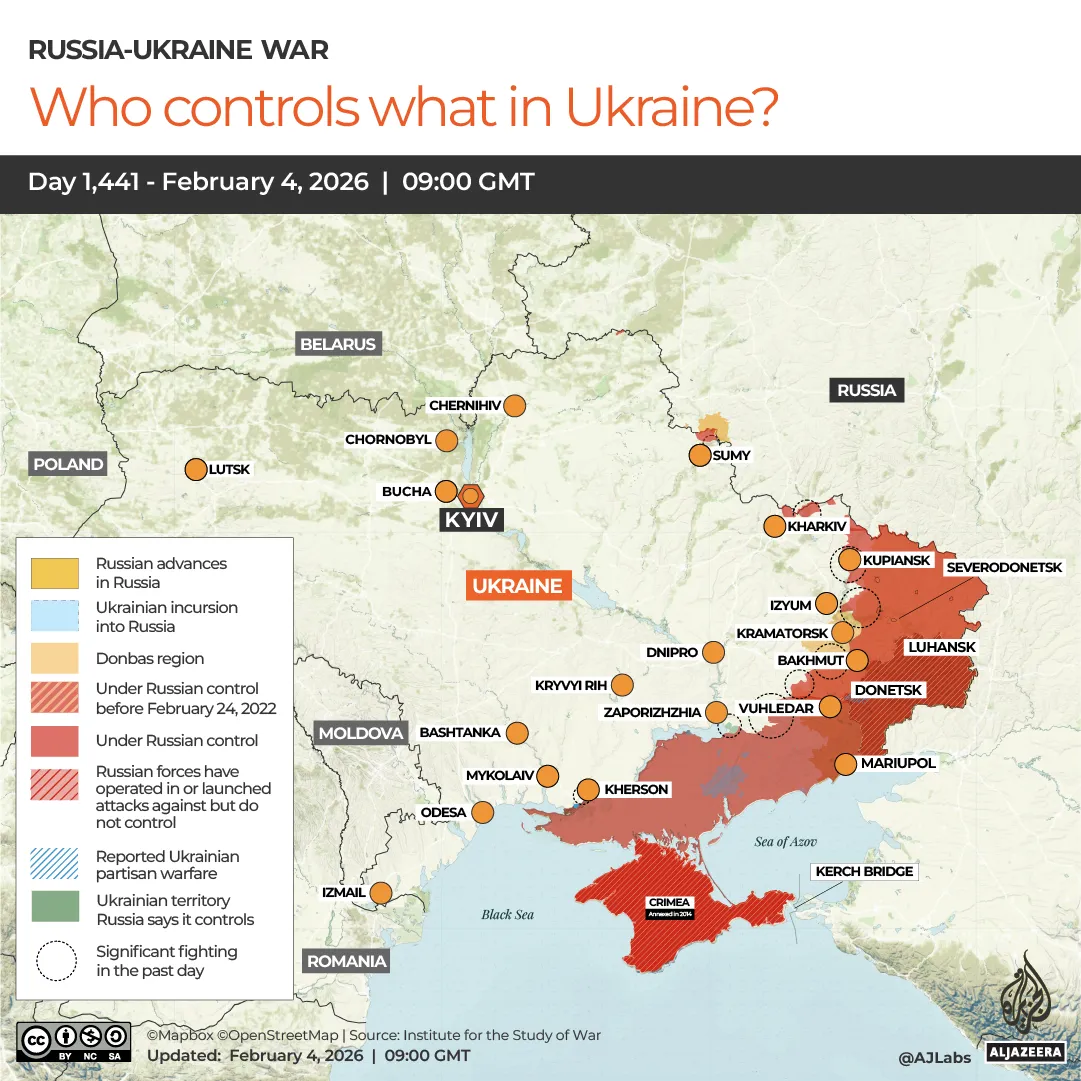
It was unclear when that conversation happened, exactly, but on Tuesday this week, Russia unleashed one of its biggest strikes ever on energy infrastructure in Kyiv and Kharkiv, deploying 71 missiles and 450 drones.
Ukraine’s Air Force spokesperson Yurii Ihnat said Ukraine had only managed to shoot down 38 of the missiles because a very high proportion of them were ballistic.
Russia’s defence ministry claimed it was targeting storage sites for unmanned aerial vehicles, defence enterprises and their energy supply.
The strike coincided with a visit to Kyiv by NATO Secretary-General Mark Rutte, and came a day before tripartite talks among Russia, Ukraine and the US resumed in Abu Dhabi.
“Last night, in our view, the Russians broke their promise,” Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said in his news conference with Rutte. “So, either Russia now thinks that a week is less than four days instead of seven, or they are genuinely betting only on war.”
The strike also came just as Kyiv had managed to reduce the number of apartment buildings without heat from 3,500 three days earlier, to about 500.
At least two people, both aged 18, were killed as they walked on a street in Zaporizhzhia, southeast Ukraine.
Even on relatively quiet days, Russia causes civilian deaths. On Sunday, February 1, Russia killed a dozen miners when a drone struck the bus that was taking them to work in Ukraine’s central Dnipro region.

Evolving drone tactics
During the few days in which it did observe the moratorium on energy-related strikes, Russia focused on striking Ukrainian logistics instead and made attempts to extend the reach of its drones.
Ukrainian Defence Ministry Adviser on Technology and Drone Warfare Serhiy “Flash” Beskrestnov reported that Russian drones were striking Ukrainian trucks 50km (31 miles) from the front line. He also said Russia had adapted its Geran drone to act “as a carrier” for smaller, first-person view (FPV) drones, doubling up two relatively cheap systems for greater range.
Ukrainian broadcaster Suspilne said Russia had begun these new tactics in mid-January.
Ukraine’s Air Force has managed to down about 90 percent of Russia’s long-range drones, and a high proportion of its missiles – almost 22,000 targets in January alone.
Zelenskyy recently demanded better results, however, and one of the Ukrainian responses to Russian tactics has been a new, short-range “small air defence” force that uses drones to counter drones.
“Hundreds of UAV [unmanned aerial vehicle] crews have already been transferred to the operational control of the Air Force grouping – they are performing tasks in the first and second echelons of interception,” wrote Ukrainian commander-in-chief Oleksandr Syrskii on Wednesday this week.
Ukraine’s second response has been to disable Russian Starlink terminals, which Russia uses extensively on the battlefield, and has recently begun mounting on UAVs.
Starlink uses low-orbit satellites and is impervious to jamming, allowing Russia to change a drone’s intended target while it is in mid-flight.
Ukraine’s newly installed defence minister, Mykhailo Fedorov, has been creating a “white list” of Starlink terminals used by the armed forces of Ukraine, and sent them to Starlink owner Elon Musk, asking him to keep these operational while shutting down all others in the Ukraine theatre.
“Soon, only verified and registered terminals will operate in Ukraine. Everything else will be disconnected,” Fedorov wrote on Telegram.
“Looks like the steps we took to stop the unauthorized use of Starlink by Russia have worked. Let us know if more needs to be done,” Musk wrote on Twitter on Sunday.
Fedorov and Beskrestnov have been asking Ukrainian soldiers and civilians to register any Starlink terminals they acquire privately on the white list.

More sanctions on the way
On the day of Russia’s large strike, Zelenskyy appealed to the US to pass a bill long in the making that would impose more sanctions on buyers of Russian oil. China is the biggest, followed by India.
The previous day, Trump said Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi had agreed to stop buying Russian oil. “He agreed to stop buying Russian Oil, and to buy much more from the United States and, potentially, Venezuela. This will help END THE WAR in Ukraine,” he wrote on his social media platform.
A Russian government source told Reuters that an assumed 30 percent drop in oil sales to India, and lower sales to other customers, could triple Moscow’s planned budget deficit this year from 1.6 percent of GDP to 3.5 percent or 4.4 percent. Government data released on Wednesday showed the Kremlin’s revenues from energy at $5.13bn in January, half the level of January 2025.
Zelenskyy also discussed a 20th sanctions package under preparation with European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen. “We can already see what is happening to the Russian economy and what could follow if the pressure is applied effectively,” he said.
Russia has made little headway in its ground war in the past three years, a fact repeatedly documented, most recently by a CSIS report. Despite this, its top officials continued to insist last week on terms of peace that would force Ukraine to give up control of four of its southeastern regions, cut down its armed forces and agree not to join NATO – terms Ukraine refuses.
The resumed talks in Abu Dhabi on Wednesday and Thursday yielded only a prisoner-of-war exchange of 157 a side.