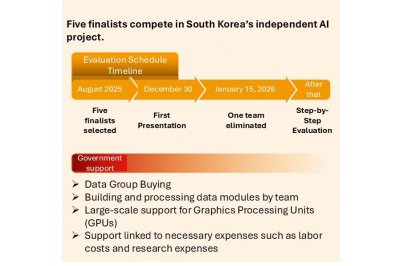
A graphic outlines the evaluation timeline and government support plan for South Korea’s sovereign AI project, including the selection of five teams, a first presentation by Dec. 30, elimination of one team by Jan. 15, 2026, and phased evaluations, alongside support such as joint data purchases, data module construction, large-scale GPU backing and funding for personnel and research costs. Graphic by Asia Today and translated by UPI
Jan. 8 (Asia Today) — South Korea’s push to develop a national artificial intelligence model has exposed a fundamental question the government has yet to answer: What, exactly, qualifies as a “sovereign” or “independent” AI?
A government-backed competition is underway to build a national AI system intended for use across society. The initiative, led by Ha Jung-woo, former Naver executive and now senior secretary for AI future planning at the presidential office, and Bae Kyung-hoon, former head of LG AI Research and now vice minister of science and ICT, aims to secure what officials call “AI sovereignty.” The stated goal is a Korean-built AI developed entirely with domestic technology.
As the competition has intensified, disputes over technical standards have moved to the forefront. The most prominent issue is whether participating models were truly built “from scratch” – a term borrowed from sports that implies starting with no preexisting foundation.
The debate first erupted when the CEO of Syonic AI publicly questioned whether Upstage’s model met that standard. Upstage CEO Kim Sung-hoon responded the following day by opening all training logs, checkpoints and experiment records for public verification. The company live-streamed the session, answered questions without prior preparation and ultimately received a public apology from the original accuser.
Senior Secretary Ha and Vice Minister Bae both praised the process on social media, calling it evidence that the national AI project is fostering a healthy and transparent ecosystem. They commended Upstage for proving the allegations unfounded through verification and credited the accuser for acknowledging the findings.
The controversy did not end there.
Attention soon shifted to Naver’s own “from scratch” claim. The company acknowledged that its model uses an encoder from China’s Qwen but said the component was not significant. In a statement, Naver said it had “strategically adopted a verified external encoder” to ensure compatibility with the global ecosystem and optimize system efficiency.
That explanation has been met with skepticism in the industry. Critics argue that the encoder is a core component of the model and that identical weights suggest a level of dependence comparable to directly adopting a foreign model. Because the entire system was trained around that structure, they say, the dependency cannot simply be removed.
The contrast in responses has drawn sharp comparisons. If a national athlete faces doping suspicions, the burden of proof lies with the athlete. Upstage disclosed everything immediately. Naver, critics argue, has asked for time without offering detailed verification. Post-hoc review, they say, is meaningless once the competition is over.
Naver has countered that innovation does not require building every technology from the ground up, arguing that AI advances by adding unique value atop proven global technologies.
But that raises a larger question: Is that what the government meant by a national AI strategy?
Industry observers say the issue is not a minor technical dispute but a political and strategic one, touching on technological sovereignty, research ethics and industrial trust. Some argue that marketing ambiguous standards risks undermining the very purpose of the project.
National AI systems are expected to underpin public services, defense, finance and other critical sectors. If their core components depend on foreign technology – particularly from countries where security assurances are uncertain – the issue extends beyond competitiveness to national economic and security risks.
What defines a “domestic AI”? Where are public funds and computing resources being directed? Who verifies technological independence, and by what criteria?
These are questions only the government can answer.
The project is officially called the Independent Foundation Model initiative. Without clear standards and qualifications, however, the national AI strategy risks losing both credibility and direction.
– Reported by Asia Today; translated by UPI© Asia Today. Unauthorized reproduction or redistribution prohibited.