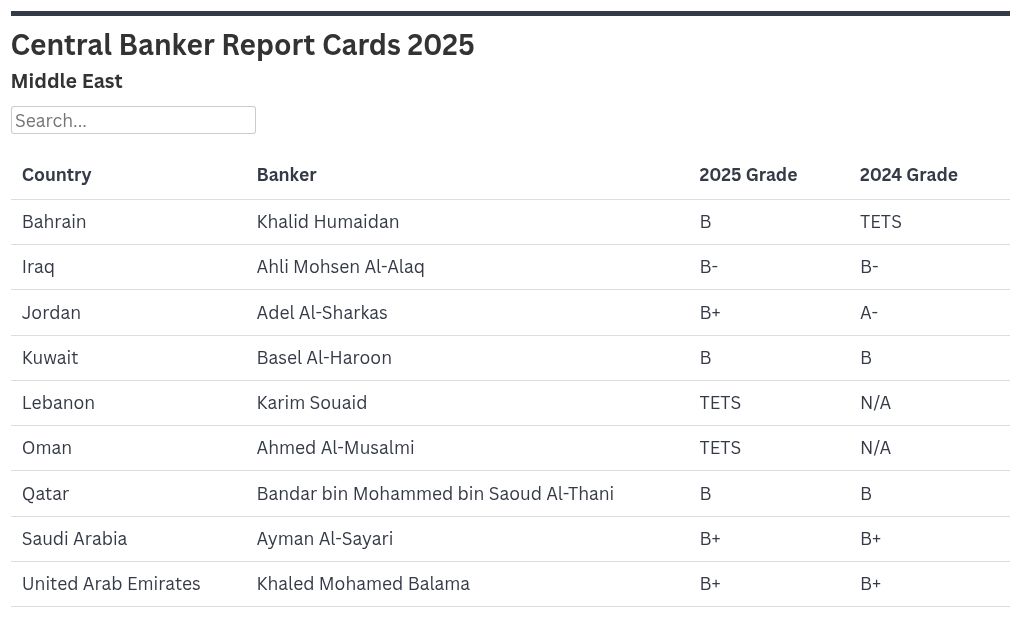
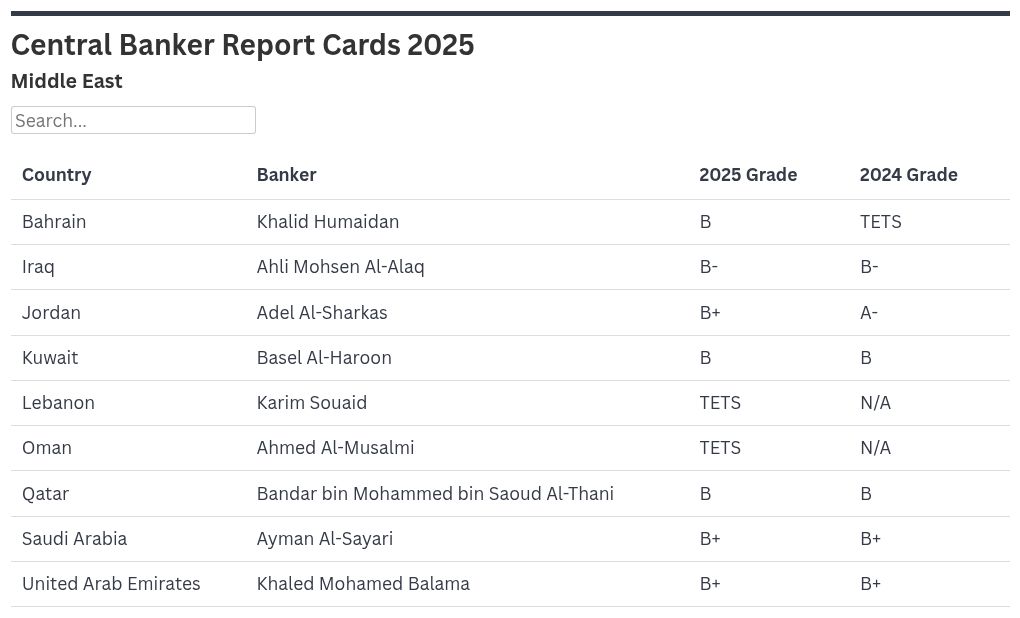
Global central banks face inflation challenges in 2026 but disagree on the right approach. Global Finance reveals the 2025 Central Banker Report Cards in Asia-Pacific.
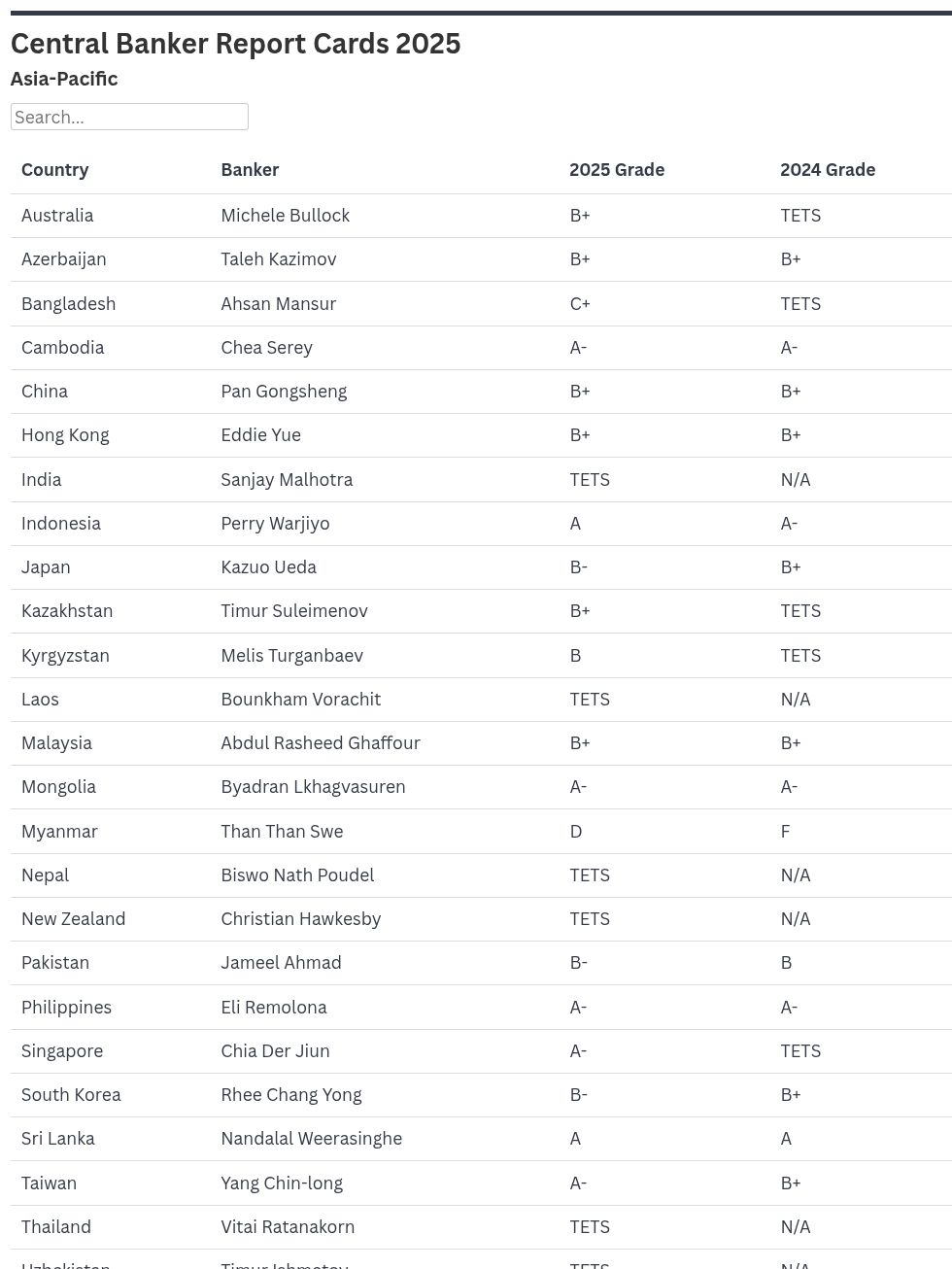
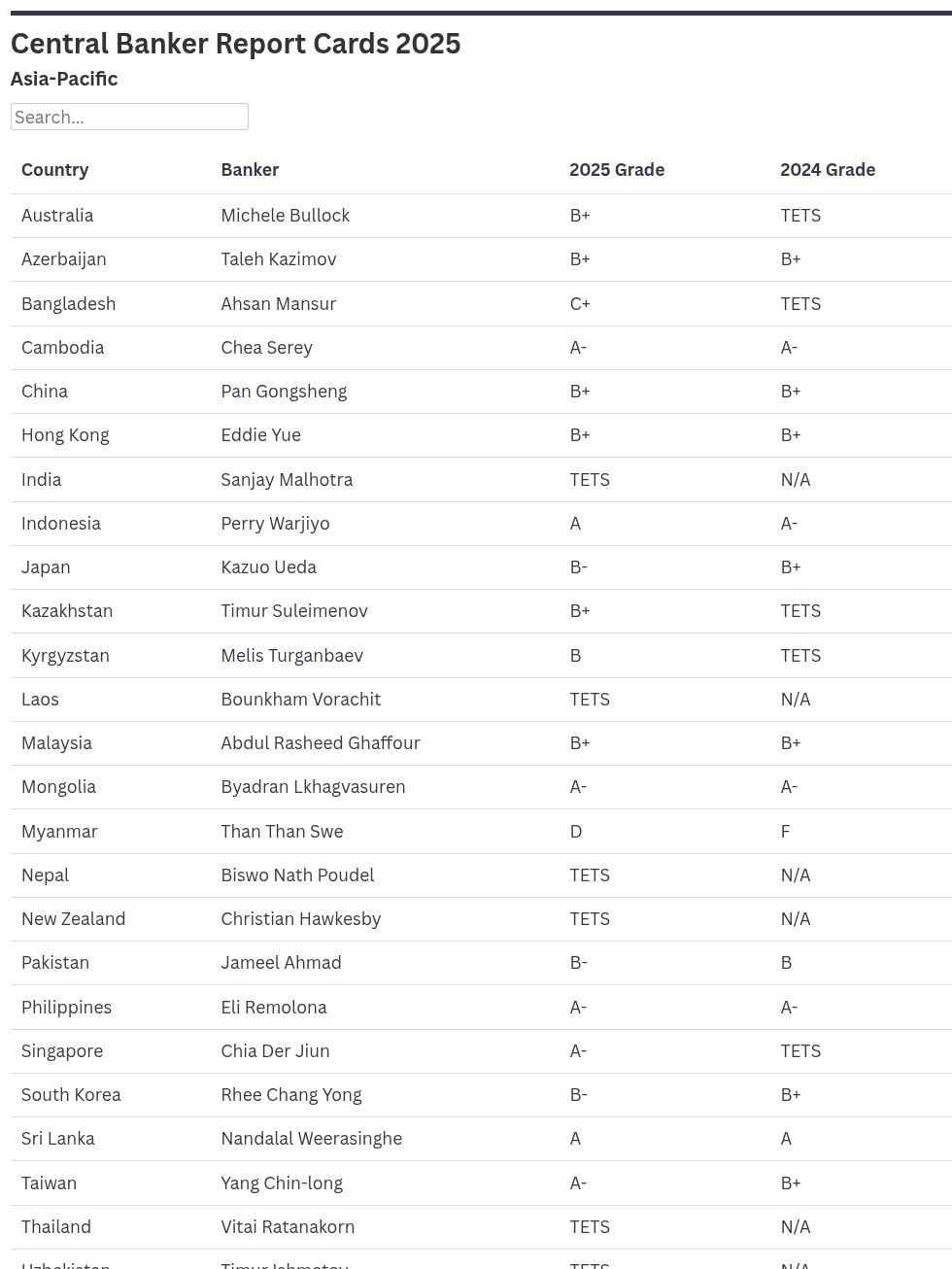
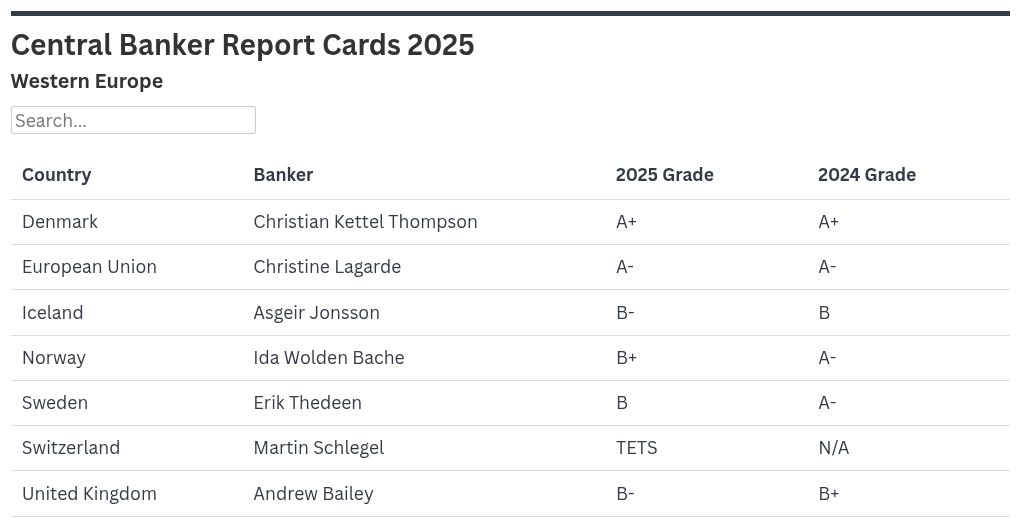
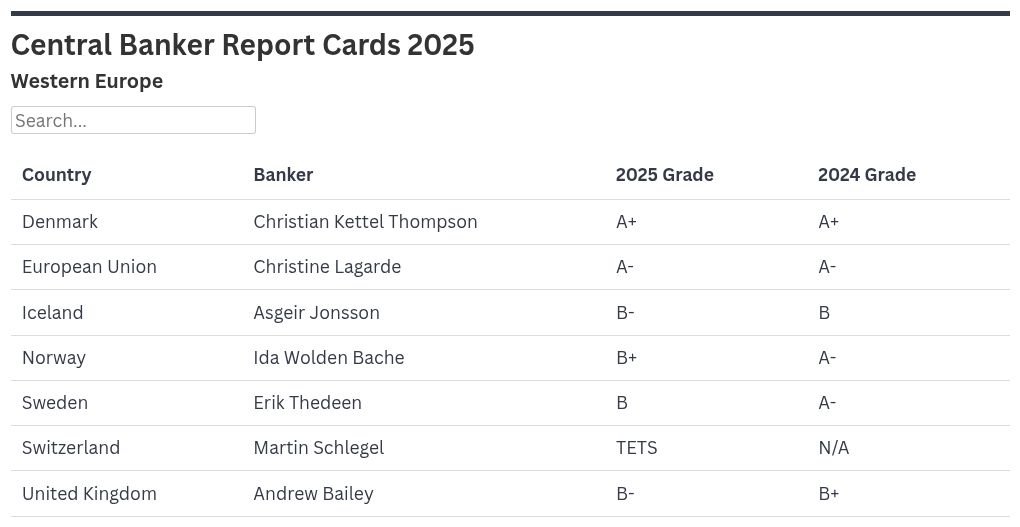
AUSTRALIA | Michele Bullock: B+
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) under Michele Bullock exasperated markets and the voluble Australian media by failing to cut the cash rate at its July meeting—even in the face of a weakening employment market, as had been revealed the previous month when the jobless rate hit a four-year high of 4.3%.
The governor’s mantra, revealed at a speech made in Sydney in July, is that the RBA’s approach to monetary policy should be “measured and gradual.” Fair enough, perhaps—the RBA had cut the cash rate twice prior to the decision to stand pat in July, down to 3.85%. It was duly cut again in August by 25 basis points (bp).
In Bullock’s favor, the inflation dynamic is auspicious: Core inflation was 2.7% in June, down from 2.9% in the March quarter, having fallen each quarter since peaking in December 2022. Meanwhile, the Australian dollar has so far weakened by around 1.8% against the US dollar without pressuring domestic inflation.
Australia faces the same issues plaguing many Western economies: sluggish growth, prohibitively priced housing stock, and high levels of government debt and of doubts surrounding fiscal sustainability.
Still, relative to many Western economies, Australia’s debt-to-GDP ratio is a relatively manageable 35.5%; though it is forecast to rise steadily over the next five years. And while the RBA forecasts 1.7% GDP growth for 2025, it is worth noting that in the 20 years up to the COVID-19 pandemic, Australia’s growth averaged 3%, indicating a declining secular trend.
AZERBAIJAN | Taleh Kazimov: B+
Central bank governor Taleh Kazimov has dialed down growth expectations for 2025, forecasting that GDP will hit 3% this year, versus an April prediction of 3.3%. This would be weaker than the 4.1% growth booked in 2024. Inflation is expected to hit 5.4% this year according to the Finance Ministry, versus 2.2% in 2024.
Strategic foreign exchange reserves grew to $77.4 billion in the year to July, for a 9.4% gain over the period. Over the past two years, reforms to modernize the regulation and supervision of financial institutions have been in process as part of the Financial Sector Development Strategy 2024-2026, which according to S&P will reduce risk in Azerbaijan’s banking industry.
BANGLADESH | Ahsan Mansur: C+
Former economist Ahsan Mansur assumed the governorship of Bangladesh Bank in August 2024,
at a moment of national strife and ensuing emergency, when the country’s leader Sheikh Hasina had fled the country for neighboring India under accusations of corruption and civil rights abuses.
In the interim, he has recognized with clarity the need to restore balance to Bangladeshi financial institutions, spur growth, and attack rampant inflation—in a bid to stabilize the taka, which has fallen about 4% to the US dollar so far this year—as well as the need to restore fundamental faith in the country as an investment proposition.
His first crucial decision came immediately after assuming office, when he raised the overnight repo policy rate by 50 bp to 9%, followed up by two hikes over subsequent months to take the rate to 10% in October.
Inflation was frothy at 10.5% during the first tightening but has since moderated, hitting 8.55% in July, vindicating the monetary stringency—Mansur predicts that it will ease to 5% by year-end.
He has resisted easing to boost growth—which the Asian Development Bank estimates at 3.9% for the fiscal year ended in June and forecasts as the full-year tally—holding the policy rate steady at 10% in July. This is a far cry from the 6.4% annual average growth clocked by Bangladesh between 2010-2020.
Meanwhile, Mansur has grasped the need to overhaul the country’s crisis-hit financial system. He has established a three-year road map for reform, under the auspices of the International Monetary Fund (IMF). This includes banking system consolidation, nonperforming-loan (NPL) resolution, and an overhaul of bankruptcy and restructuring legislation. Perhaps this will help bring the heady days of nonstop growth back to Bangladesh again.
CAMBODIA | Chea Serey: A-
Chea Serey hit the ground running when she assumed the governorship of the National Bank of Cambodia (NBC) in July 2023, presiding over 5.5% GDP growth and 2.1% inflation that year. NBC’s foreign exchange reserves surged 13% to $20 billion, for a flush seven months of import cover. Moreover, by February of 2024, reserves had grown to $22.5 billion, prompting the NBC to consider utilizing the reserves to invest in green and sustainable projects in Cambodia via bond purchases.
She has been maintaining her initial pace ever since: Growth in the first half of this year was a solid 5.9% even when Cambodia was confronted on what US President Donald Trump called “Liberation Day” with the highest tariffs levied on any country, a radically high 49%, which has since been reduced to 19%.
Core inflation was moderate at 2.9% for the period, a level from which it is expected to tail off in the year’s second half. The NBC expects a 2.4% full-year reading.
The governor has maintained the NBC’s focus on the digital economy, overseeing the launch in July of a cross-border QR-code payment system with Japan. This followed the rollout in January of a tourist-focused app utilizing the country’s digital currency, the bakong, in January.
In April, the NBC joined the Regional Payment Connectivity initiative, adding to the roster of nine central banks of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to have joined since the initiative was launched in 2022 with the aim of fostering financial integration within the ASEAN region.
CHINA | Pan Gongsheng: B+
China’s economy is weighed down by a chronic failure of demand to respond optimally to the supply-side-focused policies applied by regulators and the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) over the past few years.
Helping to explain the weak demand are the dampening effects of a brutal real estate correction, manifested in loss of consumer sentiment and weak growth in retail sales and in services. This is underpinned by an aging population demographic and ongoing trade tension.
Deflationary pressure is the result; but Pan Gongsheng, PBOC governor since July 2023, has been proactive, loosening monetary policy in May, a month after US President Trump fired his “Liberation Day” tariff salvo.
The seven-day reverse repo rate was cut by 10 bp, as were the one-year and five-year loan prime rates (now at their lowest levels since 2019). Meanwhile, the required reserve ratio (RRR) was cut by 50 bp—a move expected to unleash 1 trillion renminbi (about $140.5 billion) of long-term liquidity.
Pan’s timing was apposite—even though increased US tariffs on China were suspended and remain on hold at the time of writing—given that according to Lian Ping, chairman of the China Chief Economist Forum, exports could fall 2%-2.5% for every 10% increase in US tariffs, creating a “chain reaction in the areas of consumption and investment.”
Banks also cut deposit rates by 5 to 25 points and face constricted net interest margins that fell to 1.4% in the first quarter—an all-time low. Credit demand remains weak, and it remains to be seen whether the PBOC’s supply-side measures will contribute to the government’s 5% GDP growth target for 2025.
HONG KONG | Eddie Yue: B+
Eddie Yue, CEO of the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA), has kept a close eye on the US dollar: Hong Kong dollar interest rate differential this year, which has opened up an attractive carry trade via which speculators can borrow in cheap Hong Kong dollars and reinvest the proceeds in US dollar assets.
This has caused prolonged weakness in the Hong Kong unit over the course of this year and put the trading band that restricts the US$:HK$ exchange rate in a 7.75-7.85 band under severe pressure.
The HKMA has been actively intervening in the foreign exchange market over the summer, having intervened 11 times since late June. It drained over HK$3.37 billion (about US$433 million) in liquidity in one week in a bid to boost Hong Kong dollar funding costs and deter carry trades—a successful intervention that boosted the local unit to a three-month high.
Elsewhere, Yue has spearheaded a drive to boost the use of digital currencies in the city-state. As of July, 22 Hong Kong banks had been licensed to distribute digital assets onshore, resulting in a rise of more than 200% in transaction volume versus the previous year. He has overseen the Stablecoin Ordinance, which came into effect in August, establishing a licensing regime for fiat-referenced stablecoin issuers—to regulate their issuance, offering, and marketing in Hong Kong—and positioning the HKMA as supervisor and enforcer.
INDIA | Sanjay Malhotra: Too Early To Say
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has a new governor. Sanjay Malhotra replaced central banking legend Shaktikanta Das at the RBI last December and has large shoes to fill. Malhotra was promoted from his role as revenue secretary in the Narendra Modi government and holds a master’s degree in public policy from Princeton University. He has a notably strong working relationship with India’s Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman. In his new role, Malhotra will be under pressure to ease monetary policy in response to the 50% tariffs imposed on India in August by the Trump administration and as GDP growth declined in the third quarter to 5.4%, representing a seven-quarter low.
INDONESIA | Perry Warjiyo: A
Bank Indonesia’s Perry Warjiyo is one of the Asia-Pacific region (APAC)’s most experienced central bank governors, having been in office since 2018. During his tenure, he has demonstrated a subtle grasp of his craft, particularly in controlling inflation and maintaining growth in ASEAN’s largest economy.
While sentiment toward ASEAN’s economy remains febrile in the era of the Trump tariffs—settled for Indonesia at 19% in July—Indonesia’s GDP growth is forecast to hit 5.1% in 2025, up from the 5% registered last year. According to Warjiyo during comments made to a press conference in Jakarta in August, maybe higher.
Warjiyo responded in August to the anemic credit growth in Indonesia’s financial system, which fell to 7% in July from 7.8% the prior month, by unveiling 383 trillion rupiah (about $23.4 billion) of macroprudential liquidity incentives to be disbursed through stateowned banks, development banks, domestic private commercial banks, and foreign bank branches, to boost banking system credit growth. Various recipients were targeted, in sectors including real estate; trade; manufacturing; transportation; tourism; micro, small, and midsize enterprises (MSMEs); and green businesses.
The rupiah spiked in April, in response to US President Trump’s threats to impose a 32% tariff on Indonesia, to just over 1,700—the lowest to the dollar since the Asian Financial crisis of 1997. But it has since given way to currency stability, with the unit trading back to 1,620 by August.
JAPAN | Kazuo Ueda: B-
The yen reached an all-time low in July last year of 161 yen to the dollar, just prior to the Bank of Japan (BoJ)’s second rate-tightening of 2024, by 15 bp, which took the short-term policy rate to 0.25% and brought with it the Japanese stock market’s biggest one-day crash. BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda blamed the volatility on fears of an American recession.
That explanation was unconvincing, as Japan had just abandoned 17 years of ultra-easy money explained by domestic inflationary pressure; but now policy decisions emanating from the US in the form of President Trump’s tariffs appear to be driving the BoJ’s monetary stance. Rate tightening, viewed as a given under Ueda’s governorship, is no longer baked in.
Annual wholesale inflation slowed in June for the third successive month; and despite rising food prices, the inflation that prompted last year’s rate hikes is abating.
The Trump tariffs levied on Japan, apparently settled at 15% in July, remain unresolved; but the BoJ has already slashed Japan’s GDP growth-rate projection for 2025 from 1.2% to 0.6% because of the dampening effect of the tariffs. Japan’s exports in July posted their biggest monthly drop in four years, thanks to reduced shipments to the US.
Japanese government bonds (JGBs) have been mired in profound weakness, with a 20-year auction in August having drawn scant demand—it was just 3.1 times covered—on the back of political uncertainty and concerns of possible fiscal expansion. The BOJ has at least grasped this threat to financial stability and has been tamping back its quantitative tightening program by continuing to buy JGBs, albeit at a tempered pace.
KAZAKHSTAN | Timur Suleimenov: B+
National Bank of Kazakhstan (NBK) Governor Timur Suleimenov delivered a solid performance in the first half of 2025, presiding over a 7.4% rise in international reserves to $112.3 billion and delivering 6.2% GDP growth—the highest rate in 14 years, fueled by an 8% increase in the non-oil economy and a 5.2% rise in services. Trade was up 8.4% to $59.7 billion, and the country ran a $6 billion current account surplus.
Still-stubborn inflation remains Suleimenov’s biggest challenge. It stood at 12% at the beginning of September, even in the face of a stable exchange rate. NBK retains a 5% inflation target, and Suleimenov indicated to a joint session of Parliament in September that monetary policy will remain restrictive in a bid to reach the target.
KYRGYZSTAN | Melis Turgunbaev: B
Inflation hit a 21-month high of 8.8% in July, fueled by rising food and transportation costs, overshooting the National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic (NBKR)’s 5%-7% target and ensuring that, under Chairman Melis Turgunbaev, the NBKR will retain a tight monetary-policy stance with the 9.25% discount rate likely to remain steady. The banking sector provided a bright spot: Total assets at commercial banks rose by 24% in the first half of 2025, system liquidity remains high, and noncash transaction volume surged more than twelvefold.
LAOS | Bounkham Vorachit: Too Early To Say
The Laos economy is stabilizing, and there are signs that the Bank of the Lao PDR (BOL) under Bounkham Vorachit may have definitively seen off the dark days of the past few years—particularly the nightmare of runaway inflation, which clocked 31% in 2023. The kip has stabilized, aided by the launch of the market-based Lao FX (LFX) platform in August 2024; and prolonged tightness in fiscal and monetary policy is starting to dampen inflationary pressure.
Run by BOL and 15 partner commercial banks, with the aim of stabilizing the kip and managing foreign-currency supply, the LFX platform provides access to the US dollar, renminbi, and Thai baht, via mobile banking platforms for spot FX trades, using the kip as an intermediary currency. The gap between parallel and official interest rates has closed since LFX was launched.
Inflation moderated to 5.3% in July, down from the double digits registered at the beginning of the year. Foreign exchange reserves rose to $2.6 billion in June, sufficient for 3.1 months of import cover. At the same time the Lao government ran a record-high fiscal surplus in 2024 and is expected to run a surplus in 2025, in a sign that the government’s five-year consolidation goals are bearing fruit.
Impediments include high levels of external debt and consequent debt-service obligations that the government has met with shortterm bond issuance and debt suspension. This can lead to exchange rate pressure and the return of inflationary expectations. A full-scale debt-restructuring exercise is required, perhaps urgently.
MALAYSIA | Abdul Rasheed Ghaffour: B+
Growth minimally undershot the Malaysian government’s 4.5% forecast in the second quarter, coming in at 4.4%, a decent performance but announced by Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) with a warning that US tariffs cloud the growth outlook for the country’s export-oriented economy. The warning was backed up days later when BNM cut the overnight policy rate (OPR) for the first time in five years, by 25 bp, down to 2.75%. This move was widely expected: 17 out of 31 economists polled by Reuters had anticipated a cut. The OPR corridor was also reduced to 2.5%-3%.
Inflation hit 1.2% in June, a four-year low, a month after exports unexpectedly dropped and after BNM had eased the RRR by 100 bp, to 1.00% again for the first time in five years.
BNM Governor Abdul Rasheed Ghaffour is a relative neophyte, having assumed office in July 2023; but these bold moves demonstrate a finger on the pulse of Malaysia’s economy and the external risks it faces. The ringgit has appreciated by 5.6% versus the US dollar this year, reducing imported inflationary pressure and easing Malaysia’s external debt-service load.
It seems likely that Malaysia will undershoot the 4.5%-5.5% GDP growth target for this year that Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim announced in July. Still, the cost of five-year credit default swap (CDS) protection for the sovereign was at 39 bp in early September, some 18 bp tighter than the July CDS quote, indicating a sanguine market take on Malaysia as a risk proposition.
MONGOLIA | Byadran Lkhagvasuren: A-
Byadran Lkhagvasuren has helmed Bank of Mongolia (BOM) since 2019 and has risen with aplomb to the challenges presented by an economy heavily mineral dependent and exposed to adverse weather events.
The mining and agriculture sectors are likely to help deliver 6.6% GDP growth in 2025, according to an Asian Development Bank forecast: The mining sector is recovering strongly, driven by demand for copper; and agriculture has bounced back from harsh winter conditions. Second-quarter GDP recovered from the March quarter’s lackluster 2.4% reading to a perky 5.6%.
Inflation moderated to 8.1% in July, an eight-month low, having reached a 9.6% high in January, the latter reading having prompted BOM to tighten rates in response by 200 bps, up to 12%, two months later. The action was effective, but it seems unlikely the BOM will ease again this year as it chases its target of 5% CPI by 2026.
Macroprudential policy intervention was also initiated by BOM at the March monetary policy meeting, via a reset of the upper limit of the debt-service-to-income ratio at 50% for banks’ newly issued and restructured consumer loans.
Fitch upgraded Mongolia’s ratings to B+ from B last September, with a stable outlook, stating that the upgrade reflected the agency’s view that “larger foreign exchange reserves, lower debt and more-manageable external debt maturities have strengthened Mongolia’s ability to withstand shocks, such as a correction in commodity markets.”
MYANMAR | Than Than Swe: D
The Central Bank of Myanmar (CBM), under Governor Than Than Swe, is facing a contracting economy—growth was forecast in a World Bank report, published in June, to shrink by 2.5% this year, partially because of the devastating earthquake that had hit in March. Rampant inflation is estimated by the Asian Development Bank to be on course to hit 29.3% this year. Widespread regular power outages do not help the contractionary dynamic.
Monetary policy remains tight, with the policy rate reported at 9% in April; and the government is running a fiscal deficit equal to 5.5% of GDP. The kyat remains volatile, and a parallel market exists for the purchase of foreign currency alongside the official rate.
In March, the CBM increased the interest rate paid on excess bank reserves to 6% in a bid to stabilize the banking sector and boost liquidity, but a dysfunctional financial sector remains entrenched. There is a pressing need to create a foreign exchange trading platform along the lines of that adopted in Laos, but there are no concrete plans to do so.
NEPAL | Biswo Nath Poudel: Too Early To Say
Biswo Nath Poudel assumed office as the 18th governor of the Nepal Rastra Bank in May, having previously served as vice chairman of the National Planning Commission. Poudel, a professional economist, emerged victorious in his appointment to the governorship after fierce infighting between various political factions in Nepal’s National Assembly. Shortly after assuming office, Poudel announced a 5% CPI target for fiscal year 2025-2026 in a bid to hit the government’s 6% full-year GDP growth target.
NEW ZEALAND | Christian Hawkesby: Too Early To Say
Christian Hawkesby was appointed interim governor of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) in April for a six-month period, having worked in senior roles at the Bank of England for nine years, up until 2010, including head of market intelligence. Hawkesby had served as RBNZ deputy governor since 2022 and replaced long-serving Governor Adrian Orr after Orr resigned unexpectedly in March of this year. In a speech delivered in August, Hawkesby proposed lowering domestic lenders’ capital requirements to free up lending and boost growth.
PAKISTAN | Jameel Ahmad: B-
The State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) engaged in a turbocharged easing exercise between May 2024 and June of this year, slashing the policy rate by 1,100 bp in the face of moderating inflationary pressure and a stabilizing external financial position. The policy rate has been halved since May of last year to 11% without inducing downside volatility in the rupee, a singular achievement for the SBP under governor Jameel Ahmad.
The SBP estimated in its August Monetary Policy Report that it expects inflation to remain in a 5%-7% range through the 2026 fiscal year, a far cry from the 38% recorded in May 2023 during the peak of Pakistan’s financial crisis.
The banking sector is in robust health, with 21% capital adequacy—a decade high—and solid earnings. The government capital account moved into surplus in the first eight months of this year on recovering exports and rising overseas-worker remittances.
Given these positive tailwinds, it is not surprising that in April Fitch Ratings upgraded Pakistan’s Long-Term Issuer Default Rating to B-/Stable from CCC+. The agency cited economic recovery, structural reforms, and improving fiscal performance. In an August commentary, Fitch says, “We expect the country’s real GDP growth to accelerate to 3.5% by 2027 from 2.5% in 2024.”
THE PHILIPPINES | Eli Remolona: A-
Governor Eli Remolona of the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) has presided over the central bank with calm authority since he assumed office in July 2023. He seems unafraid to transmit the BSP’s thinking with an often-disarming candor, in the process providing a high level of transparency to investors and market participants.
When the peso sank to a 10-week low versus the US dollar in June, Remolona said in a Bloomberg interview, “It’s futile to intervene when it’s a strong-dollar story driven by safe-haven flows.” The peso has subsequently recovered to its April level.
That is something of a result, given that the BSP under Remolona has been embarking on a sustained easing program since August of 2024, with a cumulative 150 bp in policy rate cuts. The most-recent cut of 25 bps, to 5%, came in August.
The luxury of inflation rates at a six-year low—the headline rate was just 0.9% in July, below the BSP’s 2%-4% target—has enabled the aggressive monetary easing. This goes together with the aim of hitting the upper end of the government’s 5.5%-6.5% GDP growth target. Growth came in at 5.5% in the second quarter thanks to strong performance in the agricultural, forestry, and fisheries sectors, plus strength in services and industry.
Meanwhile, last December, the BSP completed the testing phase of Project Agila, its prototype wholesale central bank digital currency (CBDC). The adoption of the currency is seen as a strategic move toward modernizing the Philippines’ financial ecosystem and increasing inclusivity. Successfully executing the introduction of the CBDC, scheduled for next year, would be a legacy achievement for Governor Remolona.
SINGAPORE | Chia Der Jiun: A-
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), helmed by managing director Chia der Jiun since January of last year, eased monetary policy settings in April by reducing the slope of its policy band for the second loosening this year, citing potential headwinds to global trade stemming from the Trump tariff regime.
Singapore and Australia were levied with the lowest US tariffs in APAC—10%. Nevertheless, the dependence of Singapore’s economic model on trade and deep connectivity with global supply chains has prompted hypervigilance as the tariffs start to make themselves felt in the global economy.
“There are downside risks to Singapore’s economic outlook,” says an April MAS Monetary Policy Statement that accompanied the easing announcement. “A more abrupt or persistent weakening in global trade will have significant ramifications on Singapore’s trade-related sectors, and in turn, the broader economy.”
The Singapore dollar has been APAC’s second-best performing currency (after the yen), rising about 3.6% so far this year amid generalized dollar weakness, helping to tamp down inflationary pressure: The core rate eased to just 0.5% in July, the lowest since 2021.
Meanwhile GDP growth came in at 4.4% in the second quarter; and in a September report the MAS survey of economic forecasters predicted full-year growth of 2.4%, citing better-than-expected trade tensions, even though there remain fears that Singapore’s key exports of semiconductors and pharmaceuticals might end up subject to high sectoral tariffs.
In a thumbs up for Der Jiun’s managerial skills the MAS reported a record 19.7 billion Singapore dollars (about $15.4 billion) profit in the financial year ended March 31, thanks to a SG$31.4 billion gain in the bank’s investment portfolio.
SOUTH KOREA | Rhee Chang Yong: B-
Bank of Korea (BOK)’s Governor Rhee Chang Yong has been running the central bank against a backdrop of political turmoil—President Yoon Suk Yeol was impeached by the National Assembly in December after attempting to impose martial law and was removed from power in April—and the drop in international investor confidence toward South Korea that has flowed as a result.
BOK forecast 2025 growth at 0.9% and inflation at 2% during an August announcement in which it said the policy rate would remain unchanged at 2.5%, cautioning that household debt remains high, the housing market is inflated, and domestic demand remains sluggish—although the bank expects a “modest recovery” as the year progresses.
“Exports are likely to show favorable movements for some time but are likely to gradually slow as the impacts of US tariffs expand,” the central bank said.
Newly installed President Lee Jae Myung had met US President Trump just days before the BOK rate decision and negotiated a reduction of South Korea’s reciprocal tariffs with the US from 25% to 15%, engineered through President Lee’s stated intention to drive $350 billion of investment into the US. That tariff reduction may prove crucial going forward, as exports account for 44% of South Korean GDP, with the US the country’s second biggest export destination after China.
SRI LANKA | Nandalal Weerasinghe: A
Sri Lanka’s economy is supported by a $2.9 billion IMF program and has turned the corner from the economic crisis of three years ago, which was prompted by political turpitude and a collapse in foreign exchange reserves. Despite the crucial impact of the IMF funds, a large chunk of the credit for this relatively swift recovery must go to the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL)’s Governor Nandalal Weerasinghe, in office since April 2022 just after the crisis hit.
The recovery was cemented in the form of an estimated 5% GDP growth last year, and the World Bank forecasts 3.5% growth for 2025, while the governor predicted at a speech given at a summit in Singapore in July that it would come in at 4%-5%.
Ultralow inflation—which clocked -0.6% year-on-year in June—has allowed for an easy money stance, with the OPR last cut by 25 bps in May to 7.75%. Still, Sri Lanka’s $3 billion export outflow is under threat from the Trump tariffs, set at 44% in April before a three-month pause was implemented. The 44% was then reduced to 30% in July.
“I think we are in a right balance in the monetary policy. We have some space if we are to relax further, but I think right now we have a cautious approach,” said Weerasinghe in his July speech.
The governor initiated a simplification of the CBSL’s short-term dual policy rate mechanism—enacted via the Standing Deposit Facility Rate and Standing Lending Facility Rate, which were each cut by 250 bps in May 2023, kicking off the current easing cycle—with the OPR.
TAIWAN | Yang Chin-long: A-
According to S&P Global, Taiwan’s GDP growth recovered to 4.6% last year from 1.1% in 2023 and is set to hit 2.1% this year—having surged by 5.5% in the first quarter of this year—a rate that compares favorably to other developed economies, even though Taiwan faces a 20% reciprocal tariff rate from the Trump administration.
Taiwan’s central bank, the Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan), under the governorship of Yang Chin-long since 2018, has kept a tight grip on inflationary pressure. Headline CPI and core inflation fell last year to 2.2% and 1.9% respectively, moderating again in the first half of 2025 down to 2% and 1.65%. Import prices declined by 2.6% for US dollar-denominated goods and 1.1% for Taiwan dollar denominated imports, indicating that imported inflationary pressure is absent.
The bank has followed a progressive and gradual approach to monetary tightening, raising the policy rate six times since March 2022 and the RRR four times to dampen inflationary expectations. The rediscount rate is at a 16-year high of 2%.
In addition, the bank has been nimble in its macroprudential approach: It used moral suasion to encourage mortgage lenders to rein in real estate lending in August 2024, following up with its seventh round of selective credit control in September. This approach has been a success: Housing transactions have declined, the pace of housing-price increases has slowed, and the ratio of real estate lending to total bank lending has decreased.
THAILAND | Vitai Ratanakorn: Too Early To Say
Vitai Ratanakorn will take the helm of the Bank of Thailand in October for a five-year term, replacing former Governor Sethaput Suthiwartnarueput amid administrative turbulence involving the appointment of a new prime minister in early September. Ratanakorn served as president and CEO of the Government Savings Bank, where he led initiatives to reduce household debt and boost inclusivity for underbanked segments of the Thai population.
UZBEKISTAN | Timur Ishmetov: Too Early To Say
Timur Ishmetov was appointed governor of the Central Bank of the Republic of Uzbekistan last December, having served as the country’s finance minister between 2020 and 2022.
VIETNAM | Nguyen Thi Hong: A+
GDP growth was a barnstorming 7.5% in the first half of 2025, the highest in APAC and the highest recorded by Vietnam in 15 years. The government’s full-year growth target of 8.3%-8.5% now seems much less like a pipe dream and closer to a reality.
A lot of the kudos for that extraordinary first-half number must go to the State Bank of Vietnam (SBV) under its Governor Nguyen Thi Hong, who has managed to deliver growth without economic overheating, thanks to the SBV’s adroit handling of its relationship with the domestic financial sector.
Credit growth was 19.3% in the year to June, versus the same period in 2024, supported by a proactive macroprudential modus operandi: The SBV gave lending targets to credit institutions last December and instructed them to cut operational costs via the use of digital technology, thereby allowing provision of loans at affordable rates.
Average rates for new loans at commercial banks fell by 64 bp to 6.3% per annum in the first half. System reform of credit institutions has been a priority for the SBV, rooted in ongoing NPL resolution.
In the meantime, the SBV has provided foreign currency to domestic credit institutions when needed; and the dong has remained stable, with core inflation moderate at 3.2% in July, a three-month low.
As other enviable achievements, Vietnam enjoyed a record current account surplus of 6.6% of GDP last year; and trade has surged in 2025, hitting $43.4 billion in August, an all-time high. Headwinds could be building in the form of the Trump tariffs, levied at 20% on Vietnam, with their impact yet to be felt.