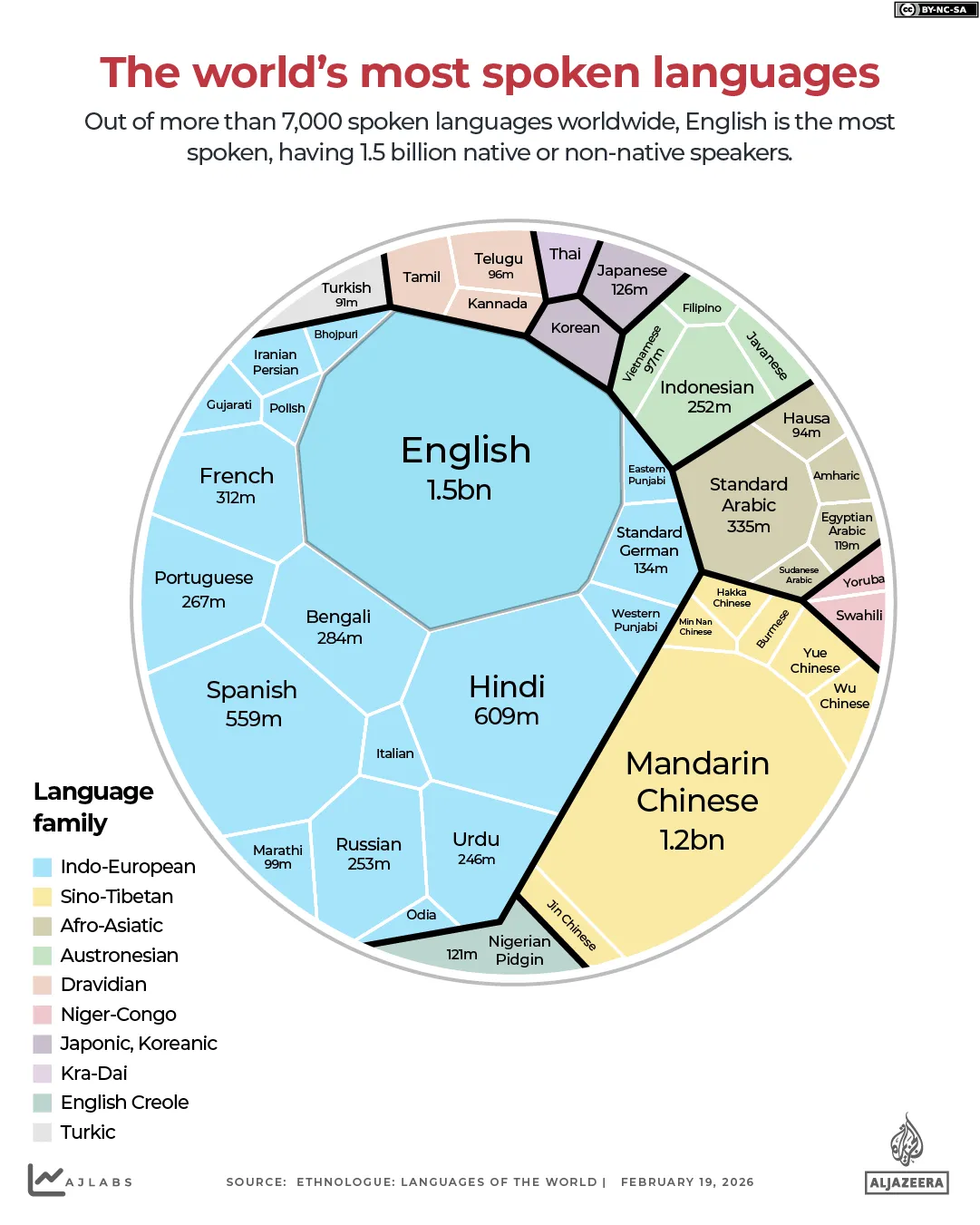
In her exploration of so-called “banned” locations Ellie Whitby set out to investigate an island in northwest Scotland, renowned for its disturbing past, and where access was strictly prohibited
A brave YouTuber has explored a remote Scottish island that was once erased from maps, but what she found was terrifying. Last year, Ellie Whitby, who runs the EllieMarieTV channel on YouTube, ventured to a mysterious island off northwest Scotland with a notoriously dark history as part of a video investigating so-called “banned” locations.
Ellie and a companion drove to Gruinard Island, also known as “Anthrax Island”, a sinister moniker it acquired after scientists contaminated the land whilst carrying out secret biological weapons experiments during World War II.
Anthrax is a potentially fatal infectious disease typically caused by the Bacillus anthracis bacterium. Following these experiments, Gruinard Island was deemed far too hazardous for both livestock and people.
The island’s grim history didn’t deter Ellie, who acknowledged it was “very scary”, but was determined to speak with local inhabitants about the site and, courageously, hoped to persuade someone to take her across to the island.
She explained: “So, we’re in the local town and see if there’s anyone willing to take me out to Anthrax Island, and I want to know their opinions on this. What do they think about this massive, secret government cover-up that happened a mile off their shores?”
Ellie proceeded to interview local residents, one of whom confirmed that the government kept the island under wraps, while another alleged that the tests resulted in the death of sheep on the mainland.
She ultimately discovered a kayaker called Will, who was willing to ferry Ellie across to the island. She remarked: “It was time to be one of very few people to ever step foot on an island hidden from the entire world and see if any of the conspiracies are true.”
Setting off across the water, she quipped: “I literally never used to leave my room out of fear of germs, and now I’m going all the way to an Anthrax Island. I think my therapist would be proud of me or, actually, very concerned.”
Ultimately, they landed on the island near a cave system, but Ellie seemed to have a change of heart. Once she determined there were no “nuclear bunkers”, she declared that she wasn’t “stupid enough” to remain any longer.
Back in 1942, then-Prime Minister Winston Churchill, concerned that Nazi Germany had developed a biological weapon, instructed scientists to investigate ways of weaponising the lethal bacterial infection, the BBC reports.
Located in Gruinard Bay, the 522-acre island served as a testing ground; residents in nearby settlements were unaware of these experiments, but rumours reportedly started to circulate once livestock began dying.
In a 2022 documentary, The Mystery of Anthrax Island, Edward Spiers, emeritus professor at the University of Leeds, stated: “The aim was to test whether the anthrax would survive an explosion in the field. They didn’t know that, and then would it remain virulent thereafter.
“Eighty-odd sheep were tethered at various stages downwind of the likely explosion. The explosion was done by remote control. It isn’t a great bang, a draught of highly potent spores moving down on the wind and causing infection and death wherever it goes.”
This led to devastating consequences, as the sheep rapidly developed symptoms and died; their bodies were then incinerated or buried under debris.
The covert trials lasted until 1943, but the impact of the experiments would be long-lasting. The highly resistant anthrax can reportedly remain in the soil for decades, and access to the island became strictly prohibited.
As reported by Lethbridge News, Gruinard Island was even erased from some maps due to fears that terrorist groups “would travel to the island to procure samples” of the deadly bacteria.
Deemed a success, the scientists concluded their work and returned to Porton Down, a secretive government facility in Wiltshire where research into diseases and chemical weapons is conducted.
Churchill’s proposed biological weapon was never used, and a militant group known as the Dark Harvest Commando of the Scottish Citizen Army (DHC) sought action from the government to decontaminate the island.
One of their strategies involved leaving a bucket of contaminated soil outside Porton Down. Years later, efforts were made to cleanse the island, which seemingly proved successful.
In 1990, the UK government officially announced that the island was free from anthrax, bringing a 48-year quarantine period to a close.