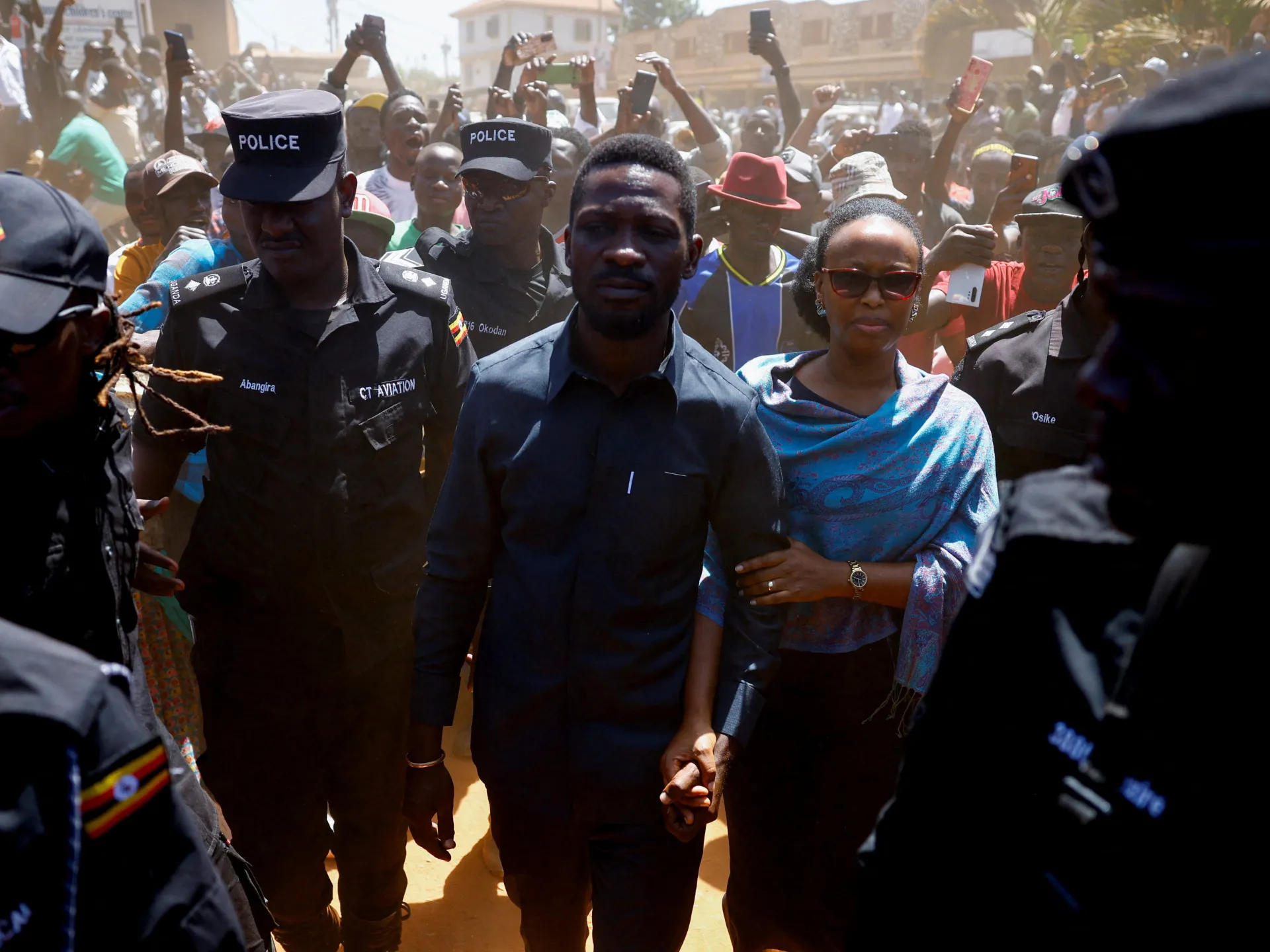Uganda’s Wine says escaped raid on house amid disputed presidential vote | Elections News
Opposition leader claims escaping police and army raid as Museveni, 81, looks set to win the presidential election.
Published On 17 Jan 2026
Ugandan opposition leader Bobi Wine says he escaped a police and army raid on his house as veteran incumbent Yoweri Museveni looks set to secure an overwhelming victory in the presidential election.
“I want to confirm that I managed to escape from them,” Bobi Wine, a former pop star whose real name is Robert Kyagulanyi, wrote in a post on X on Saturday.
Recommended Stories
list of 4 itemsend of list
“Currently, I am not at home, although my wife and other family members remain under house arrest. I know that these criminals are looking for me everywhere, and I am trying my best to keep safe.”
Bobi Wine on Friday said security forces had placed him under house arrest. His party later wrote on X that he had been “forcibly taken” from his residence by an army helicopter. The military rejected the allegation.
Bobi Wine, the country’s top opposition figure, had challenged longtime President Museveni in an election campaign that the United Nations said was marred by “widespread repression and intimidation”.
Museveni, 81, looked set to be declared the winner and extend his 40-year rule, in an election marred by reports of at least 10 deaths and intimidation of the opposition and civil society.