From Reagan to Trump: A history of government shutdowns

Oct. 8 (UPI) — Government shutdowns are the mark of some of the most tumultuous times on Capitol Hill in the United States, grinding government operations to a halt as lawmakers reach an impasse over funding.
Last week, the U.S. government was shut down after Congress failed to pass an appropriations bill or continuing resolution to continue funding employees and programs.
Republicans and Democrats stand apart on funding for Medicaid after the Republican majority and President Donald Trump passed a plan to cut access for an estimated 15 million people.
It is the third time the government has shut down during a Trump presidency.
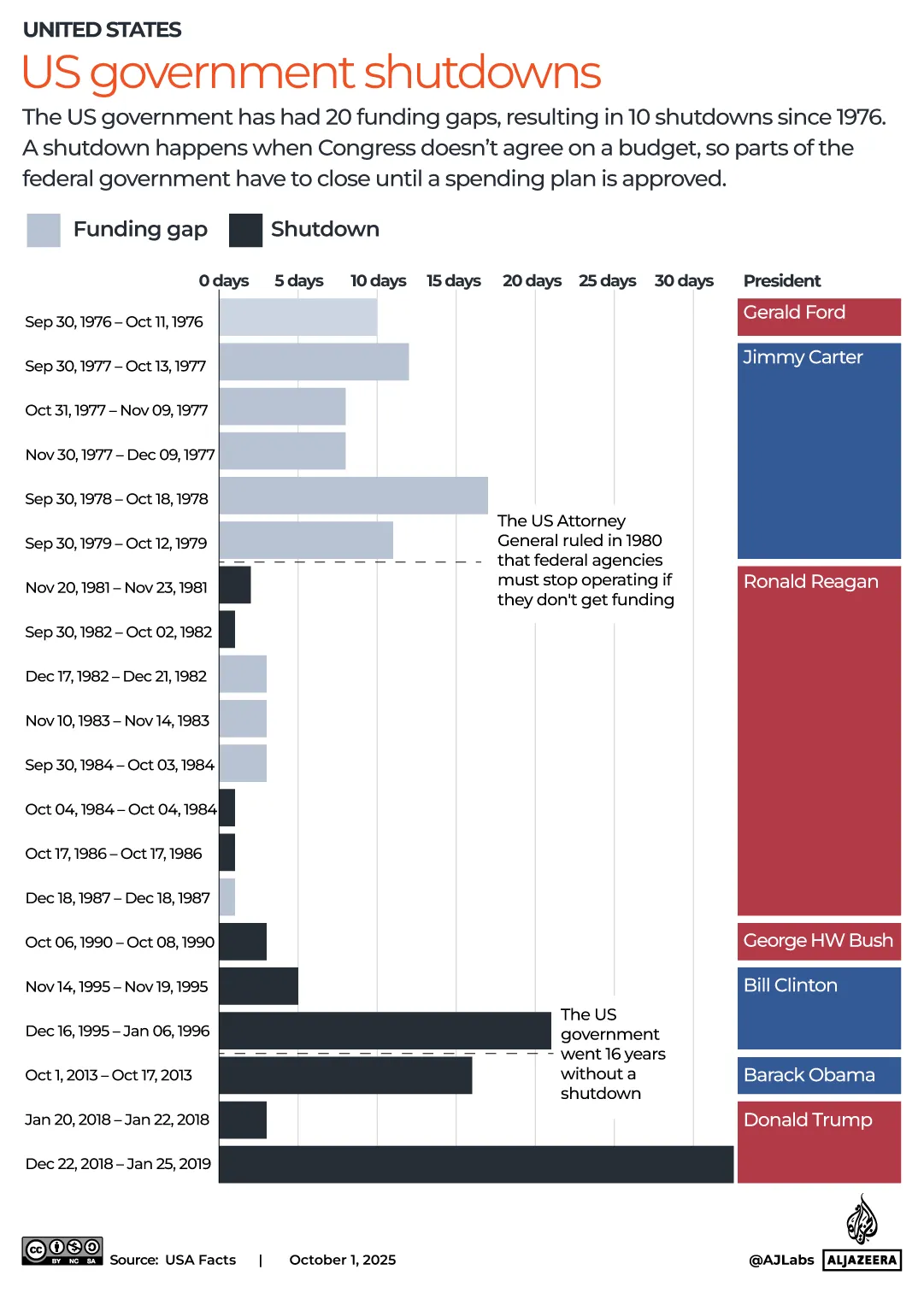
In the last 50 years the government has come to at least a partial shutdown 11 times. Some have lasted a day or more. Others have stretched into weeks.
The Civiletti opinions
The U.S. government has faced a number of funding gaps that did not result in government shutdowns. Between 1976 and 1979, there were six funding gaps that lasted eight days or more. Government agencies continued to function.
In 1980 and 1981, everything changed. U.S. Attorney General Benjamin Civiletti penned a series of opinions that outlined how and why a government shutdown would happen.
Charged with interpreting the Antideficiency Act, a law passed by Congress in 1870, Civiletti determined that government agencies are not allowed to spend funds without approval under congressional appropriations unless “necessary for the safety of human life or the protection of property.”
Based on this interpretation, most federal employees would be furloughed during a funding gap.
Civiletti loosened his interpretation slightly in a third opinion, stating that agencies can do what is necessary to shut down in an orderly manner.
Since Civiletti’s opinions, funding gaps have resulted in government shutdowns.
Reagan administration
The federal government had funding gaps on eight occasions during the presidency of Ronald Reagan, leading to at least some government agencies shutting down. It is the most shutdowns under a single president.
Three times during Reagan’s presidency, federal employees were furloughed.
In November 1981, the government shut down for two days after Reagan vetoed an emergency resolution put forward by Congress because he sought deeper funding cuts to domestic spending while maintaining defense spending.
The House, under a Democratic majority, sought to cut defense spending, and protect spending on social safety-net programs domestically.
On Nov. 23, 1981, Congress passed a joint resolution with broad support to make continuing appropriations. Reagan signed the bill that in effect bought time for the two sides to work out a longer term funding strategy.
In 1984, Reagan and Congress sparred over a crime bill, the Comprehensive Crime Control Act. It resulted in a two-day shutdown with about 500,000 federal workers being furloughed.
Reagan wanted the bill to impose stricter penalties and limit the efficacy of the insanity defense. Democrats sought to reverse a U.S. Supreme Court decision that peeled back Title IX protections.
Democrats also wanted to approve funding for local clean water projects, which Reagan opposed.
Democrats ultimately did not get the provisions they wanted in the final bill. Reagan meanwhile achieved his goal of installing stricter sentencing guidelines such as mandatory minimum sentences for drug-related crimes and no-bail detentions. The bill also raised the standard for defendants to prove insanity.
The third shutdown during Reagan’s presidency lasted about two days. On Oct. 16, 1986, a continuing resolution that averted a shutdown earlier expired.
Welfare was at the center of the disagreement between House Democrats and Reagan. Democrats again attempted to protect and enhance social safety nets with an expansion of welfare access for families with dependent children.
Reagan’s vision was starkly different. He framed welfare as a tool that made people dependent on government support.
Democrats yielded on their push to expand welfare access with a promise that it would be discussed again in the future.Congress passed an omnibus spending bill after two days of a shutdown.
The debate over welfare in 1986 set the stage for the Family Support Act of 1988, a bipartisan bill that established the Job Opportunities and Basic Skills Training program and created a new framework for child support payments, including wage withholding.
The 1990s
The first government shutdown of the 1990s was under the watch of President George H.W. Bush. The president wanted a funding bill that included a plan to reduce the federal deficit.
Democrats had a majority in the House and Senate.
On Oct. 5, 1990, government operations halted as Bush threatened to veto any bill that did not include the federal deficit plan he wanted. He vetoed such a bill the day after the shutdown began.
Two days later, the House and Senate passed a continuing resolution that was effectively the same as the bill they proposed just days earlier. Congress had the votes to sustain Bush’s veto this time, passing a bill to open the government.
The first of two shutdowns under President Bill Clinton began on Nov. 13, 1995, but the battle at the center of it caused a second shutdown to follow just weeks later.
Clinton and the Republican majority in the U.S. House, led by Speaker Newt Gingrich, were apart on spending cuts. Republicans were seeking cuts to Medicare as well as agenda items Clinton favored such as public health, public education and environmental programs.
Republicans put forward a spending proposal that included the cuts Clinton opposed. Gingrich said the House would not raise the debt limit either. After five days, the shutdown ended when Congress agreed to a stopgap funding bill.
On Dec. 15, the stopgap funding expired and a long-term agreement had not been made. The longest government shutdown to that point commenced through the holiday season, lasting 21 days.
Senate-majority leader Bob Dole, Clinton’s opponent in the 1996 election, urged his side to end the standstill and both sides agreed to a compromised budget bill. The bill included tax increases and restored funding to education, health and environmental programs.
Healthcare and immigration
The Affordable Care Act has been one of the more polarizing pieces of legislation on Capitol Hill in modern history. In 2013, House Republicans attempted to undercut the law by defunding it and delaying its implementation.
The Democratic majority in the Senate rejected attempts by the Republican-led House to strip funding from the ACA on multiple occasions throughout the budget negotiation process. The deadline to pass a budget bill came and went with no resolution and a 16-day shutdown began.
On Oct. 17, Congress passed the Continuing Appropriations Act to fund the government and suspend the debt limit in 2014. The bill did not include the Republican cuts to the ACA.
The first of three shutdowns under Trump began on Jan. 20, 2018. Congress failed to pass a government funding bill due to disputes between Trump’s Republican Party and Democrats over the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals policy.
The Trump administration attempted to end the Obama-era policy, calling on Congress to replace it within six months. A federal judge thwarted Trump’s plan and the U.S. Supreme Court eventually ruled against the president but the policy remained central to budget negotiations in the months to come.
The shutdown lasted less than three days before Congress passed a continuing resolution. A replacement for DACA was not included and the courts rejected Trump’s attempt to end the program by the time the continuing resolution expired. No protections for dreamers were included either.
Immigration remained a key issue when the government shut down again in late 2018. Trump called for funding for a border wall across the southern border to be included in the next budget bill. He demanded more than $5 billion for the project, saying the shutdown would not end until that funding was approved.
The shutdown lasted 35 days, the longest of any government shutdown in U.S. history. It began on Dec. 21, 2018 and ended on Jan. 25, 2019.
About 800,000 federal workers were furloughed during those 35 days. The Congressional Budget Office estimated it costs the United States about $11 billion in gross domestic product lost.
Trump signed a continuing resolution to open the government back up without any border wall funding included. When the continuing resolution expired, Congress approved $1.375 billion for border fencing, more than $4 billion less than what Trump demanded.