Brace for surge of ‘winter killer’ that targets infants, doctors warn – the key symptom all parents must know
WITH chillier months fast approaching, Brits will be grappling with the many illnesses that like to circulate at high levels during winter.
One infection in particularly experts are raising alarm bells about is pertussis, or whooping cough, which they are warning can be fatal in young infants.
Whooping cough is a highly contagious bacterial infection affecting the lungs and airways that causes severe coughing fits, often ending in a ‘whooping’ sound as the person gasps for breath.
According to figures from the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA), cases have been rising since late 2023, with significant increases observed in 2024 and 2025.
This increase is part of a natural, cyclical pattern where cases peak every three to five years – with a peak being overdue after a period of very low numbers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
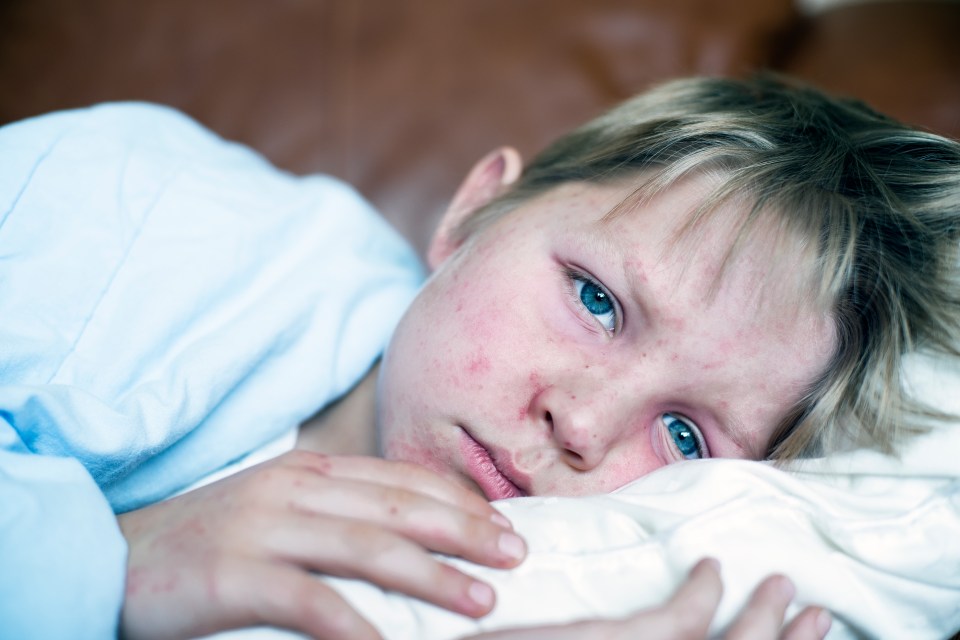
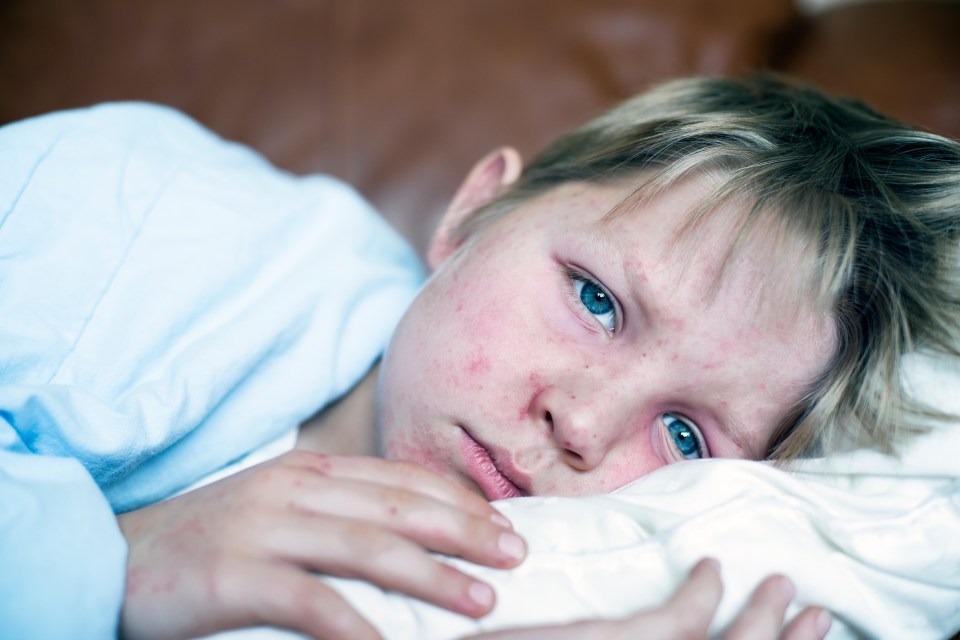
While in adults and older children the cough can be bothersome and last for months, whooping cough in young children can be life-threatening.
Read more on whooping cough
In the UK’s 2024 resurgence, infants under three months of age experienced the highest incidence and risk of severe complications, with 328 cases reported between January and June 2024.
This age group is particularly vulnerable due to their undeveloped immune systems.
In an article published in Pediatrics, experts strongly encourage getting vaccinated to protect against the illness.
According to leading author Caitlin Li, infectious disease specialist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinburg School of Medicine, said whooping cough symptoms are different in infants.
Coughing bouts that last for a few minutes and make a ‘whoop’ sound is one of the main symptoms listed by the NHS.
But DrLi said there’s a key symptom to look out for in kids.
She said: “The characteristic whooping cough may be absent, but apnea, or breathing interruption, is common.”
Whooping cough in infants can also present with very high white blood cell count, which paediatricians might mistake for cancer or other non-infectious conditions.
Extremely high white blood cell counts in infants should prompt strong consideration of pertussis, according to the authors.
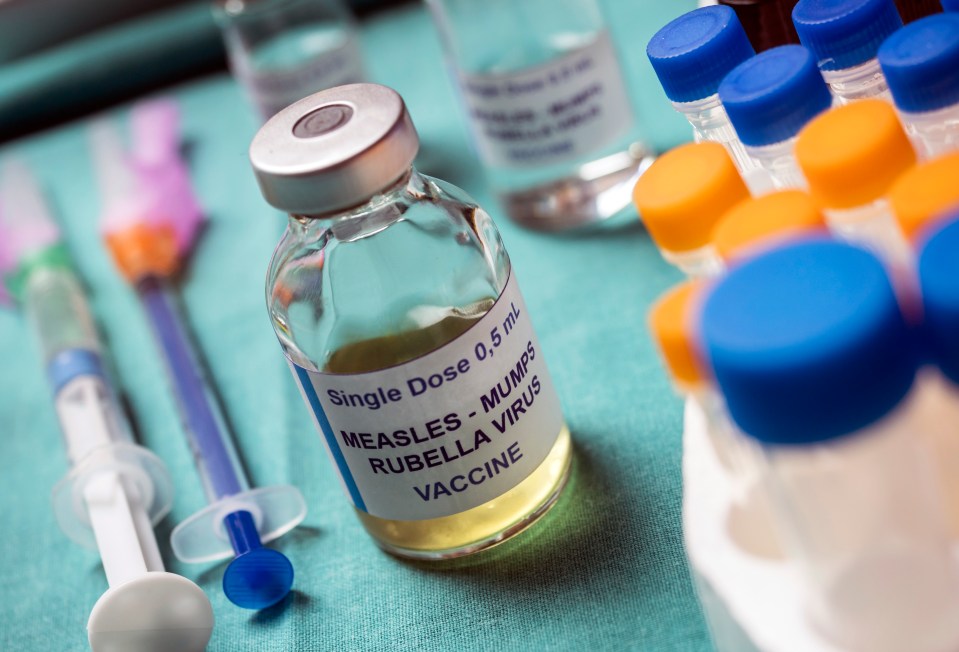
“Given that infants are at high risk for complications, pertussis vaccination of mothers during pregnancy is critical, as it protects newborns against this potentially fatal illness,” stressed Dr Li.
“Widespread vaccination is also an important tool to protect everyone.”
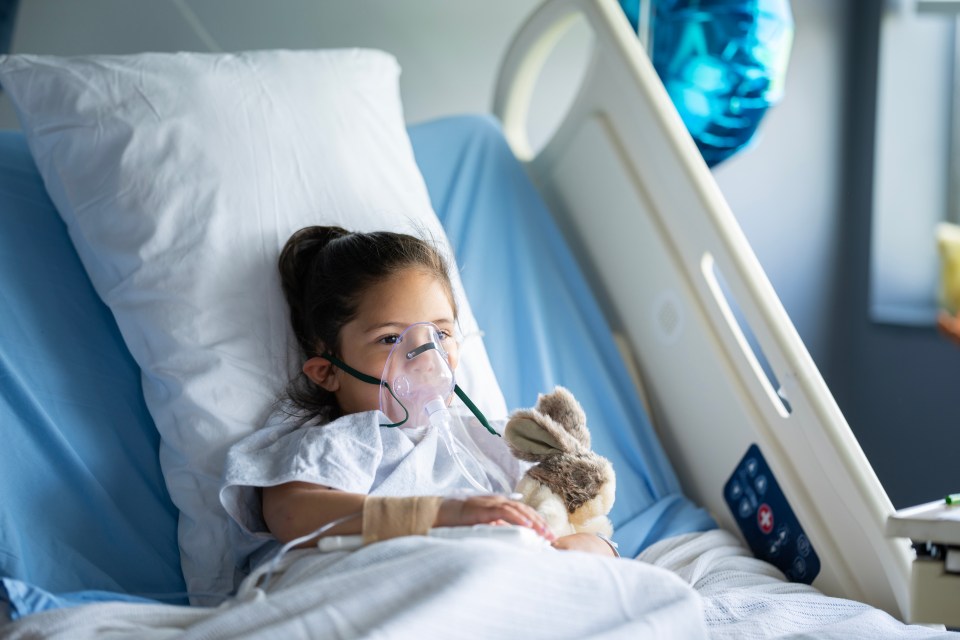
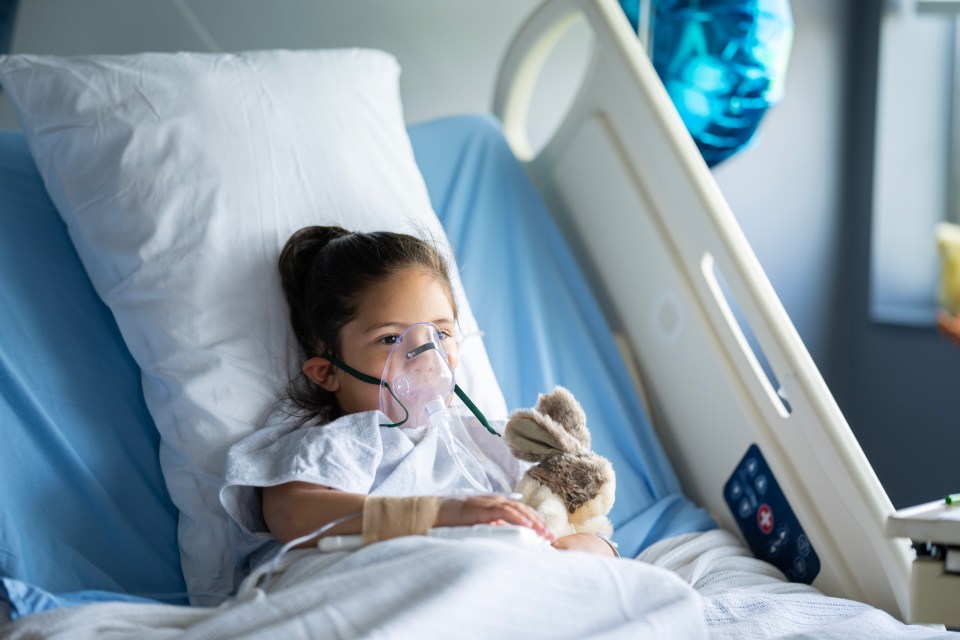
Babies under 12 months old with whooping cough have an increased chance of having problems such as dehydration, breathing difficulties, pneumonia, and seizures (fits), according to the NHS.
But in the UK, the whooping cough vaccine is routinely given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine – for babies at eight, 12 and 16 weeks – and the 4-in-1 pre-school booster – for children aged three years four months.
People who are pregnant are also recommended to have the whooping cough vaccine.
You usually have it when you’re around 20 weeks pregnant to help protect your baby for the first few weeks of their life.
Rapid initiation of antibiotics is recommended for all patients with confirmed or suspected whooping cough.
If given early, this may improve symptoms, while later treatment is unlikely to impact symptoms, although it does reduce transmission.
The NHS also recommends some things you can do to help ease the symptoms of whooping cough – get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids, and take paracetamol or ibuprofen if you or your child are uncomfortable
But it urges you call 999 or go to A&E if:
- your or your child’s lips, tongue, face or skin suddenly turn blue or grey (on black or brown skin this may be easier to see on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet)
- you or your child are finding it hard to breathe properly (shallow breathing)
- you or your child have chest pain that’s worse when breathing or coughing – this could be a sign of pneumonia
- your child is having seizures (fits)
Full list of symptoms of whooping cough
WHOOPING cough is a bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes.
The first signs of the condition tend to be similar to a cold – such as a runny nose, a sore throat, red and watery eyes, and a slightly raised temperature.
After about a week, other signs start to appear. These include:
- Coughing bouts that last for a few minutes and are worse at night
- “Whoop” sounds as your gasp for breath between coughs
- Difficulty breathing after a coughing bout
- Turning blue or grey (children)
- Becoming very red in the face (adults)
- Bringing up thick mucus, which can make you vomit
- Bleeding under the skin or in the eyes
- Feeling very tired after coughing
The cough may last several weeks or months.
Babies under six months have an increased risk of problems such as dehydration, breathing problems, pneumonia and seizures.
Older children and adults may experience sore ribs, hernia, middle ear infections, and urinary incontinence.
Source: NHS