SCIENTISTS have ranked the worst types of pain people can experience – including childbirth, gunshot wounds and a slipped disk.
Unsurprisingly, labour pains ranked pretty high in terms of pain – but they were surpassed by a little known condition.
Called cluster headaches, the rare headache disorder sees sufferers struck with sharp, burning or piercing pain on one side of their head, sometimes for hours at a time.
Cluster headaches affect about one in 1,000 people – an estimated 65,000 people in the UK.
It has been described as one of the most painful conditions known to man, according to Brain Research UK, sometimes described as a “suicide headache” as the agony can lead to suicidal thoughts.
Most patients have “episodic” cluster headache, meaning they’ll get “clusters” of headache episodes that last from four to 12 weeks.
American researchers found that cluster headaches were thought to be more excruciating than childbirth pains, heart attacks, gunshot wounds and broken bones.
They asked 1,604 people who experienced cluster headaches to to rank the amount of pain they endured during an attack against other agonising conditions.
Participants has to give a pain rating for each condition on a scale of 0 to 10.
Anything above a seven was deemed to be “severe pain”.
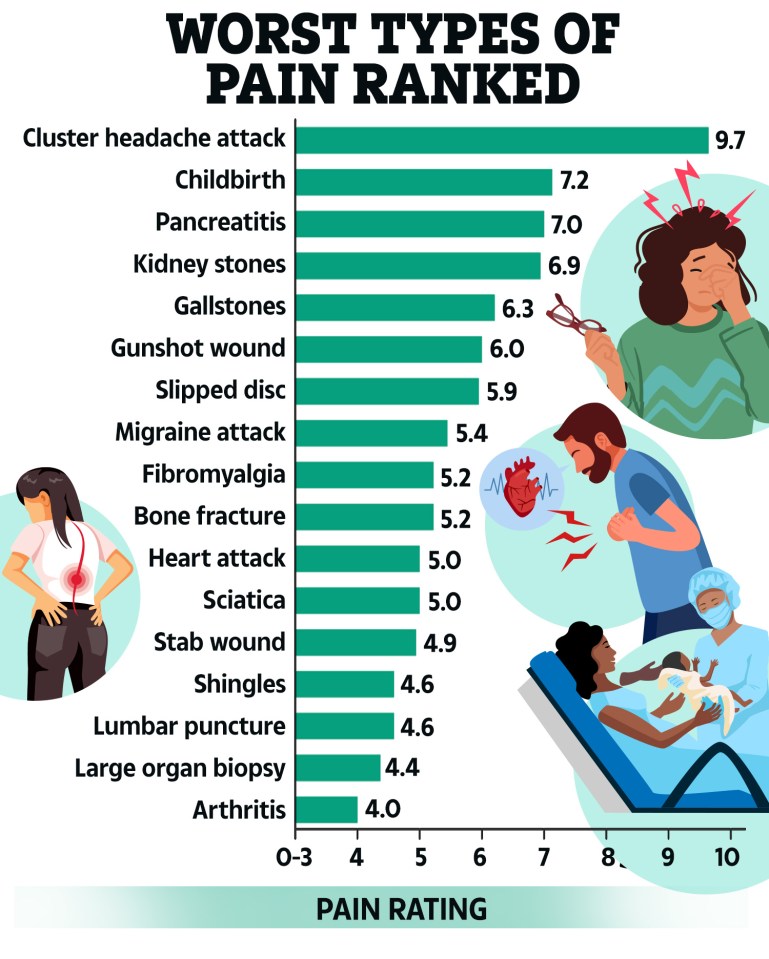
Cluster headaches ranked first on the list, with an average pain score of 9.7 out of 10.
Next came labour pain, with a rating of 7.2.
Pancreatitis – a serious condition where digestive juices or enzymes attack the pancreas, making it painfully inflamed – was thought to be the third most painful condition.
Drinking too much alcohol and gallstones are thought to fuel the condition, which was given a pain score of seven by participants.
Fourth on the list were kidney stones – when waste products in the blood form crystals that collect in the kidneys and build up into hard lumps.
The body will try and expel kidney stones by peeing, causing untold agony. Participants ranked this at a 7.9.
You’re more likely to develop the condition if you haven’t been drinking enough fluids or you take certain types of medication.
Gallstones, hardened deposits of bile that can form in your gallbladder, ranked fifth on the pain scale with a score of 6.3 – as the condition can cause sudden and severe abdominal pain.
Some of the cluster headache sufferers appear to have suffered gunshot wounds, as they rated them sixth in terms of pain.
A slipped disc – when a soft cushion of tissue between spinal bones bulges outwards and presses on nerves – came in seventh.
Ten types of headache and how to treat them
Tension headache
- How common: 75 per cent of adults
- Symptoms: tension on scalp, both sides, feels like a tight vice
- Cause: stress, sleep problems, caffeine
- Treatment: rest, relaxation, painkillers
Vision induced headache
- How common: fairly common
- Symptoms: tiredness or soreness behind the eyes
- Cause: glasses, contact lenses, screens
- Treatment: eye test, cutting down screen time
Migraine
- How common: 10million people in the UK
- Symptoms: severe headache with throbbing on one side, sometimes with aura symptoms (visual or auditory disturbances)
- Cause: genetics, menstrual cycle, caffeine, alcohol, stress, fatigue, smoking, anxiety, depression
- Treatment: paracetamol, contraception, decrease caffeine intake, prescription medication
Cluster headache
- How common: one in 1,000 people in the UK
- Symptoms: severe headache usually on one side, around one eye, red watery eye, swollen eyelid or drooping of eye
- Cause: unknown
- Treatment: oxygen, triptans, beta blockers
Medication overuse headache
- How common: one to two per cent of the UK population
- Symptoms: dull, constant headache
- Cause: frequent painkiller use
- Treatment: alternative medications, decreasing painkiller use
Nerve pain headache
- How common: eight in 100,000 people
- Symptoms: sudden attack of severe, sharp, shooting facial pain that lasts from a few seconds to about two minutes
- Cause: pressure by an artery, tumour, talking, smiling, chewing, head movements, multiple sclerosis, shingles
- Treatment: prescription medication
Thunderclap headache
- How common: 50 in 100,000 adults
- Symptoms: severe pain out of the blue and can be accompanied by vomiting, fever, seizures and an altered mental state
- Cause: brain bleed, blood clot, stroke, meningitis, encephalitis
- Treatment: urgent care in A&E
Pressure headache
- How common: fairly common
- Symptoms: pulsating sensation that comes on quickly and lasts for short periods
- Cause: coughing, exercise, sex, hypertension, space-occupying lesion
- Treatment: GP appointment, avoiding triggers
Infection headache
- How common: 60 to 100 per cent of people with infections
- Symptoms: combined with symptoms like blocked sinuses
- Cause: infection (e.g. flu, sinusitis), fever
- Treatment: over-the-counter painkillers, antipyretics
Trauma headache
- How common: 30 per cent of people with head injury
- Symptoms: nausea, dizziness, lethargy
- Cause: head injury
- Treatment: paracetamol, avoid alcohol, rest
Aside from lower back pain, this condition can cause numbness and tingling in the back, arms, hands, legs or feet, and pain that radiates from the neck to the buttocks, hips and legs.
The intense throbbing head pain of migraines were ranked eighth, and fibromyalgia ninth.
This is a chronic condition that causes pain, tenderness and stiffness all over the body.
Finally, bone fractures took tenth place on the pain scale.
Meanwhile, heart attacks came in eleventh – with a pain score of 5.
Other agonising conditions mentioned by participants included stab wounds, sciatica and shingles.
Researchers noted several limitations to their study, including that participants may not be able to accurately recall just how painful these conditions were.
But they concluded that “cluster headache is reported by a large group of international respondents to be more intense than every other pain disorders examined”.
Cluster headaches can start and stop suddenly and without warning, lasting between 15 minutes and three hours.
They’ll cause a sharp, burning or piercing pain on one side of the head, usually around the eye.
Sufferers may also feel sick, notice their eye is red, swollen or watering, and get a blocked or runny nose.
In some cases, common painkillers can do little to dull the agony.
The NHS recommends you speak to a GP if you think you’re experiencing cluster headaches.