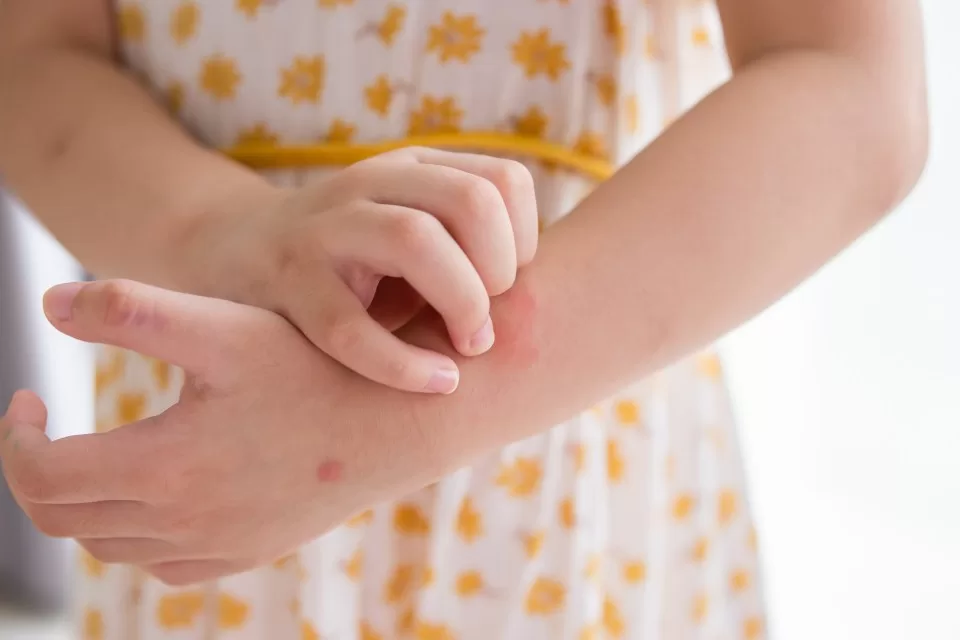
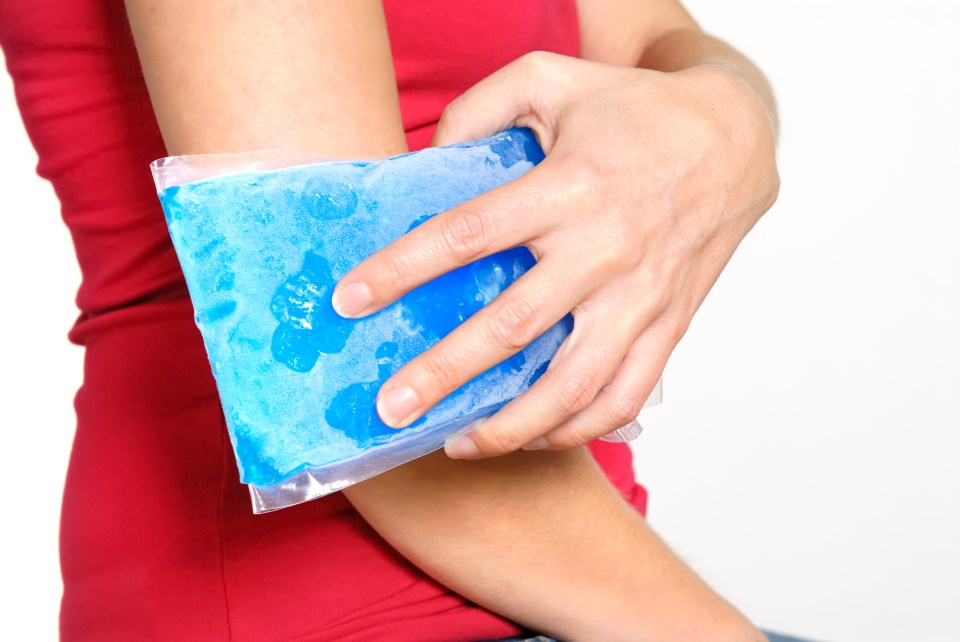
IT can be truly devastating watching your little one scratch their skin red-raw.
Eczema is a cruel condition that causes intense itching and affects at least one in five children.
Many go on to have a life-long condition as adults.
Controlling a child’s eczema – and helping them learn how to as well – can prevent it from persisting past childhood.
But it’s easier said than done. Keeping on top of a youngster’s condition requires consistency and knowledge.
Jae Rance, creator of ScratchSleeves and co-writer of the new book The Calm Skin Guide (£10.76, Amazon), has written a full guide to help parents navigate their child’s chronic condition.
Read more on kid’s health
THE ITCH-SCRATCH CYCLE
First, it’s important to understand what eczema is and why your child cannot stop scratching.
Jae says: “Eczema is often referred to as the itch that rashes because the itch often starts before the rash appears – and we all know how hard it is not to scratch an itch.
“The problem with scratching eczema is that when you break the surface of the skin, bacteria and allergens can find their way in irritating the skin further and increasing the itching.
“Then, as the scratches scab over, the scabs themselves itch.
“The more itching, the more scratching and the scratch-itch cycle just keeps going.”
Itching often starts due to a ‘flare-up’ – when eczema returns with aggression after a period of being stable.
Jae says: “Flare-ups lead to itching which lead to broken skin and possible infection and more itching. We need to break this cycle fast.”
Scratching can also become a habit, rather than a response to an ‘itch’.
Here Jae shares her 12 top tips to help ease your child’s agony….
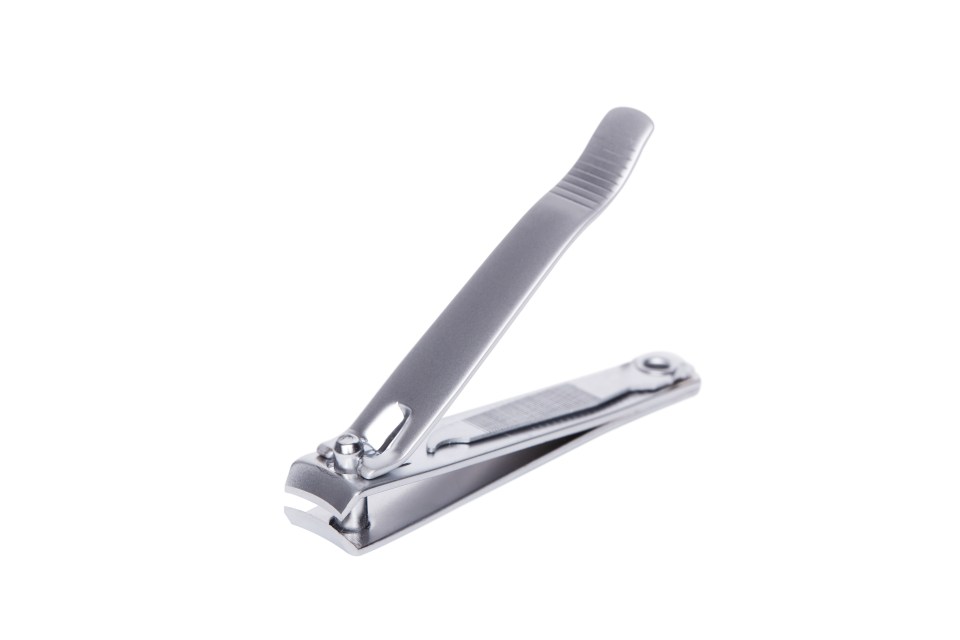
1. Cut nails
Babies can be very resistant to having their fingers moved about and may yank them out of your grasp.
It’s best to tackle this task while they are deeply asleep.
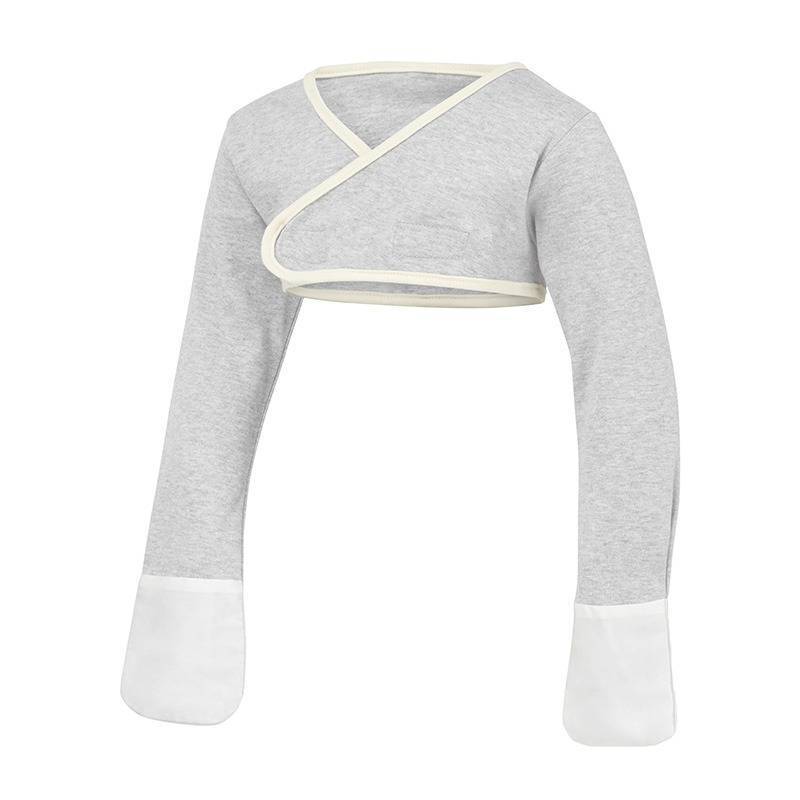
2. Cover hands
There are plenty of options available for scratch mitts, including ScratchSleeves.
Babies will usually be perfectly happy wearing mitts.
However, as children get older, this becomes a less practical option.
3. Cover the itchy bits
Eczema often occurs inside the elbow or on the backs of the knees.
Keeping these areas covered can help to minimise scratching damage.
Elbow and knee sleeves designed for eczema are great for this as they use smooth fabrics that don’t bunch up.
The ones from tepso.co.uk are really good, albeit expensive.
4. Keep emollients in the fridge
Smoothing on cold emollient is a great way to soothe a localised itch.
Rather than filling up your fridge with huge tubs of emollient, ask your GP to include smaller tubes in your child’s prescription for this purpose.
5. Tapping
Another great way to help your little ones to avoid scratching themselves raw is to lightly tap the itch with your fingers until it goes away.
It’s thought that light tapping causes a vibration on the skin which can interfere with the nerve signals that cause the itch. Light pinching can also help.
You may be able to achieve the same relief with a massage roller or Scratch Star from Cosi Care.
These tools help relieve the itch without breaking the skin, as nails do.
6. Distraction
For itches that just won’t go, you can try the distraction strategy.
Encourage your child to play with fiddly toys such as Lego or a Rubik’s cube.
Most kids will scratch more when they are tired or relaxed watching telly, so give them something to occupy their hands during these times.
It is best to treat flare-ups hard and fast to prevent complications
Jae
7. Cold packs
Pressing something cold such as a cold pack, bottle of water or even an ice pack wrapped in a tea towel can help to ease the itchiness of eczema.
This is an excellent way of instantly relieving your child from itchy skin, and making them feel as though you are doing something practical.
8. Itch relief creams
Some creams containing anti-itch agents (crotamiton or lauromacrogols) can be bought over the counter.
Your GP can prescribe other creams such as doxepin, which has antihistamine action when applied in cream form.
E45 Itch Relief cream is licensed for anyone over one month old.
9. A lukewarm bath
For some children, a lukewarm bath does the trick.
And with a few budget bath toys added, it can serve as a useful distraction too.
Cover them with emollient before putting them in the bath, and don’t let them soak for too long otherwise you might cause the skin to become dry.
Let them play with whatever you have around, or buy a couple of for as little as £4 from Smyths Toys, and remember to apply lots of emollient afterwards.
10. Smooth environment
Rather than scratching, babies often rub their itchy face against anything they find themselves near.
Avoid wearing scratchy woollen jumpers or embellished tops when you are cuddling your itchy little one.
Also, make sure that everything in their environment is smooth, and watch out for velcro on activity toys.
11. Cold room
Make sure the bedroom is cool, around 16 to 18C and that your child’s cot or bed is well away from any radiators.
In hot weather, bottles of frozen water next to your child’s bed will cool the air, especially if you point a fan at them.
12. Raising awareness
Scratching is often habitual and not actually related to itching.
Avoid telling your child not to scratch; gently touching or moving the scratching hand feels less critical.
Or, you could silently offer an alternative such as a cold pack.
Coming up with a secret or silly sign might be fun too.
WHEN TO USE EMOILLIENTS
Emollients will be a word you’ve heard if your child has eczema, as they are the first line – and cornerstone – of treatment.
But there are so many available, which one should you use, and when?
Jae says: “Emollients work by forming an oily layer over the skin surface which traps water beneath it.
“This moisturises the dry skin, helping to soothe it and relieve the itch.
“This protective layer also prevents irritants, allergens and bacteria getting into the skin.
“Emollients come in various forms and there are many different brands available, both on prescription and over the counter.
“Finding the right emollient for your child really is a case of trial and error.
“Most GPs will prescribe a simple paraffin-based emollient cream, like Diprobase, in the first instance.
“These simple creams have minimal risk of side effects and are easy to use.”
Emollients range from light (lotions) to creamy and thick and greasy (ointments).
Lotions and creams, which are more lightweight for the day time, should be applied every three to four hours, at least.
Ointments – the most effective at holding water in the skin and repairing the skin barrier – can protect the skin for up to eight hours and are best for at night.
WHEN TO OPT FOR STEROIDS
Steroid creams are no cure. But they are fast-acting and can produce miraculous results.
Jae says: “A short period (one to two weeks) of using steroid creams will bring most eczema flares ups back under control.
“Emollients should help prevent the eczema from worsening.
“However, during a flare-up, it’s unlikely emollients will be enough.
“Topical corticosteroid creams, also known as ‘steroid creams’ or ‘TCS creams’, are the first-line therapy for treating eczema flare-ups.”
Jae acknowledges that many parents have fears about using steroid creams, amid the rise in awareness of topical steroid withdrawal.
She says parents concerned about using steroids are less likely to follow their doctor’s advice.
An aggressive approach is thought to be especially important for early-onset eczema
Jae
“This is leading to eczema not being treated properly which can cause additional distress to your baby and also increases the likelihood of complications and more aggressive treatments (including stronger steroid creams) in the future,” she adds.
“It is best to treat flare-ups hard and fast to prevent complications (in the form of infections and allergies) and increased steroid use in the long run.
“This aggressive approach is thought to be especially important for early-onset eczema (three to four months) as there is growing evidence that the compromised skin barrier caused by eczema in early life can result in the later development of food allergies.”
Research shows that the use of steroids intermittently to treat flare-ups (as opposed to using it frequently for prevention) has low risk of harm.
“Although dependency on steroid creams does happen, it is extremely rare and usually associated with prolonged use (e.g. daily for more than a year) and high potencies.”
Jae’s tips for using steroids appropriately are:
- Only use them once a day, unless you have been told otherwise by your doctor.
- Apply enough to make the skin glisten and leave 15 minutes before applying emollients.
- Continue using the steroid cream for two days after the skin looks normal to ensure the skin has healed fully. For strong steroid creams, follow your doctor’s advice for tapering their usage.
- Steroid creams should work quickly. If the flare isn’t coming under control within a week of starting them or your child’s eczema flares again soon afterwards, you stop using the steroid cream, contact your doctor. Your child may need stronger steroids.
Products that help eczema
Jae Rance, creator of ScratchSleeves and author of The Calm Skin Guide, shares her top products to help eczema.
For eczema around the mouth: Try an SLS free toothpaste like Oranurse.
Prevent itching at night: Covering your child’s hands at night may help. ScratchSleeves have built-in mitts to cover the hands. Socks are an immediate solution when you have nothing to hand, but are easier to rip off.
For cleaning skin: Using plain water and a microfibre wash mitt can do wonders for keeping your baby clean. You can also use your regular emollient for washing.
To remove potential laundy detergent triggers: Contrary to popular belief, biological detergents are not a common trigger for eczema. Instead it’s the optical brighteners and fragrances that typically cause the problem. Fragrance free versions of eco brands like Ecover Zero are a good option.
To help itch relief: Some eczema creams like E45 Itch Relief include anti-itch ingredients which act as a local anaesthetic. These creams can usually only be used twice a day but can be really useful when the itch is really annoying, especially at bedtime. Oatmeal has anti-itch properties. Aveeno is the best known oatmeal based brand, AproDerm also has a good range.
Boost the skin barrier: Ceramides can help to re-establish the balance of fats necessary for the skin barrier to function effectively. One ceramide-containing cream is looking particularly hopeful – EpiCeram, which is prescription only. CeraVe Moisturising Cream for dry and very dry skin, which also contains ceramides, available over the counter.