“I often leave an eight-hour shift with only about $60 in hand,” Monroe told Al Jazeera.
With credit card, phone and insurance bills piling up, her current pay is just not cutting it for her. Often, she has to decide which gets paid and what has to wait.
“I usually have to call the car and insurance companies and tell them I either need to pay late or pause payments entirely,” she added.
Monroe is like the millions of Americans whose financial situation hinges on the outcome of the US presidential election. President Joe Biden is set to focus on a number of economic wins during his first term, including record job growth, low unemployment and tumbling gas prices, among other key economic indicators that have made it evident that the US economy is on the upswing.
But the incumbent president, his Republican opponents, third-party candidates and Biden’s longshot Democratic challengers face the harsh realities of underemployment in the United States.
However, with significant economic growth, the question is: Do Americans like Monroe have a better chance for social mobility under the eventual Democratic nominee – most likely Biden – or the most likely Republican nominee, former President Donald Trump?
According to data compiled by the Economic Policy Institute, underemployment sits slightly below 7 percent – the lowest since the agency began tracking the data in 1990. When Trump left office, underemployment was at more than 14 percent. After a peak in March 2021, there has been a steady decline since.
“Since the recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic, unemployment has declined pretty steeply and quickly,” said Lonnie Golden, professor of economics and labour-human resources at the Pennsylvania State University.
Cost-of-living surge
While the Biden administration saw record job growth, it is not clear that the new jobs in question are well-paying sustainable jobs that meet the cost of living across the US.
“In the last year, we’ve seen an uptick in the way the Bureau of Labor Statistics measures the number of people working part-time but would prefer to be working full-time hours,” said Golden.
“These figures kind of mask the extent of underemployment for people because they’re seeking a second job for more income,” she added.
Despite the economic gains, child poverty is up 137 percent, and average rent prices have surged nationally.
According to a new report out from Zillow, the percentage of income needed to rent a median-price apartment in the US jumped by 40 percent since before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In some cities, it is even higher.
In Miami, Florida, renters need to spend 43 percent of the average income to afford a median-price rental apartment. The minimum wage in Miami is $12 an hour.
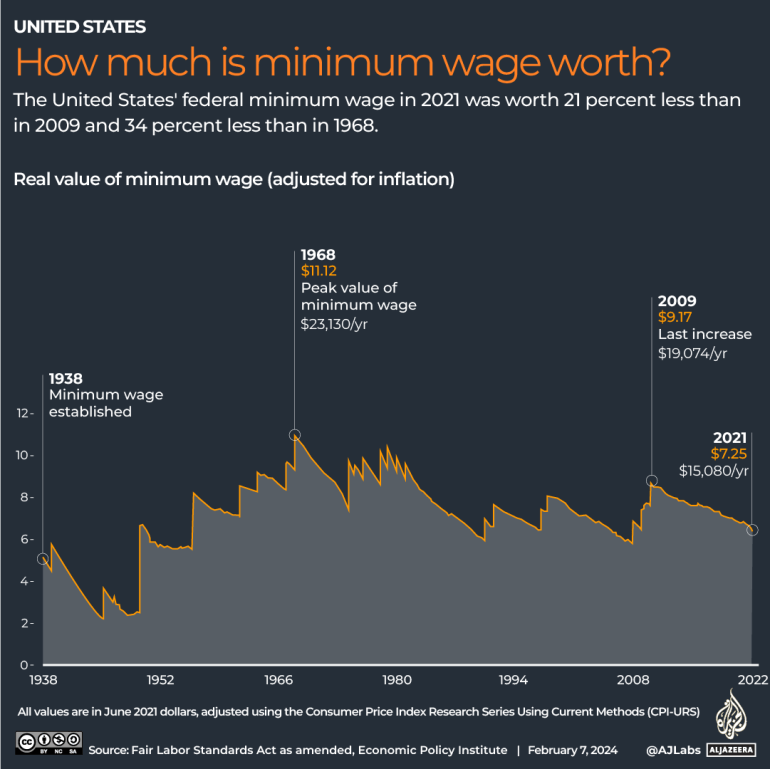
Nationally, the minimum wage’s buying power peaked in 1968 and has not kept up with the cost of living since.
According to a report by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, the number of those underemployed is much higher – 33 percent among college graduates. That is because its metric considers graduates working jobs that do not require a college degree.
Amid the recovery, much of the consistent job gains were in the leisure and hospitality sector – an industry that is notorious for low wages.
“The low wage pool is what’s growing the American workforce,” Saru Jayaraman, founder of One Fair Wage, told Al Jazeera.
Jayaraman asserts that Biden, who historically is more pro-worker than his Republican challengers, could do much better strategically if he fully embraces issues about payment.
“It’s getting harder and harder to tell workers to vote for a Democrat who will raise wages when that doesn’t happen,” Jayaraman said.
However, during the last election cycle, Biden did follow through on many of his promises.
One of Biden’s first actions as president was to raise wages across the board via the Raise the Wage Act. But that did not pass as the bill was blocked by Republicans. Biden, however, was able to raise the minimum wage for all federal contractors. The US government is the nation’s biggest employer.
Biden has not acted on abolishing the subminimum wage that allows tipped workers to make a wage of only $2.13 an hour – although many states require higher direct wage amounts for tipped employees. The rest is supposed to be made up in tips – a move that is widely accepted in the food service industry and other domestic industries.
The Trump administration, however, actively tried to limit tipped wages for these same restaurant workers. The former president pushed for business owners to take control of tips and pass them along to workers as they see fit.
Proposed solutions to underemployment include a number of compounding proposals, one of which is the nonprofit One Fair Wage’s push to abolish the subminimum wage nationally.
One Fair Wages efforts have helped get wage measures on the ballot all over the country, garnering more votes than either presidential candidate.
“In 2020, more people voted for a $15 minimum wage in Florida than [the number of votes for] either Trump or Biden,” Jayaraman said.
Faults in proposed fixes
One proposed fix has been a Universal Basic Income. Americans got a taste of that in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic when the government released one-time payments. That stimulated the economy. Consumer spending surged.
In May 2020, personal spending rose 8.2 percent from the month prior. That had the same effect during the second round of government payouts. Consumer spending ticked up by more than 4 percent in the months following the second release, which was in early 2021.
However, that was one of the many reasons why inflation soared in the years following.
Printing more money means that the individual dollar is less valuable than it once was, driving up prices. Yet wages did not grow nearly fast enough.
“Only a few years ago, it used to be that one in three Americans working full time lived in poverty. We are inching closer to one in two,” Jayaraman said.
The Department of Labor for its part is taking steps to address massive shifts in the economic makeup of the US. In September, the department announced a $57m grant to expand job training programmes, including in large population centres like New York, California, Illinois and Ohio.
The move is aimed at helping those who are underemployed pivot into high-demand and expanding industries related to addressing climate change and staffing up the US’s infrastructure projects.
While the programme is expected to have widespread effects, the Labor Department says it will help about 10,000 workers.
It also comes alongside a wave of unionisation efforts across big businesses like Amazon to even small independent coffee shops. Several companies and trade have successfully lobbied for higher wages and fairer contracts.
That, however, came from empowered workers in individual sectors rather than overarching policies from Washington.
The Biden administration has been largely supportive of unions that have called for fairer contracts like the United Auto Workers, for instance.
Movement, however, is slow. Wage increases are often staggered marginally over several years. The required wage increases for federal contractors were unilaterally implemented by executive order in April 2021 – three months into Biden’s presidency. It took effect a few weeks ago.
But as Washington hypothesises over a myriad of potential solutions, people like Monroe still have rent and electricity bills piling up.
“I’m basically living paycheque to paycheque right now,” Monroe said.